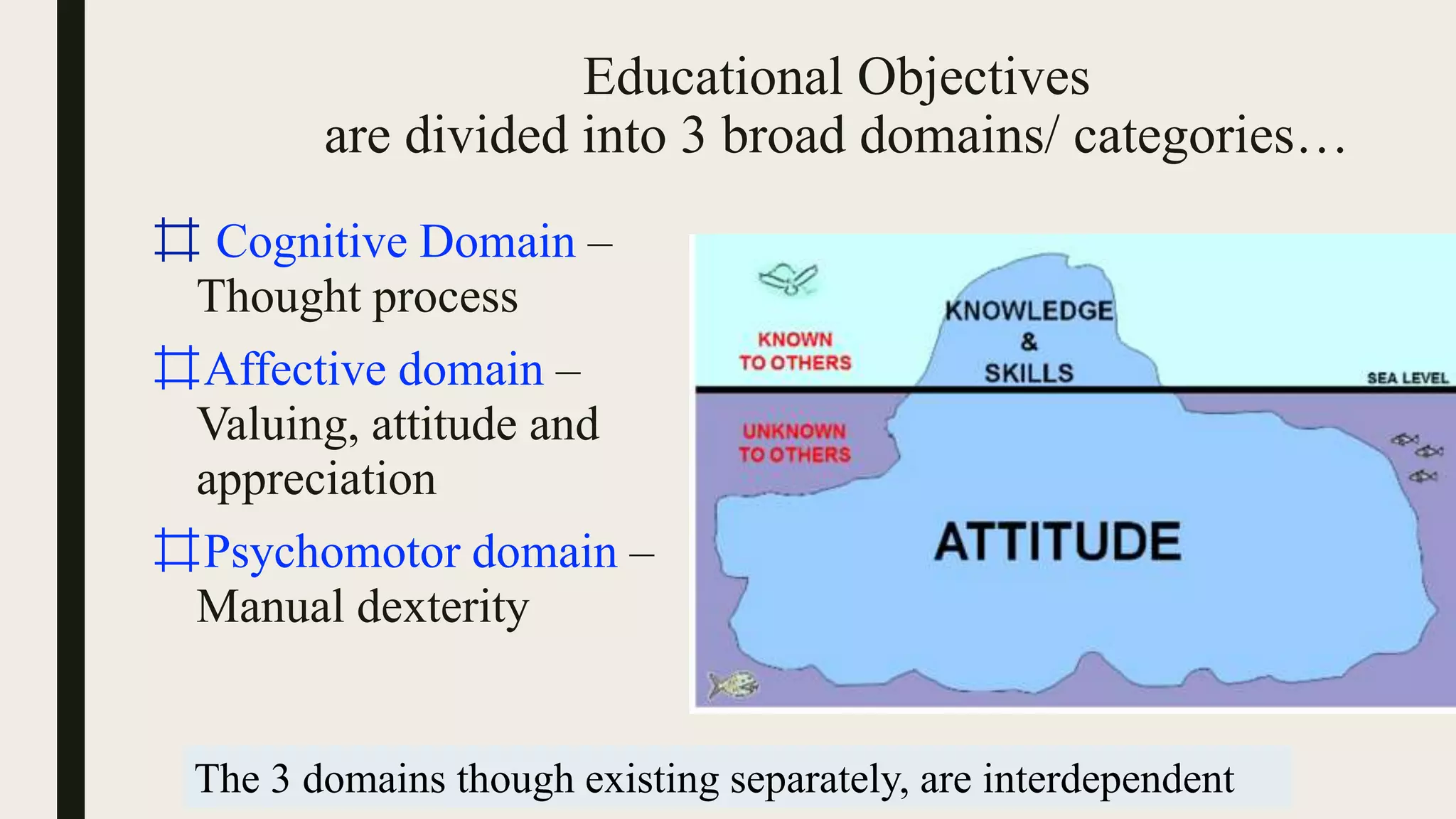
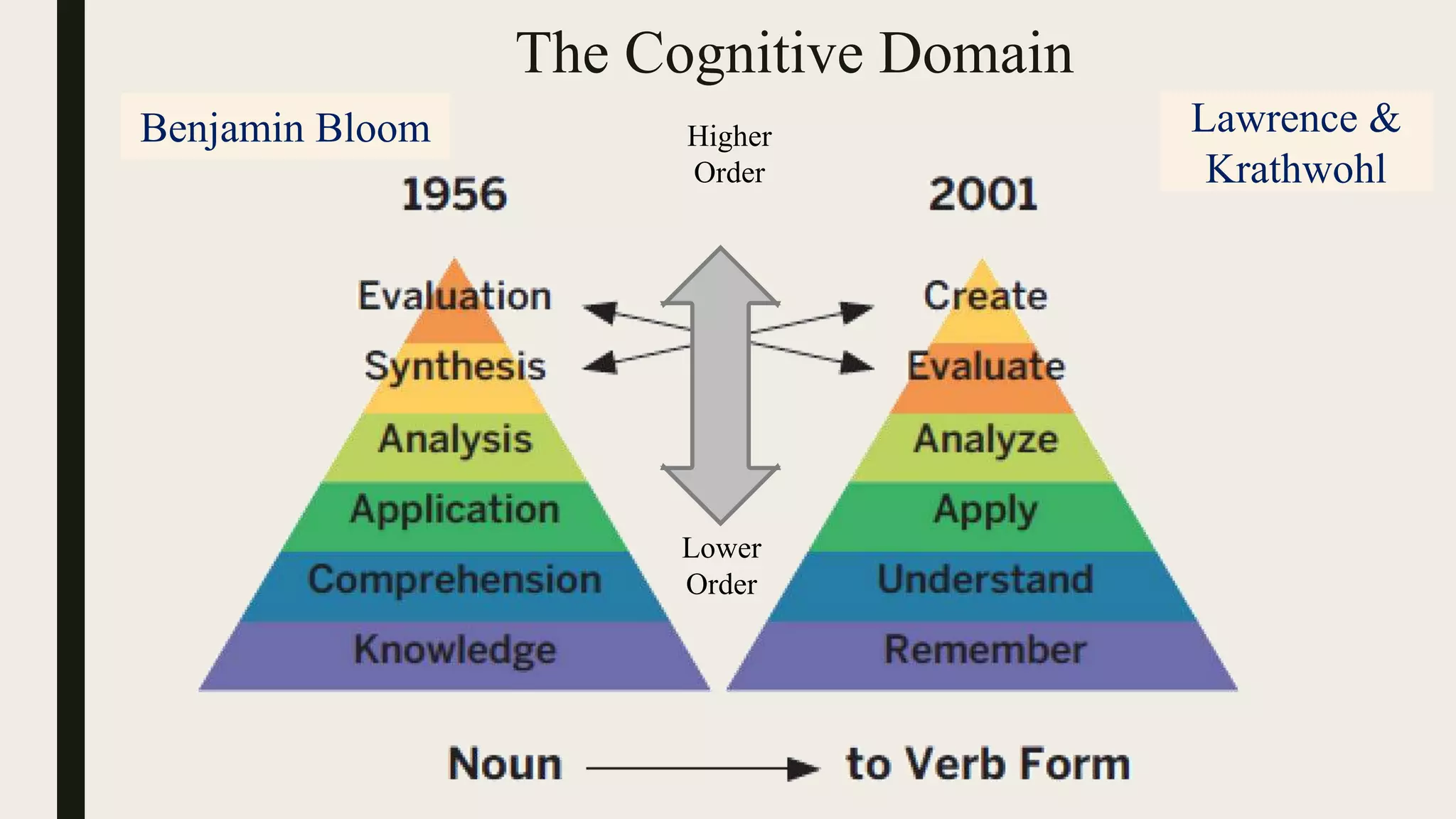
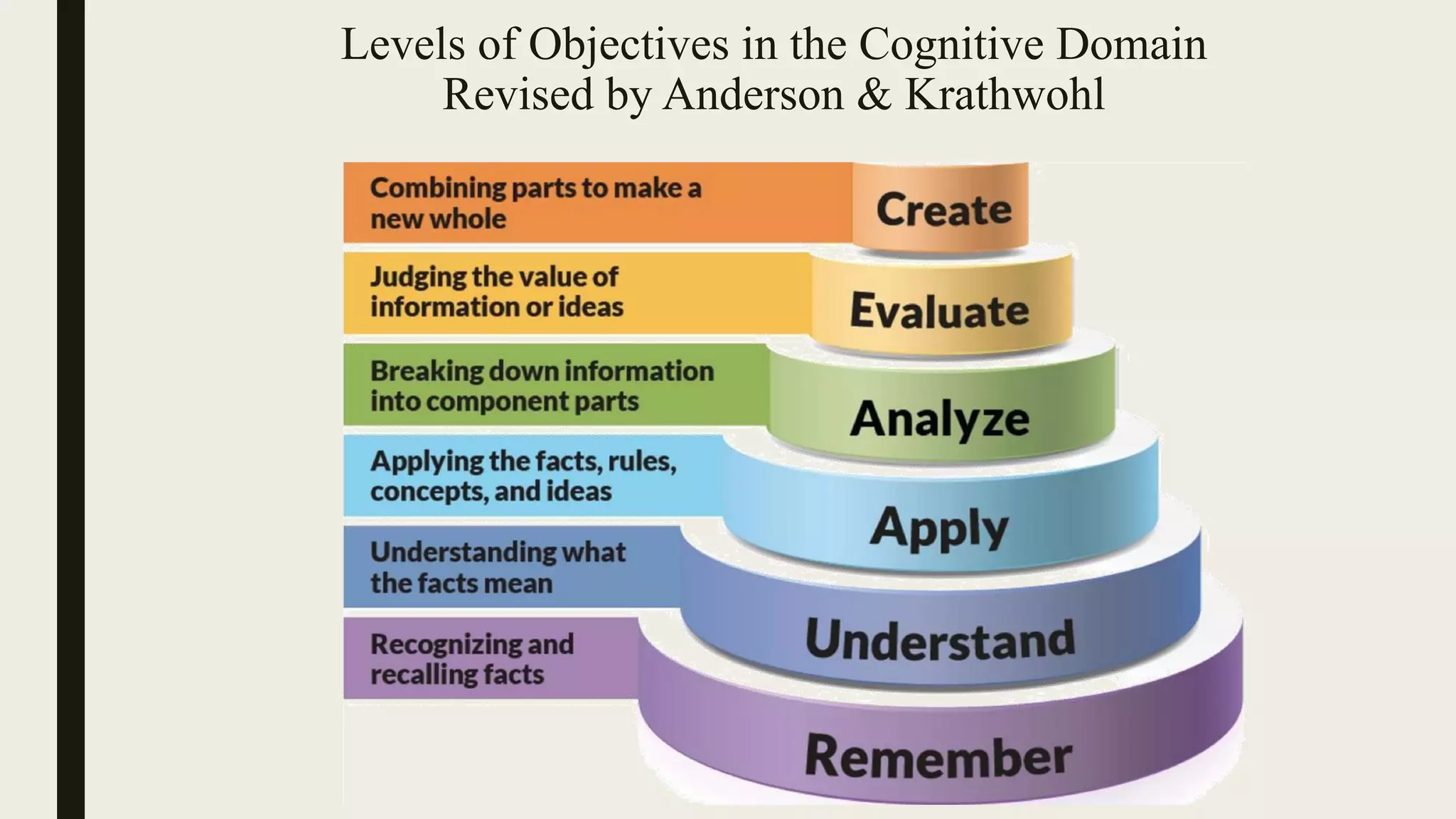
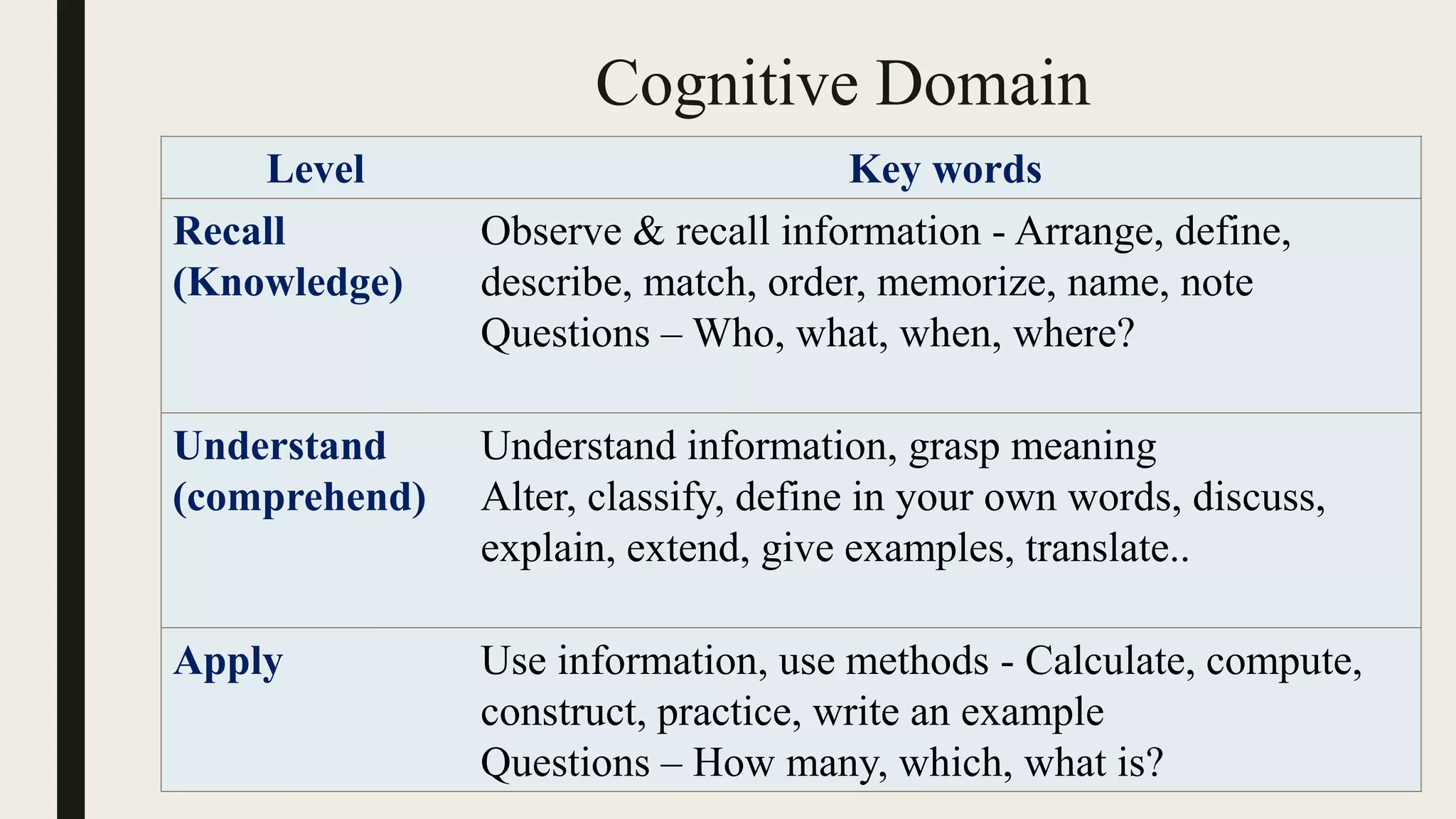
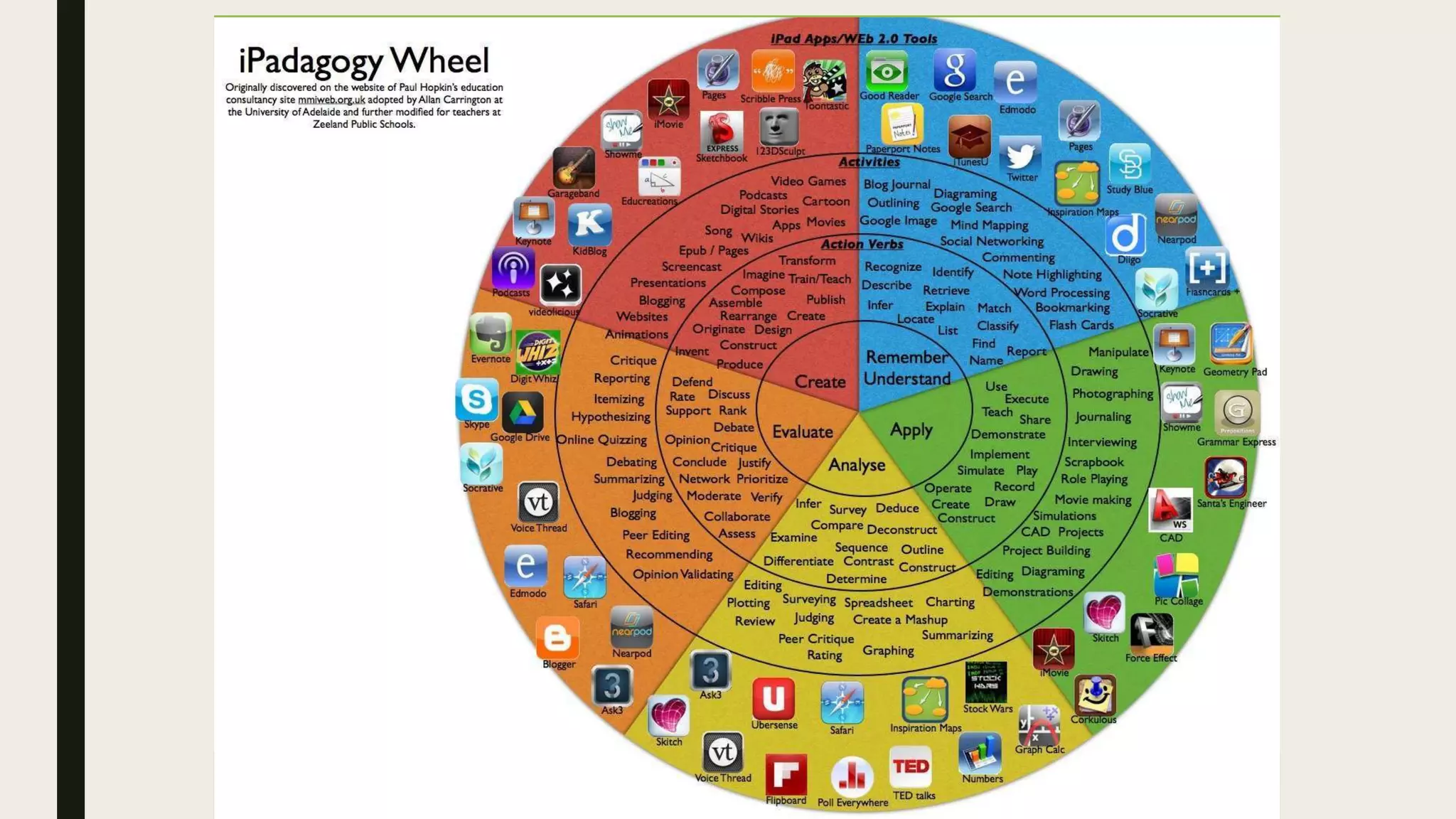
This document discusses Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives, specifically focusing on the cognitive domain. It defines taxonomy as the classification of things according to their relationships. In education, taxonomy is used to define and arrange levels of behavior by type and complexity. Educational objectives are divided into three domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. The cognitive domain involves knowledge and intellectual skills. It contains six levels of complexity for classifying objectives - from simple recall to evaluation and creation. Examples are provided of writing objectives for lessons on congestive heart failure and newborn care at each of Bloom's six cognitive levels.