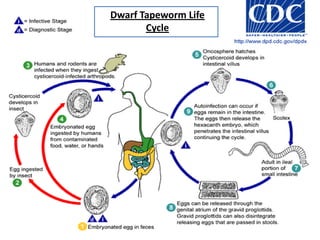
The document provides information on several types of tapeworms:
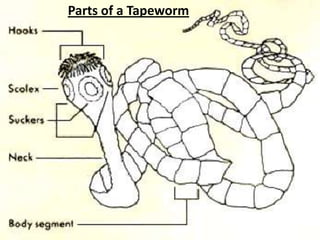
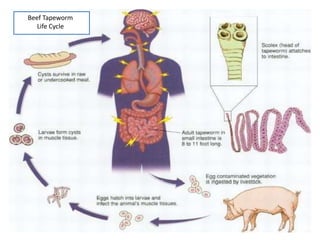
- Tapeworms can grow up to 16 feet long and live in the internal organs of their hosts, eating whatever the host eats. They are transmitted when people consume undercooked meat containing tapeworm cysts.
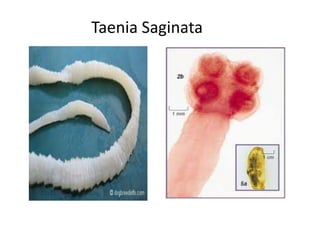
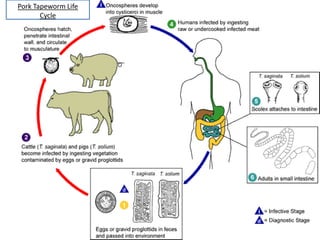
- Taenia saginata, the beef tapeworm, infects both cattle and humans. Humans are infected by eating undercooked beef containing larvae. It can grow over 12 meters and have over 2000 segments.
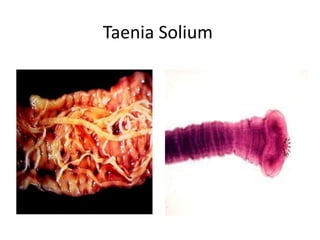
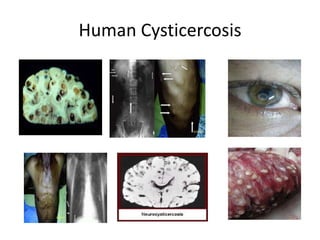
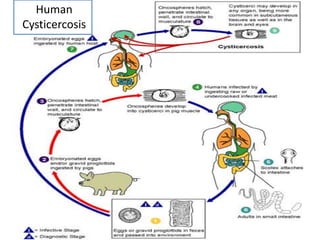
- Taenia solium, the pork tapeworm, infects both pigs and humans. Humans are infected by eating undercooked pork containing larvae. It causes cysticercosis if the eggs infect tissues