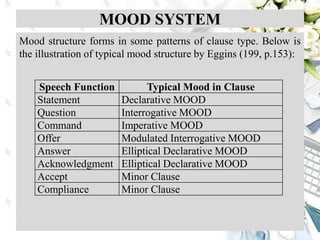
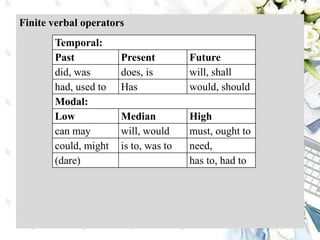
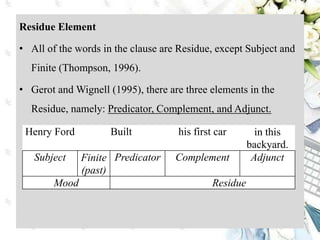
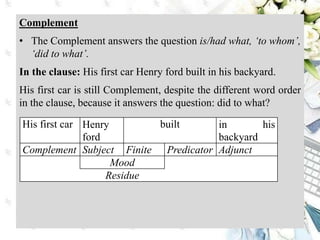
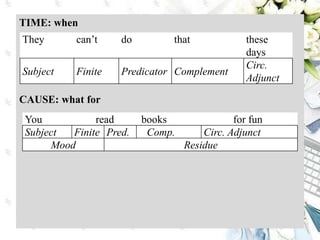
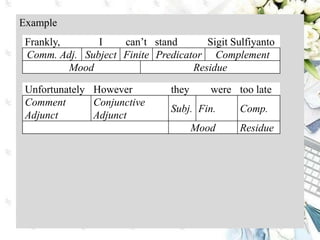
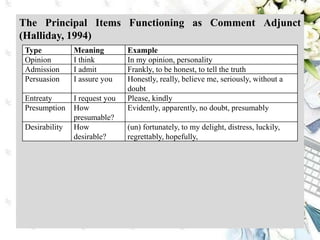
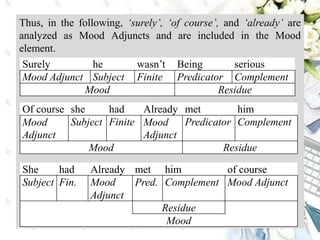
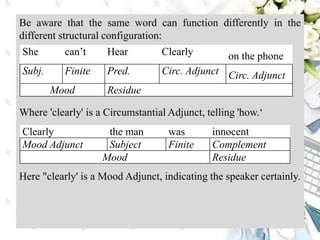
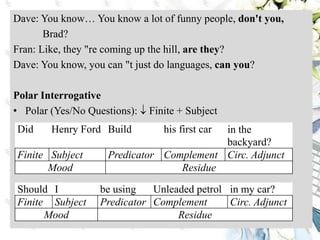
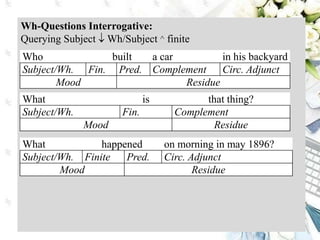
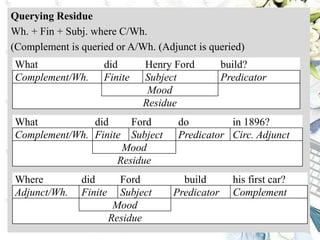
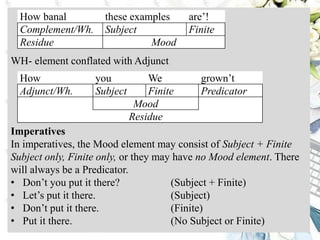
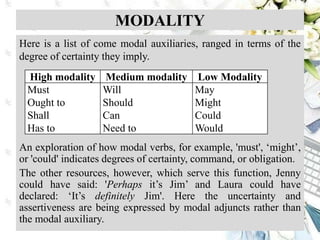
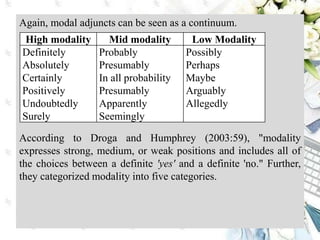
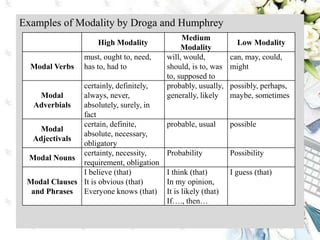
This document discusses interpersonal meanings in systemic functional linguistics. It explains that interpersonal meaning expresses a speaker's attitudes and judgments, and is realized through the analysis of mood and modality. Mood is analyzed using elements such as subject, finite, residue, and adjuncts. The mood types include declarative, interrogative, imperative and others. Interpersonal meaning provides insights into a speaker's perspective through examination of linguistic features like modality and mood.