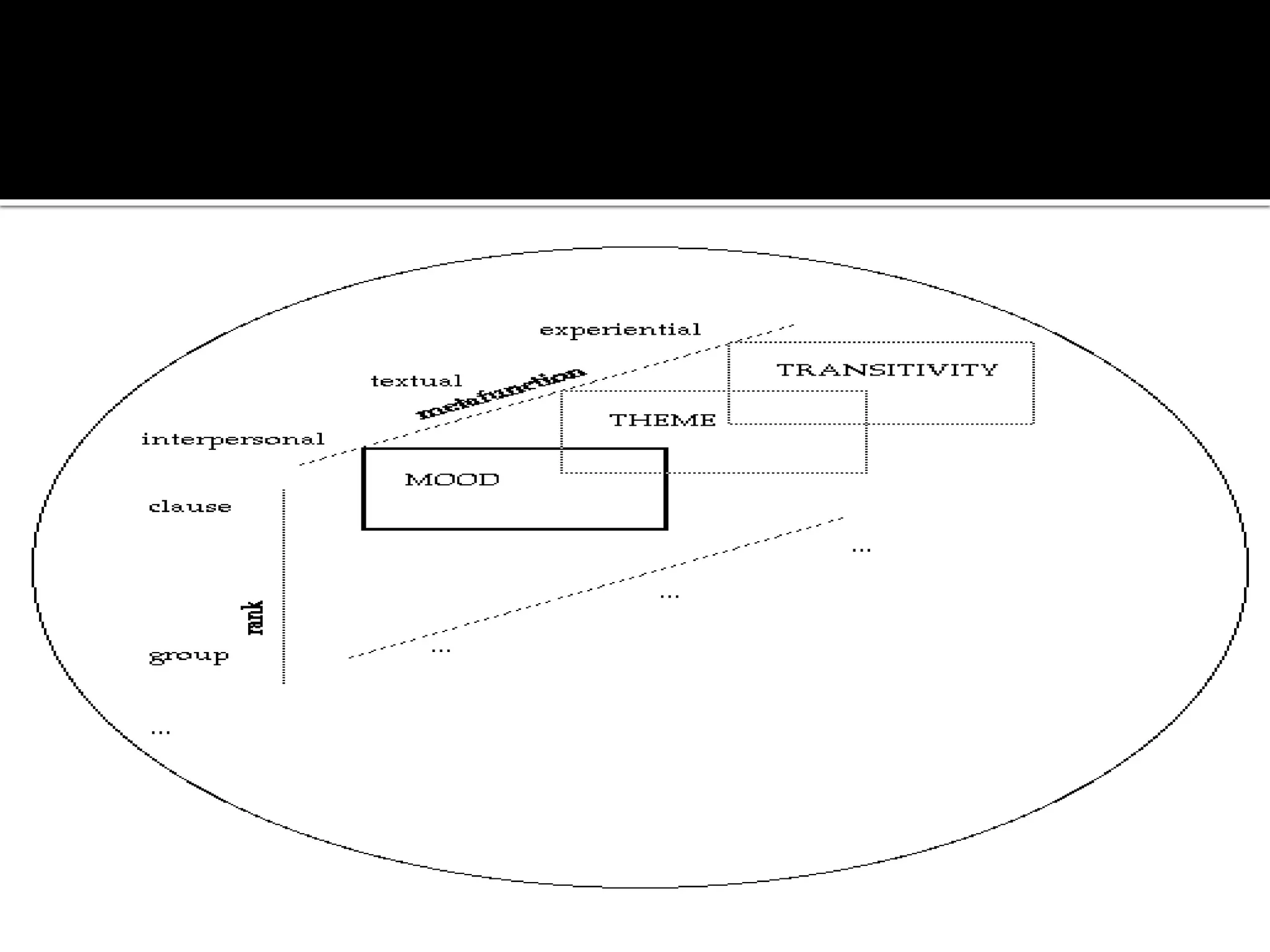
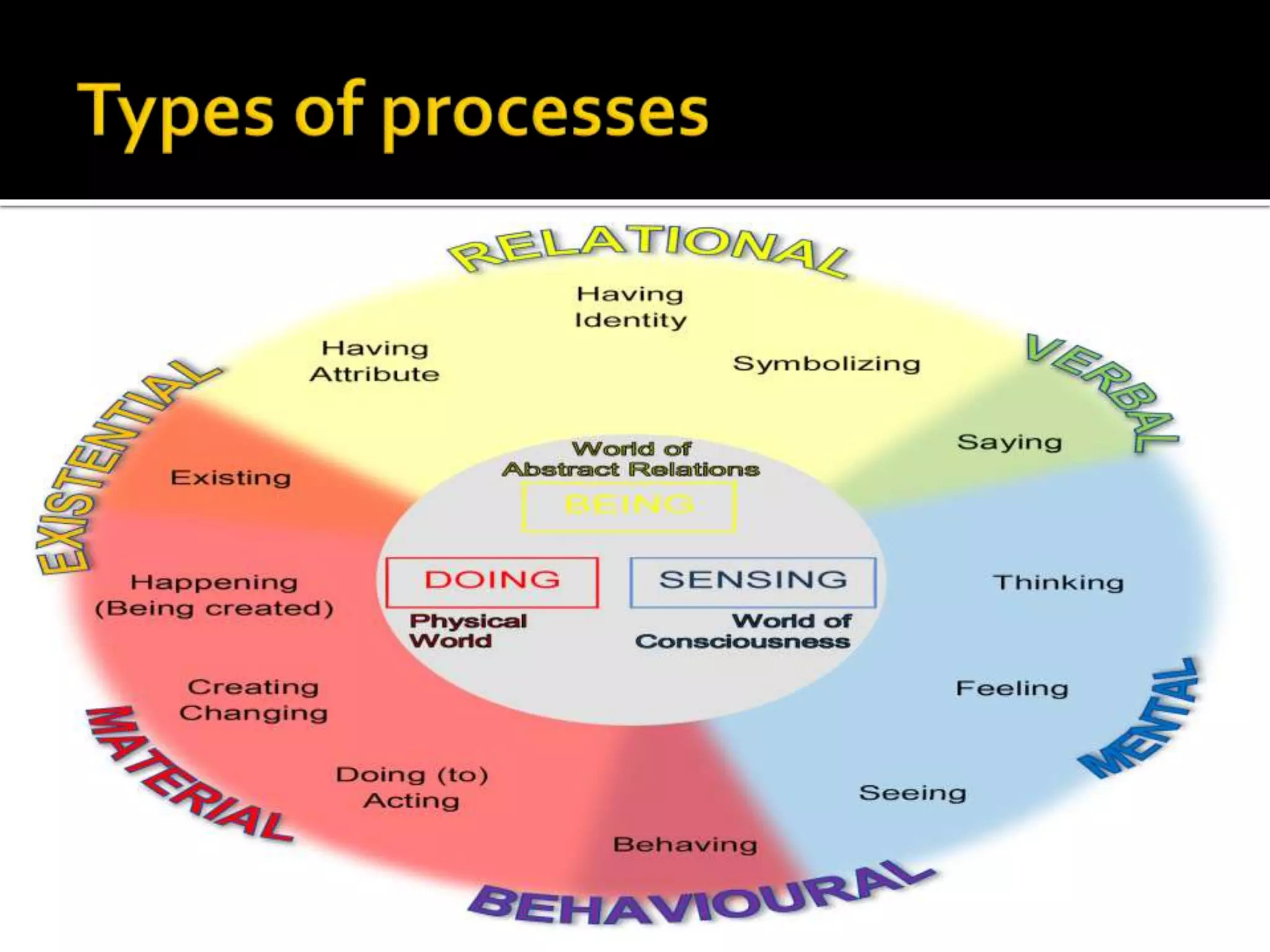
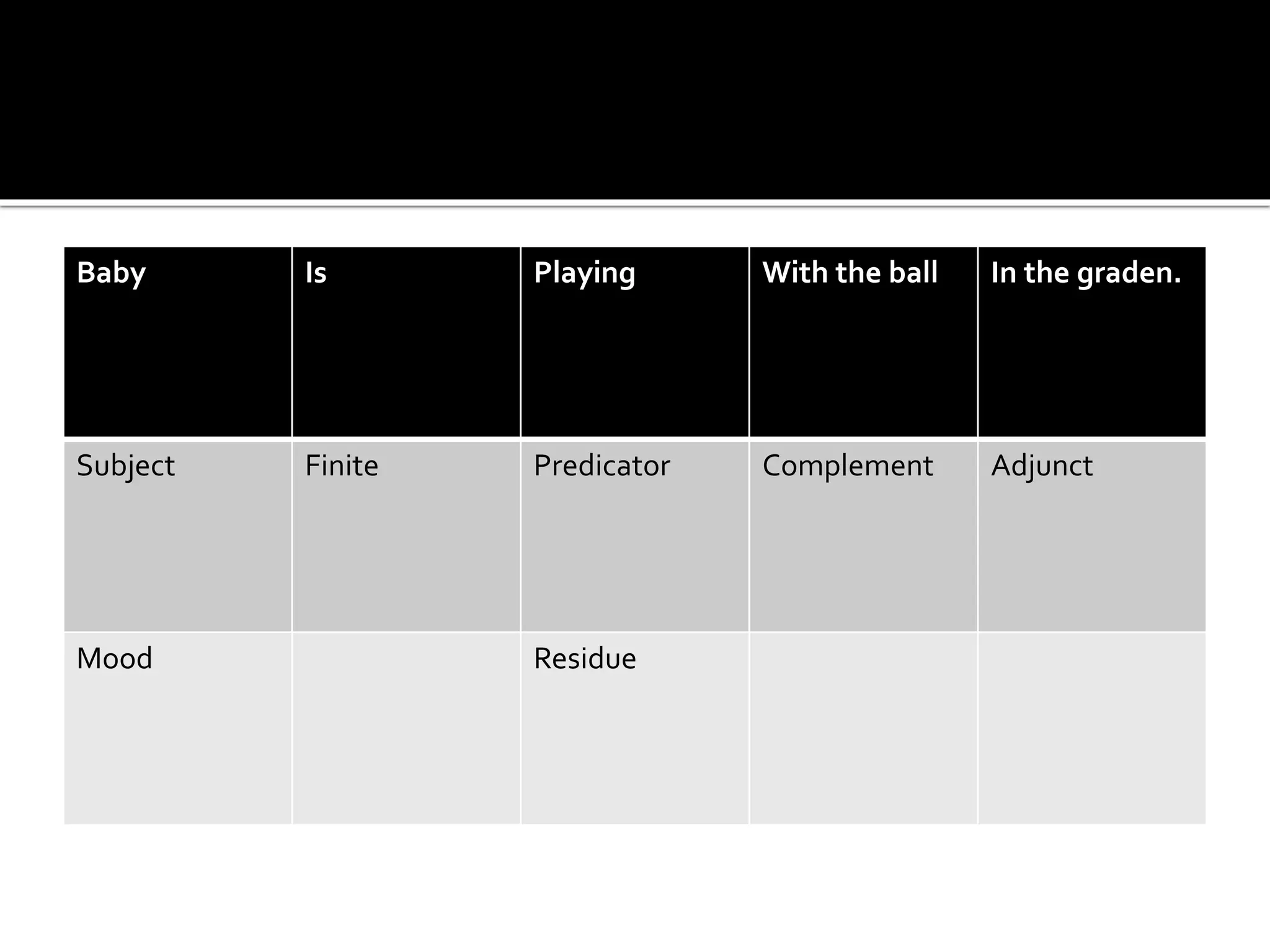
The document discusses Systemic Functional Grammar, which views a clause as realizing three metafunctions: ideational, interpersonal, and textual. The ideational metafunction represents experiences through transitivity. The interpersonal metafunction concerns social exchanges through the mood system. The textual metafunction concerns information flow through the theme system. These metafunctions work interdependently in language.