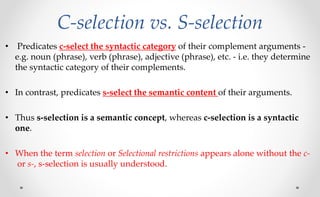
The document discusses the structure of arguments in language. It defines an argument as an expression that helps complete the meaning of a predicate. Predicates take one, two, or three arguments to form a predicate-argument structure. An adjunct is an optional part of a sentence that does not affect the sentence if removed. Valency theory explores the nature of predicates, arguments, and adjuncts. Transitivity relates to whether a verb can take direct objects and how many. Selectional properties determine the semantic content of a predicate's arguments. Theta theory assigns thematic roles like agent and patient to arguments.








![2-Explanation
In government and binding theory the theta criterion states that in any grammatical
sentence each argument must be assigned to one theta role and each theta role must be
realized by some argument.
Consequently in a grammatical sentence all predicates, meaning verbs, have a
thematic structure. This means that thematic roles, or theta roles (θ-role), describe the
relation between predicates and their arguments. As a result arguments stand in
different semantic relationships with the verb.
For Example:
Thomas gave the books to Marry.
[AGENT]_[THEME]_[EXPERIENCER/GOAL]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-thestructureofarguments-200625160556/85/The-structure-of-arguments-10-320.jpg)




