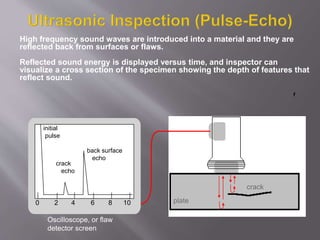
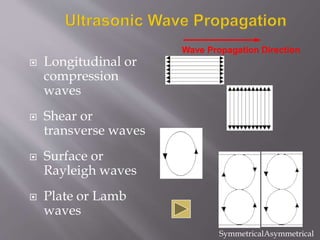
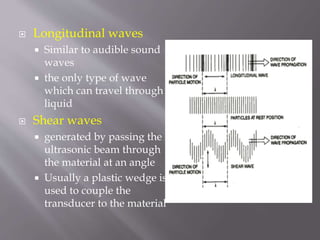
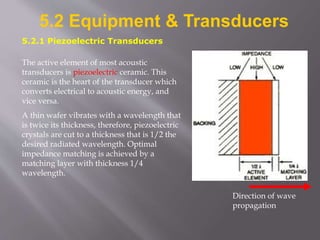
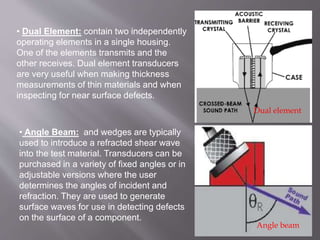
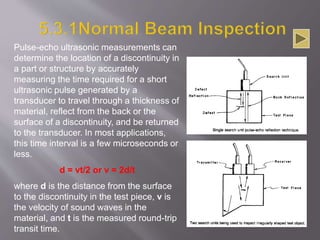
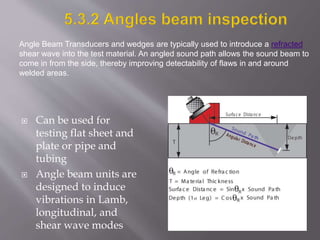
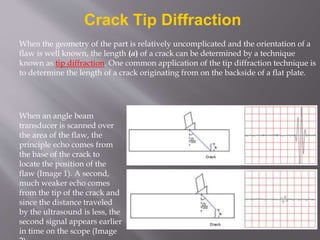
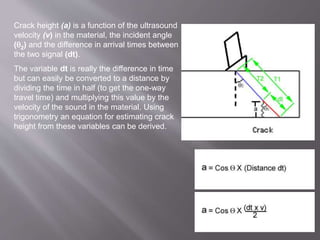
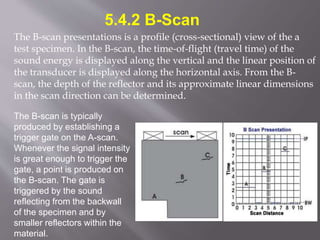
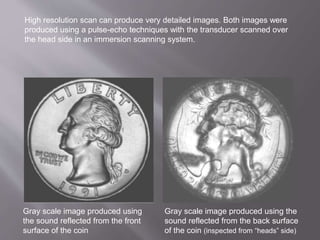
The document discusses ultrasonic testing techniques. It describes how ultrasonic pulses are transmitted into a material and reflections from internal imperfections or surfaces are detected. The time interval between pulse transmission and reception provides clues about the material's internal structure. Common techniques include pulse-echo testing and using transducers to generate and detect longitudinal or shear waves. Reflected signals are visualized on an oscilloscope as A-scans, B-scans, or C-scans to evaluate material features.