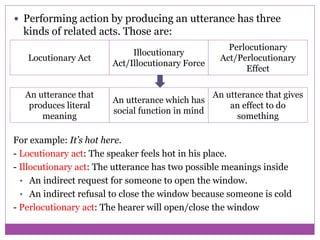
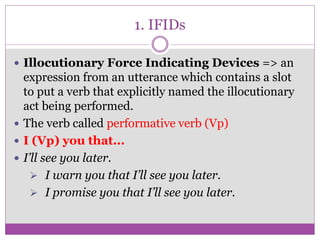
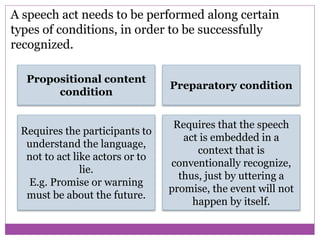
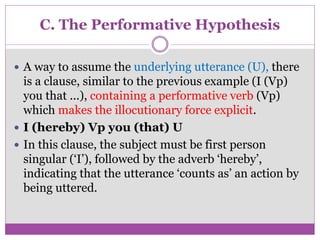
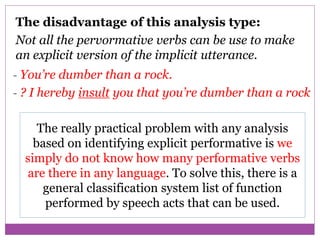
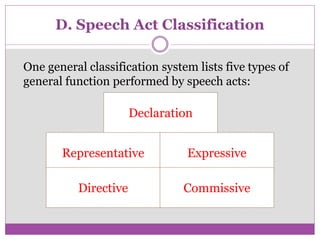
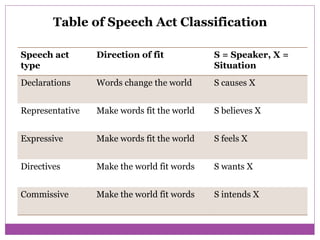
The document discusses speech acts and related concepts in pragmatics. It defines speech acts as actions performed through utterances, beyond just grammatical structures. There are three types of related acts: locutionary (literal meaning), illocutionary (social function), and perlocutionary (effect on listener). Illocutionary force indicates the main action of an utterance. Indirect speech acts convey meaning through implied functions rather than direct structure-function relationships. A speech event involves utterances between participants with a shared context, topic, and goal.