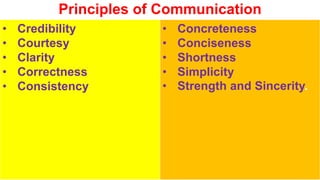
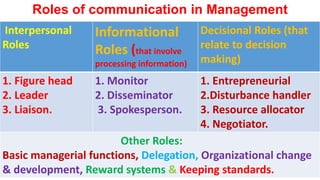
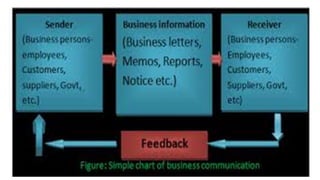
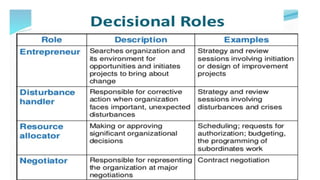
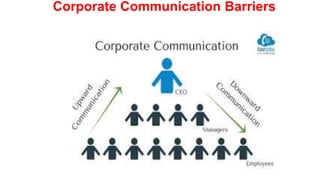
This document provides an overview of the topics and activities covered in an introductory communication session for an MBA/EMBA program. The session objectives are to define key communication concepts and explore factors that influence communication. Topics covered include the meaning, nature, scope and principles of communication; factors and functions of communication; roles of communication in management; differences between social and business communication; and barriers to communication. Activities include defining terms, group work, and suggesting measures to overcome communication barriers.