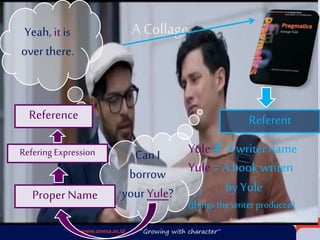
This document discusses the concepts of reference and inference in pragmatics. It defines reference as using linguistic forms like referring expressions to identify things, and inference as connecting prior knowledge to understand implied meanings beyond what is directly stated. There are four main categories of referring expressions: proper nouns, definite noun phrases, indefinite noun phrases, and pronouns. For successful reference, both the linguistic context and physical context must be considered to determine the intended referent. Reference relies on anaphora to continue identifying entities, while ellipsis and implicature also play a role through omitted references understood through inference.


























![Cook ? = was omitted=[the slices/them]
Ellipsis = Cook [the peeled onionslices]
• When the interpretationrequires us to identifyan entity,
and nolinguistic expressionispresented.
• It frequently uses verbal anaphora
“Peel an Onionand Sliceit. Drop the slices intohot
oil.Cook for three minutes”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/referenceppt-150608073300-lva1-app6891/85/Reference-Pragmatics-28-320.jpg)

