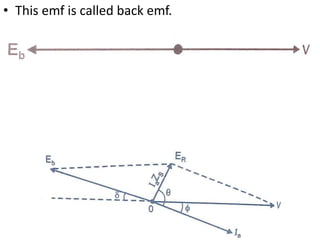
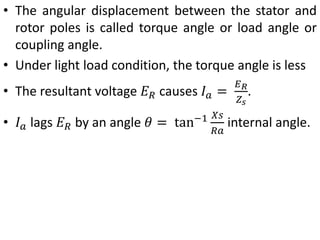
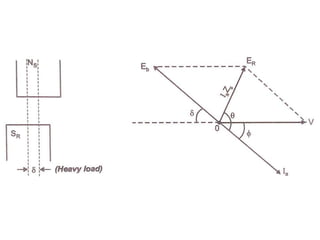
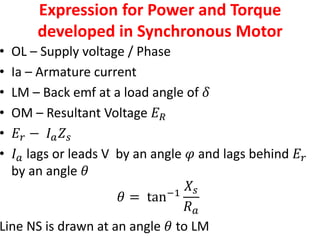
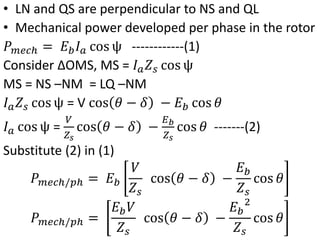
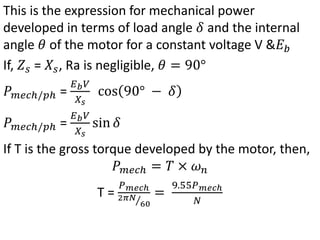
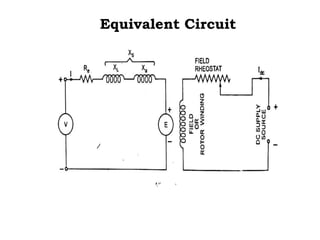
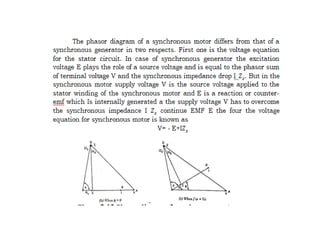
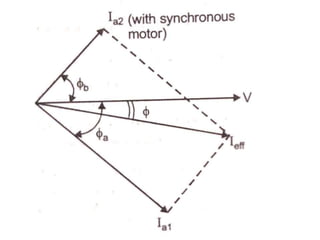
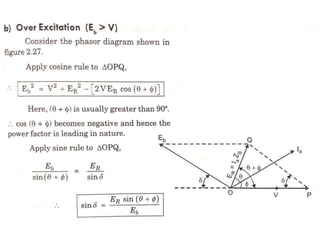
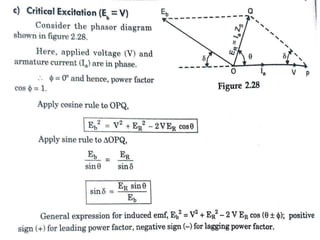
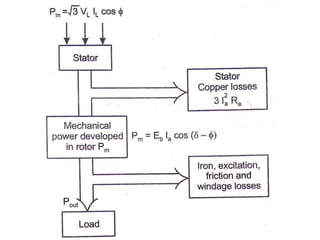
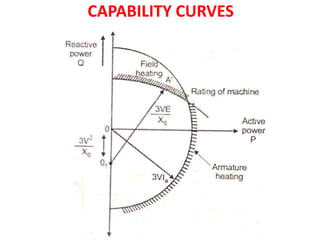
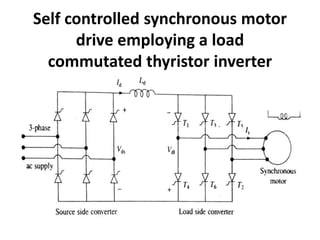
This document summarizes the operation of a synchronous motor. It discusses:
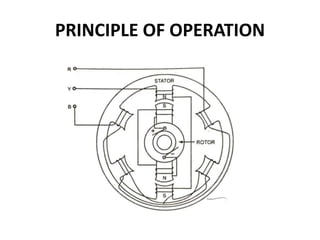
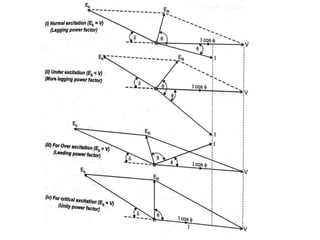
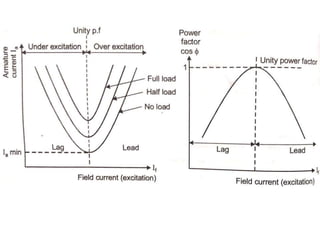
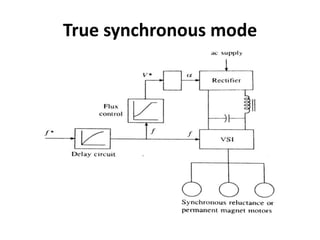
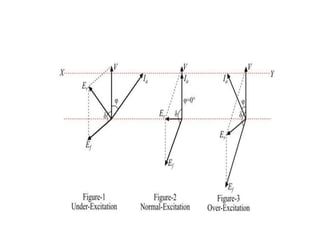
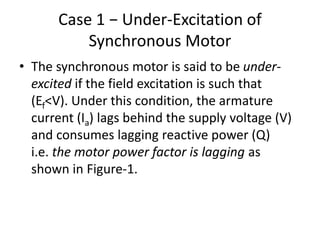
1) The synchronous motor operates at a constant speed determined by pole count and frequency. It can improve power factor by varying field excitation from lagging to leading.
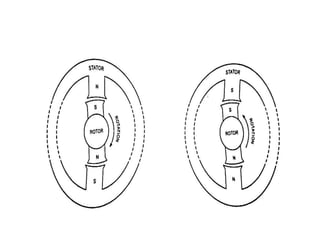
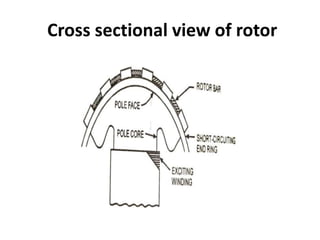
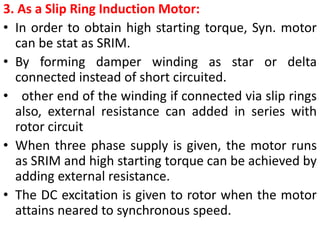
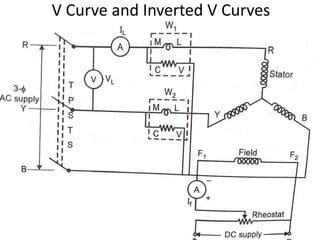
2) Starting methods include using a DC motor or damper windings to start as an induction motor before synchronizing.
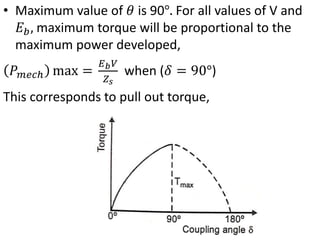
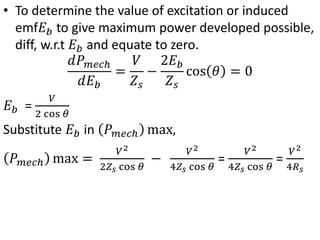
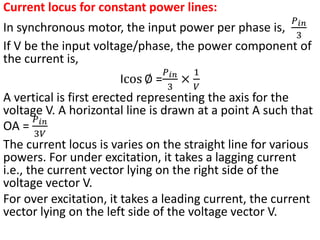
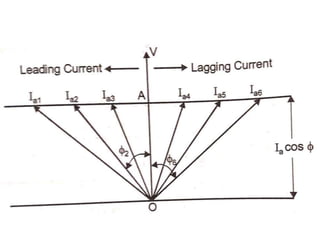
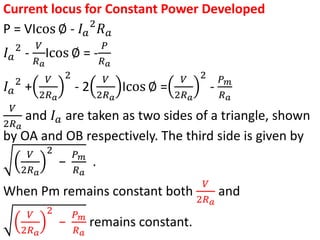
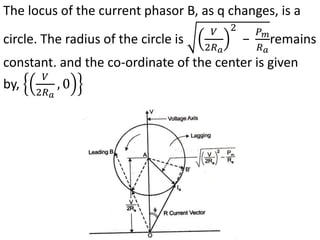
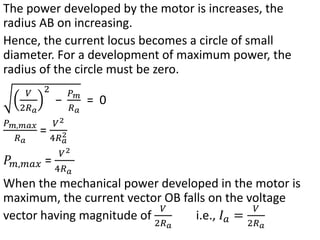
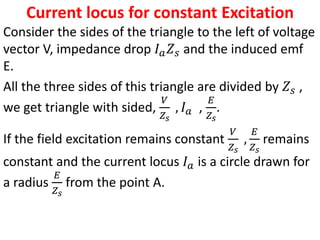
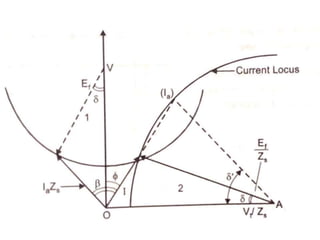
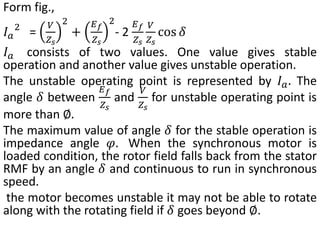
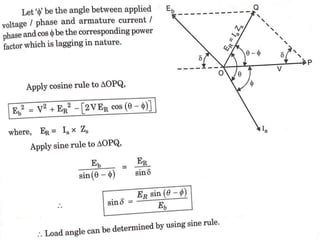
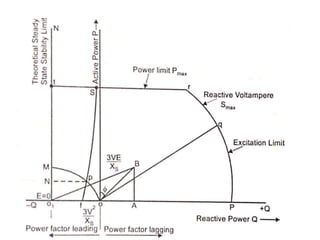
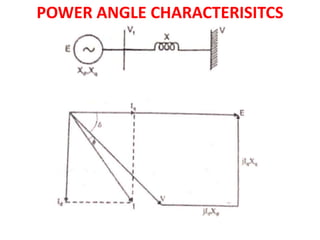
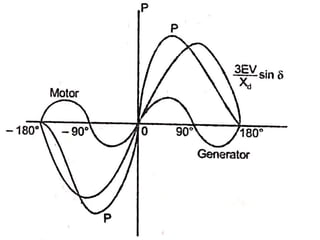
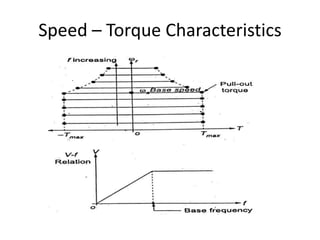
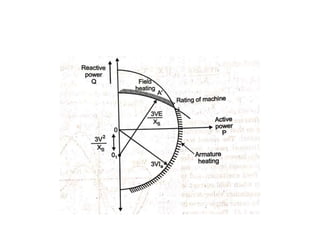
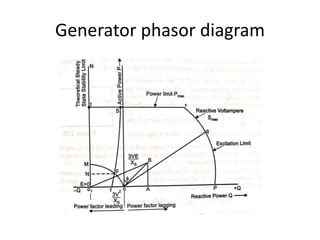
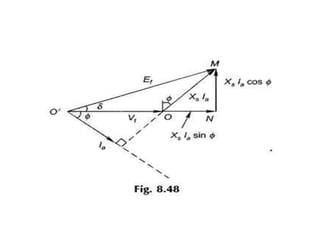
3) Torque curves show maximum torque occurs at a load angle of 90 degrees. Power input varies with excitation and voltage. The current locus is circular for constant excitation or power.
4) Synchronous condensers improve power factor by supplying leading current when over-excited while not loaded.