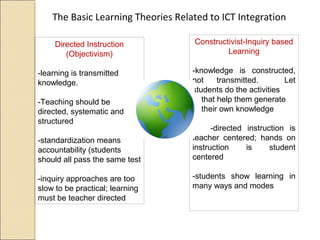
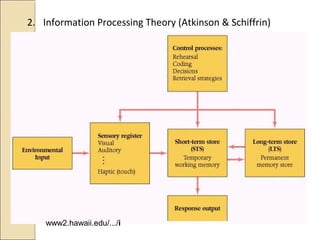
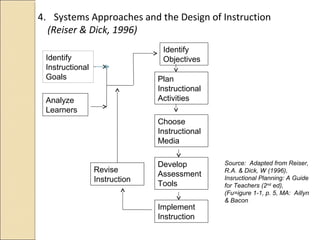
The document discusses integrating technology into teaching and learning. It defines ICT integration as strategically incorporating information and communication technologies into all aspects of education, including administrative functions and business models that support learning. The purpose is to improve quality, accessibility, and cost-efficiency of education delivery while taking advantage of networking learning communities. Effective ICT integration involves students actively using technology to support meaningful learning and attainment of curriculum objectives. Common barriers to integration include lack of resources and teacher skills, while facilitators include strong leadership and professional development.