Krashen's Monitor Model involves five hypotheses about second language acquisition:
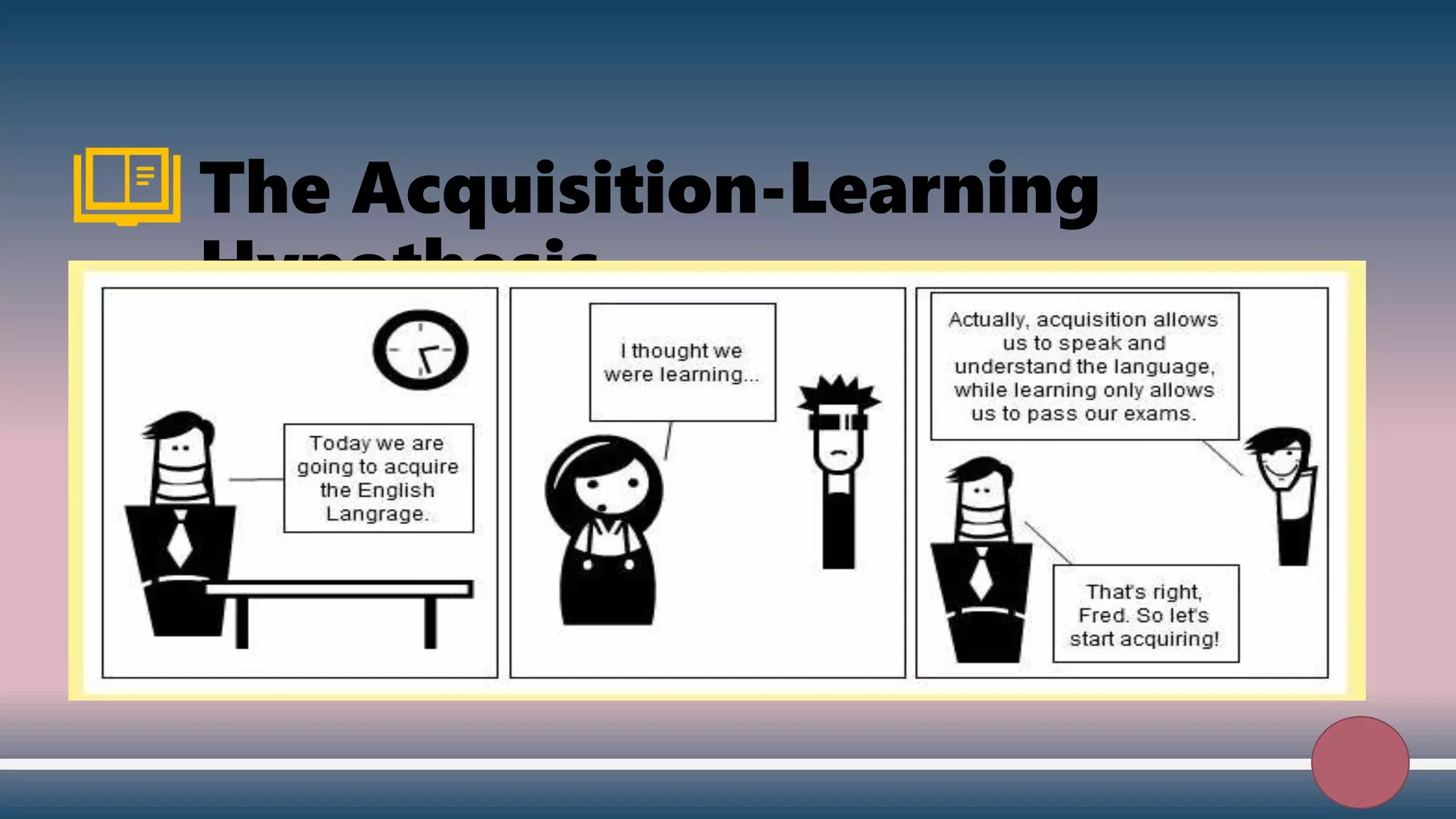
1) The Acquisition-Learning Hypothesis distinguishes between acquiring a language naturally versus learning it consciously. Language is acquired, not learned.
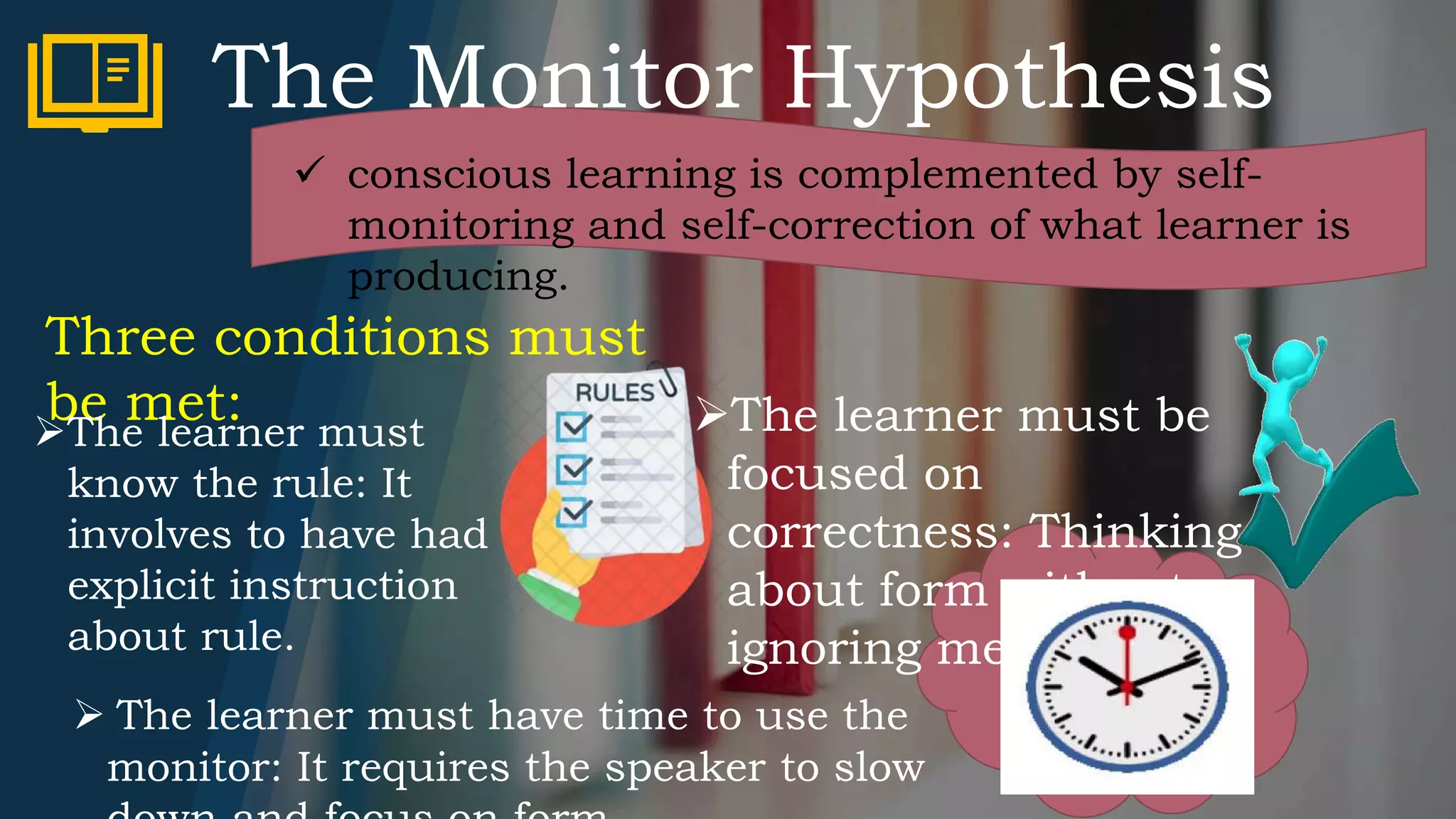
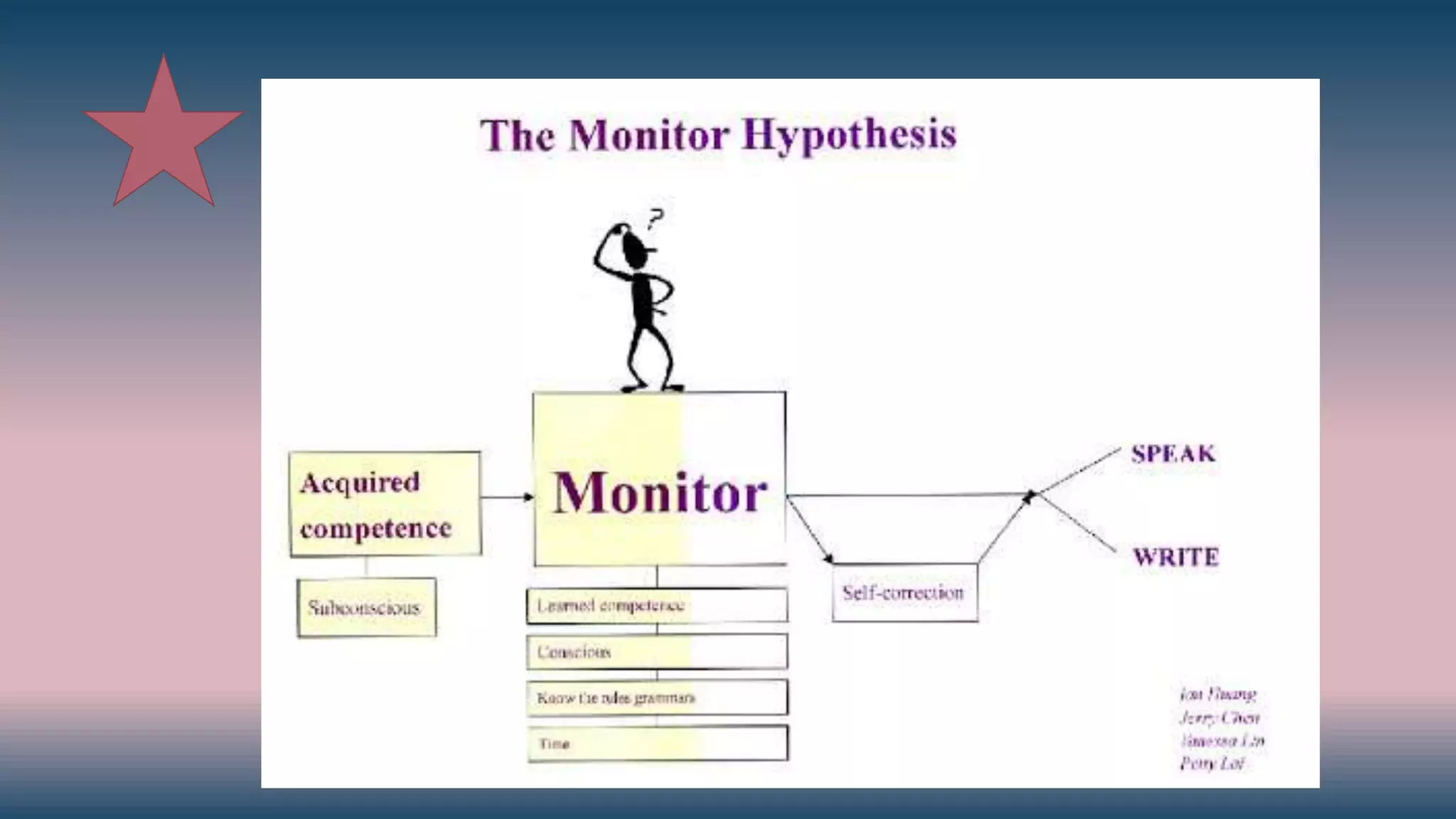
2) The Monitor Hypothesis states that conscious learning involves self-monitoring speech but only as a "fix-it" device after the message is produced.
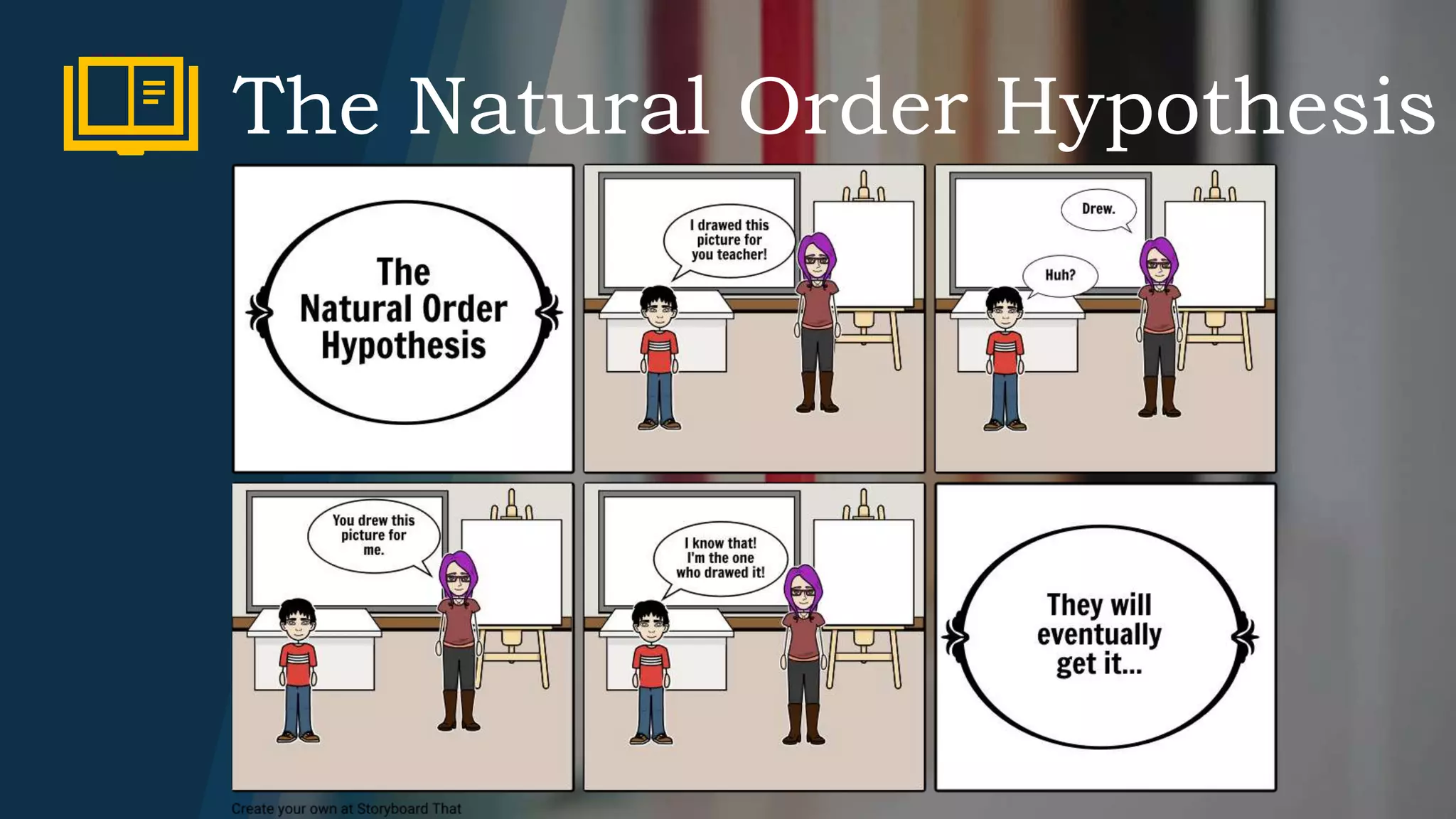
3) The Natural Order Hypothesis suggests that grammatical structures are acquired in a predictable sequence, regardless of the learner's first language.
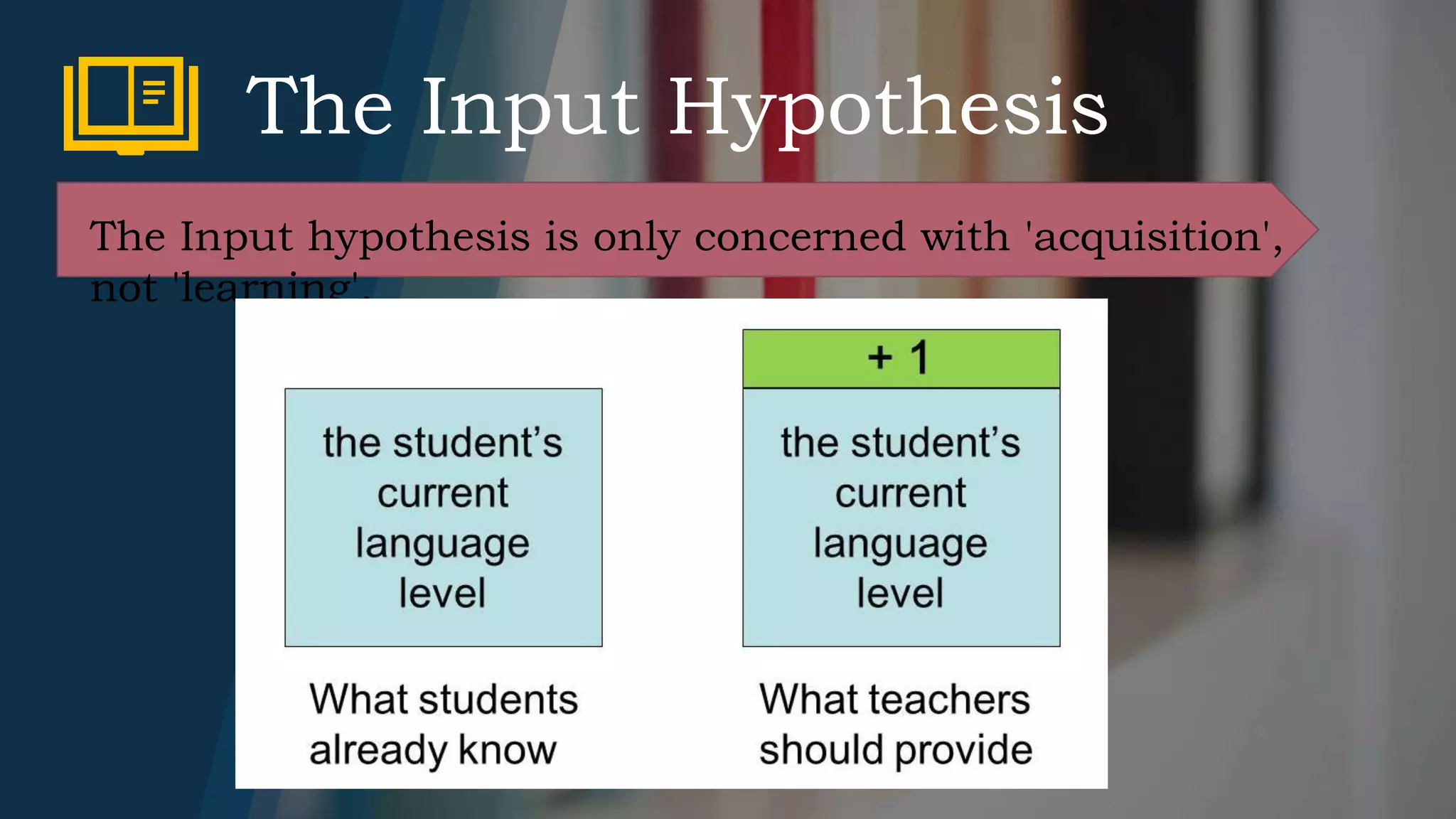
4) The Input Hypothesis claims that acquisition occurs when learners receive input that is comprehensible but contains structures at the next level of difficulty.
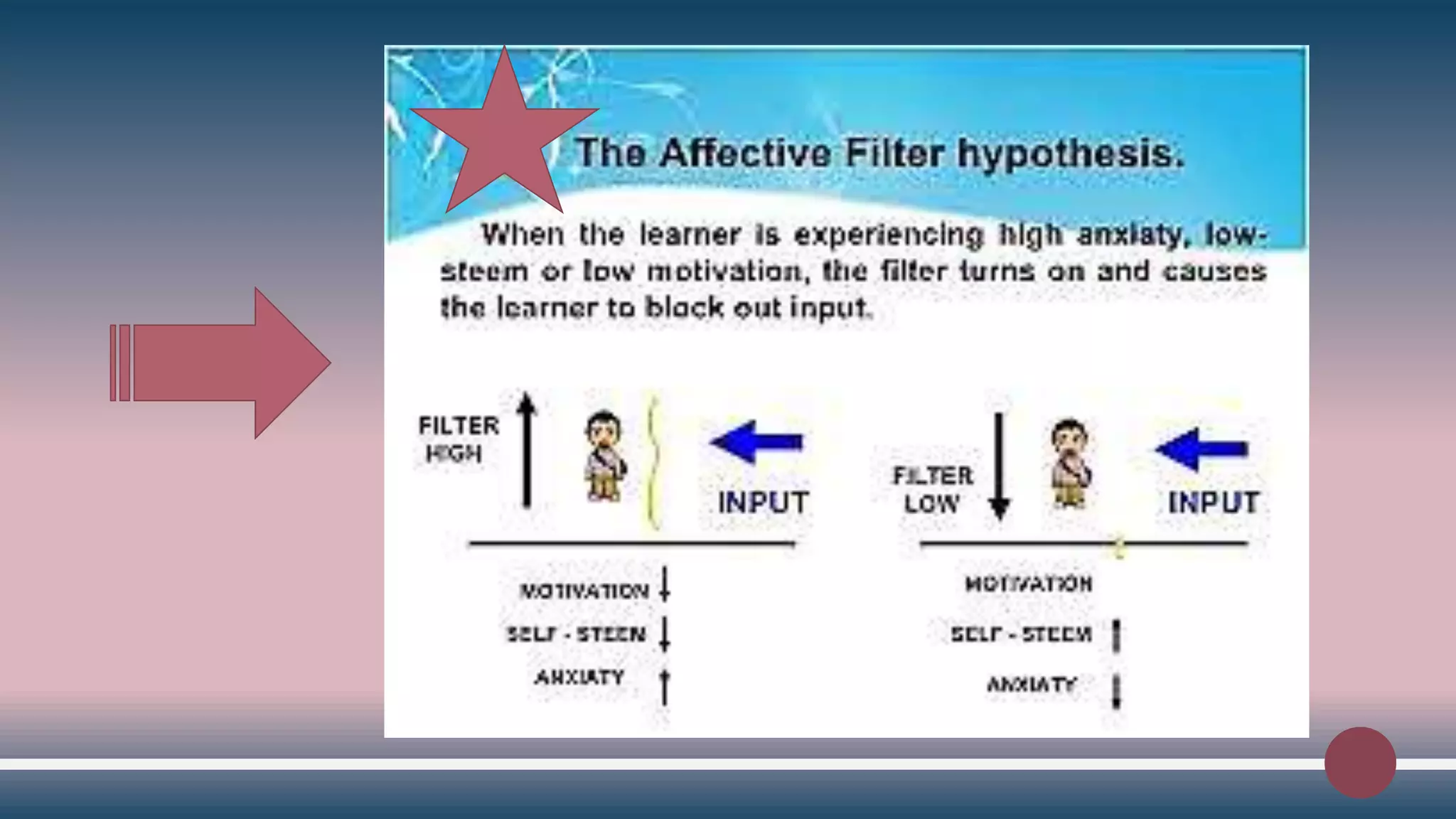
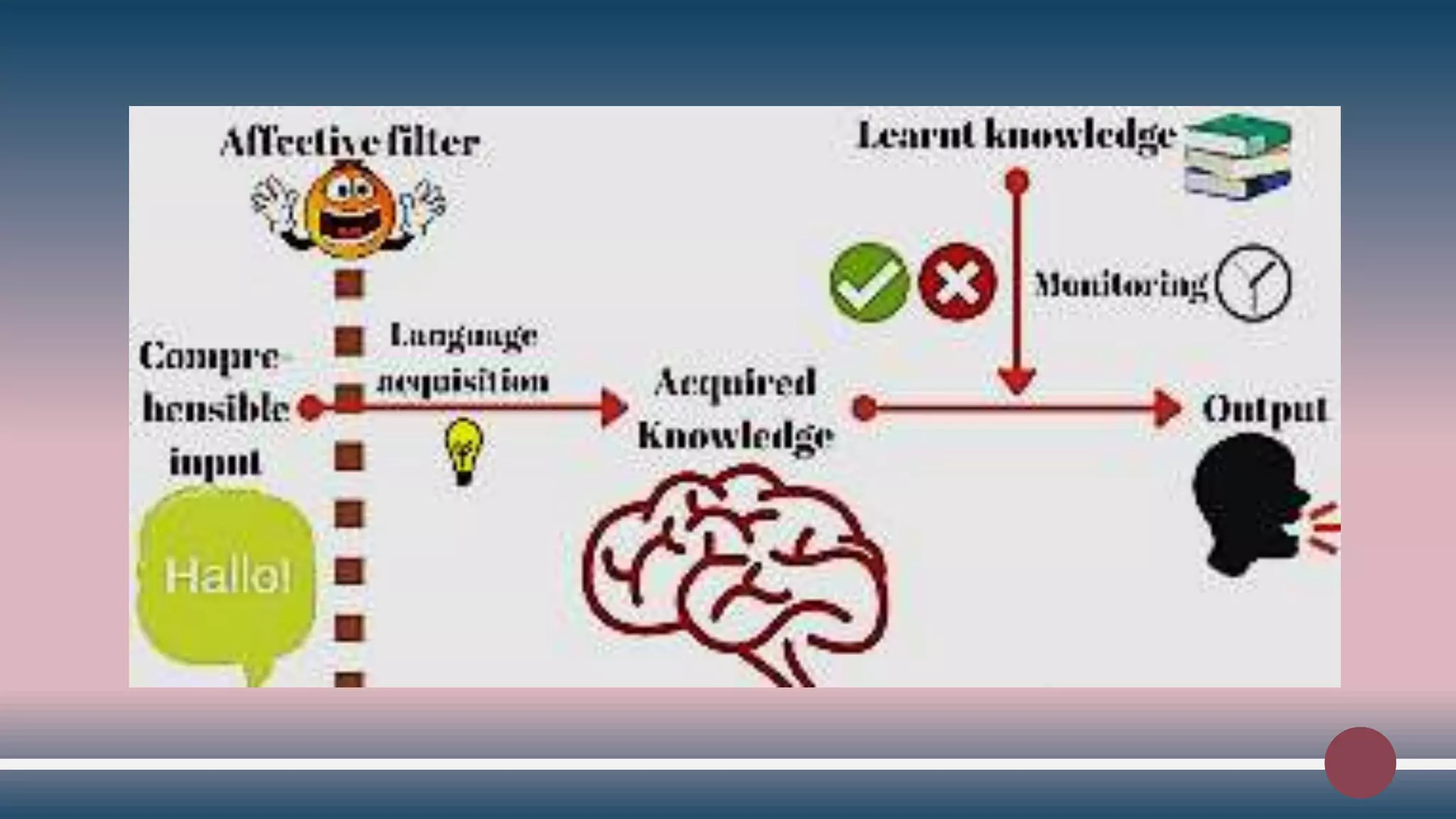
5) The Affect