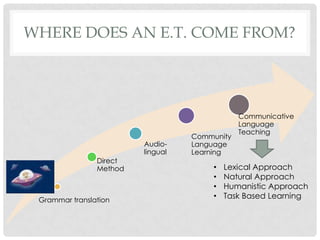
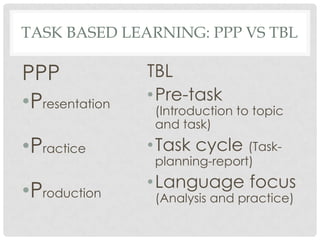
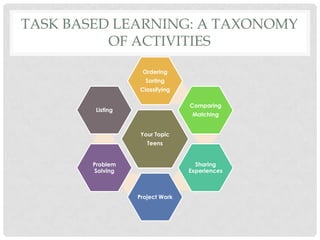
The document summarizes the principles of task-based language teaching. It explains that task-based learning focuses on meaningful tasks rather than language forms. Students work to complete real-world tasks using the target language, and language instruction focuses on forms that emerge from task completion. The document compares task-based learning to the presentation-practice-production model, and provides examples of tasks and ways to implement task-based principles in the classroom, such as making instructions more precise and adding post-task reports.