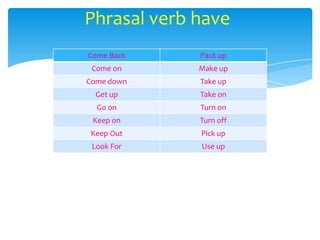
This document provides an overview of different types of verbs in English. It defines verbs and divides them into three main categories: main verbs, auxiliaries, and modal auxiliaries. It then proceeds to explain eight specific types of verbs in more detail, including regular and irregular verbs, transitive and intransitive verbs, special verbs, state verbs, linking verbs, phrasal verbs, verb tenses, and gerund and infinitive verbs. Examples are provided to illustrate the key characteristics and uses of each verb type.