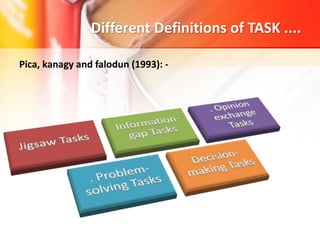
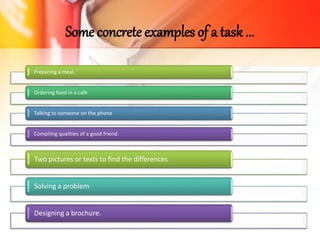
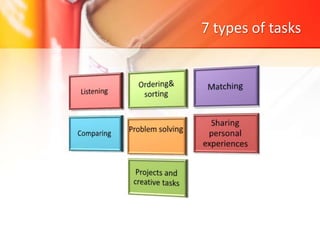
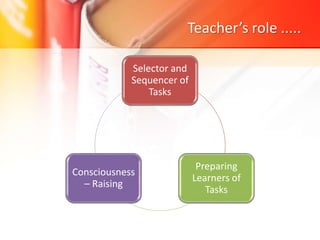
The document discusses Task-Based Language Teaching (TBLT), outlining its historical background, key definitions, and principles. TBLT focuses on using meaningful tasks to facilitate second language acquisition by engaging students effectively and encouraging natural language use. The approach emphasizes that learning occurs best when students are motivated and able to interact in meaningful contexts, supporting their development in a second language.