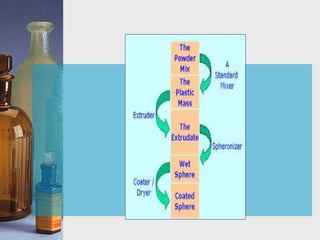
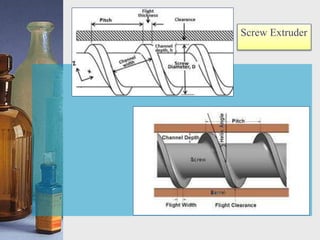
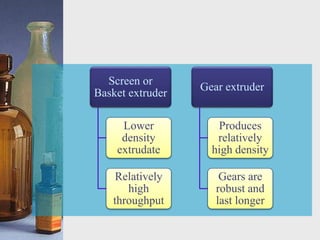
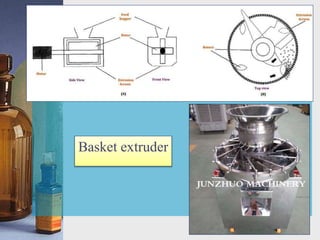
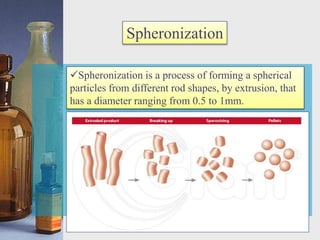
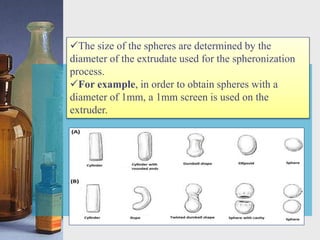
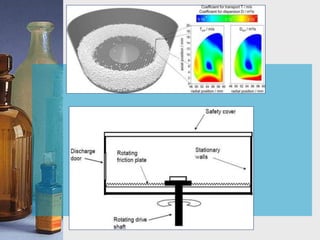
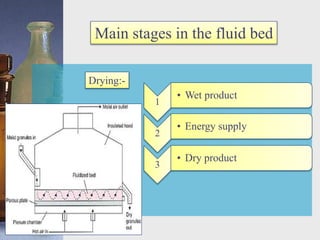
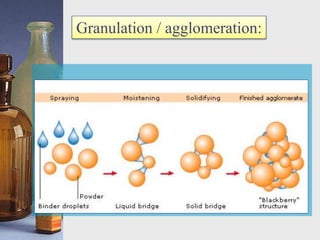
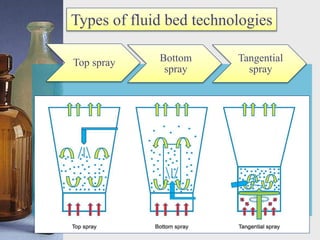
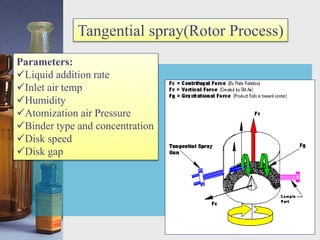
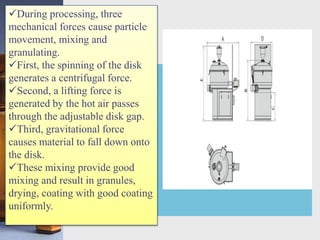
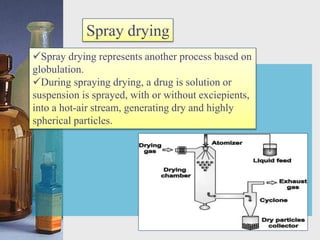
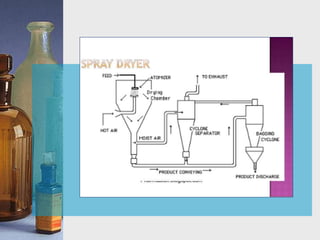
This document discusses different techniques for pelletization, including extrusion-spheronization, fluid bed granulation, spray drying, and spray congealing. Extrusion-spheronization involves extruding the material through a screen to form rods, which are then rounded into spheres using a spheronization machine. Fluid bed granulation coats particles in a fluidized bed with sprayed binding liquid. Spray drying and spray congealing involve spraying melted or dissolved formulations into cooled air to form solid spheres.