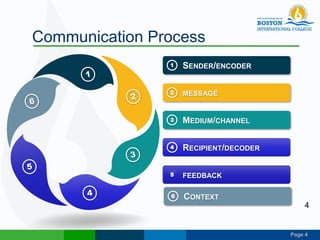
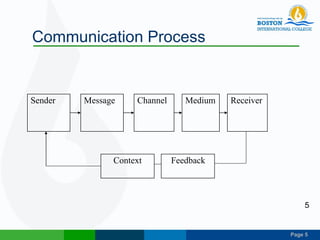
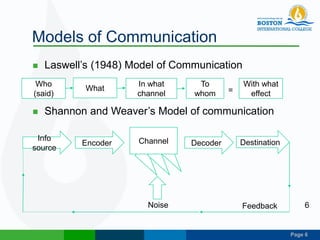
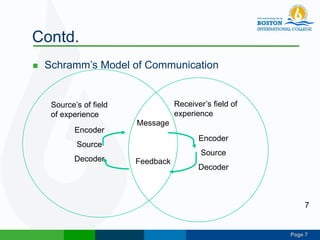
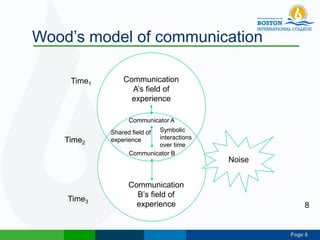
This document discusses technical communication and communication models. It defines communication as the transmission of meaning between individuals or groups. Communication involves at least two parties and can be one-way or two-way. Several models of communication are described, including Laswell's model of who says what through which channel to whom, Shannon and Weaver's model of an information source, encoder, channel, decoder and destination, and Schramm's model emphasizing feedback between sender and receiver. Principles of effective communication include clarity, completeness, conciseness, concreteness, consideration, correctness and courtesy. Communication can be categorized by fields, contexts, modes and audiences.