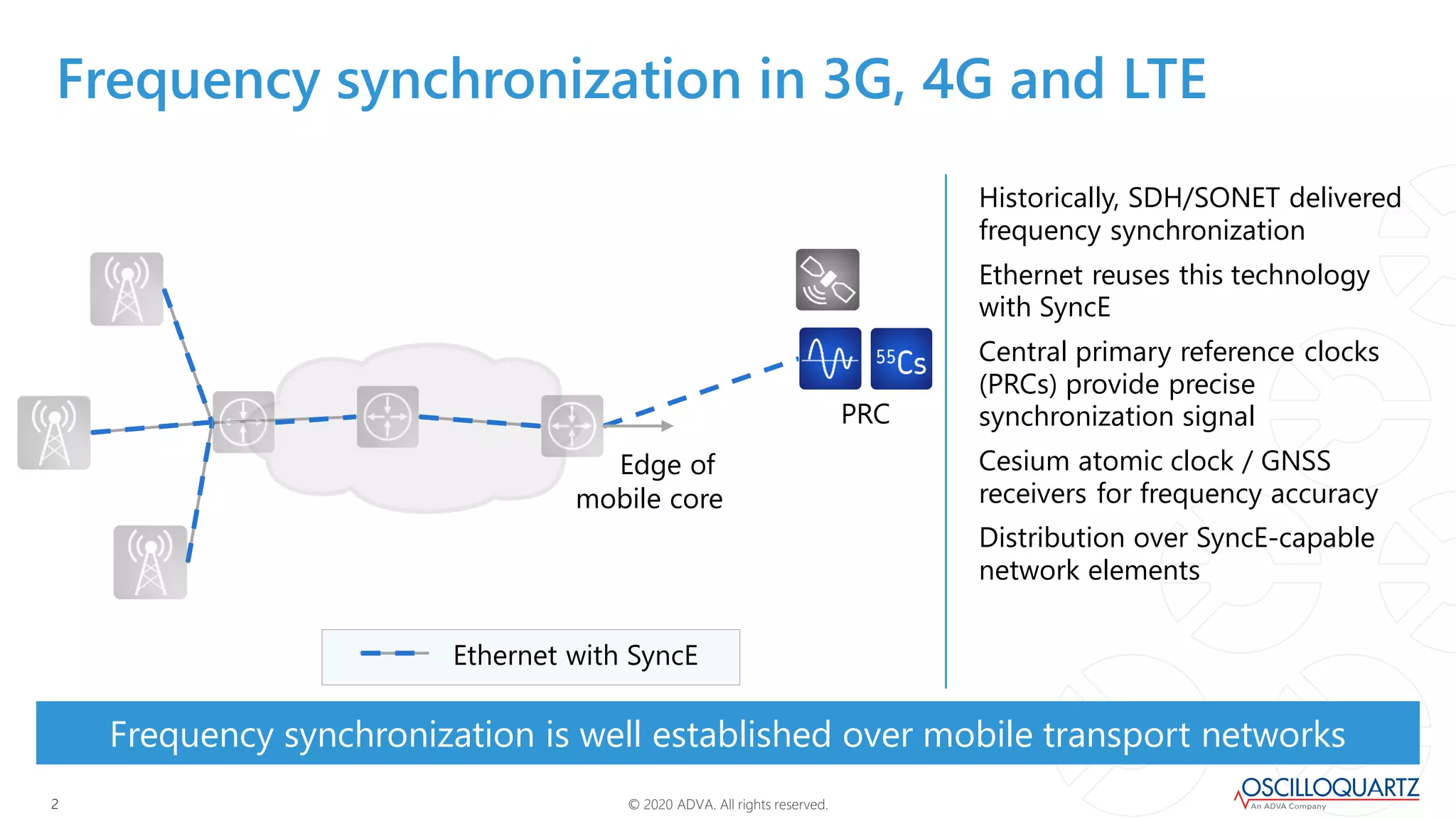
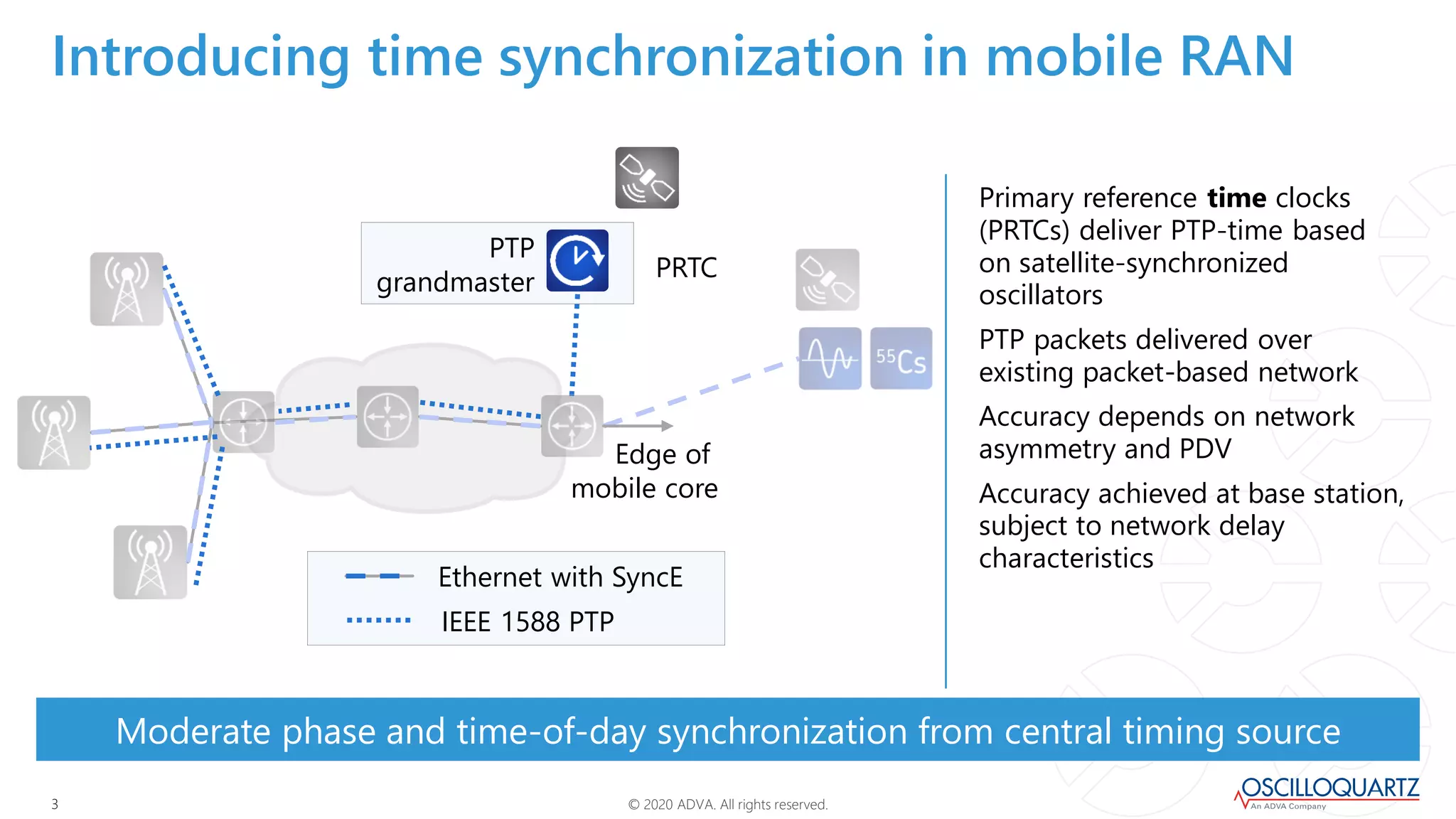
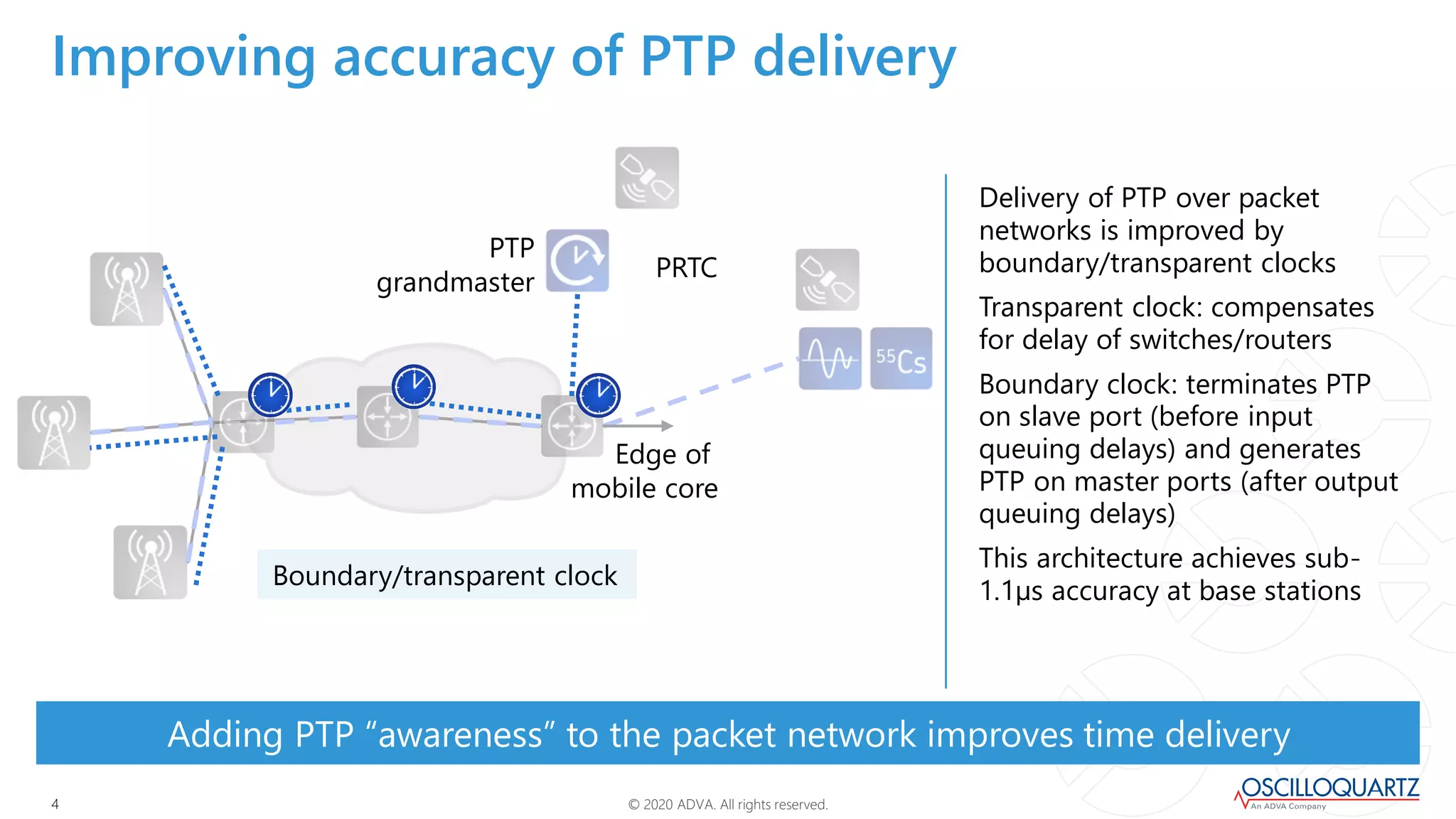
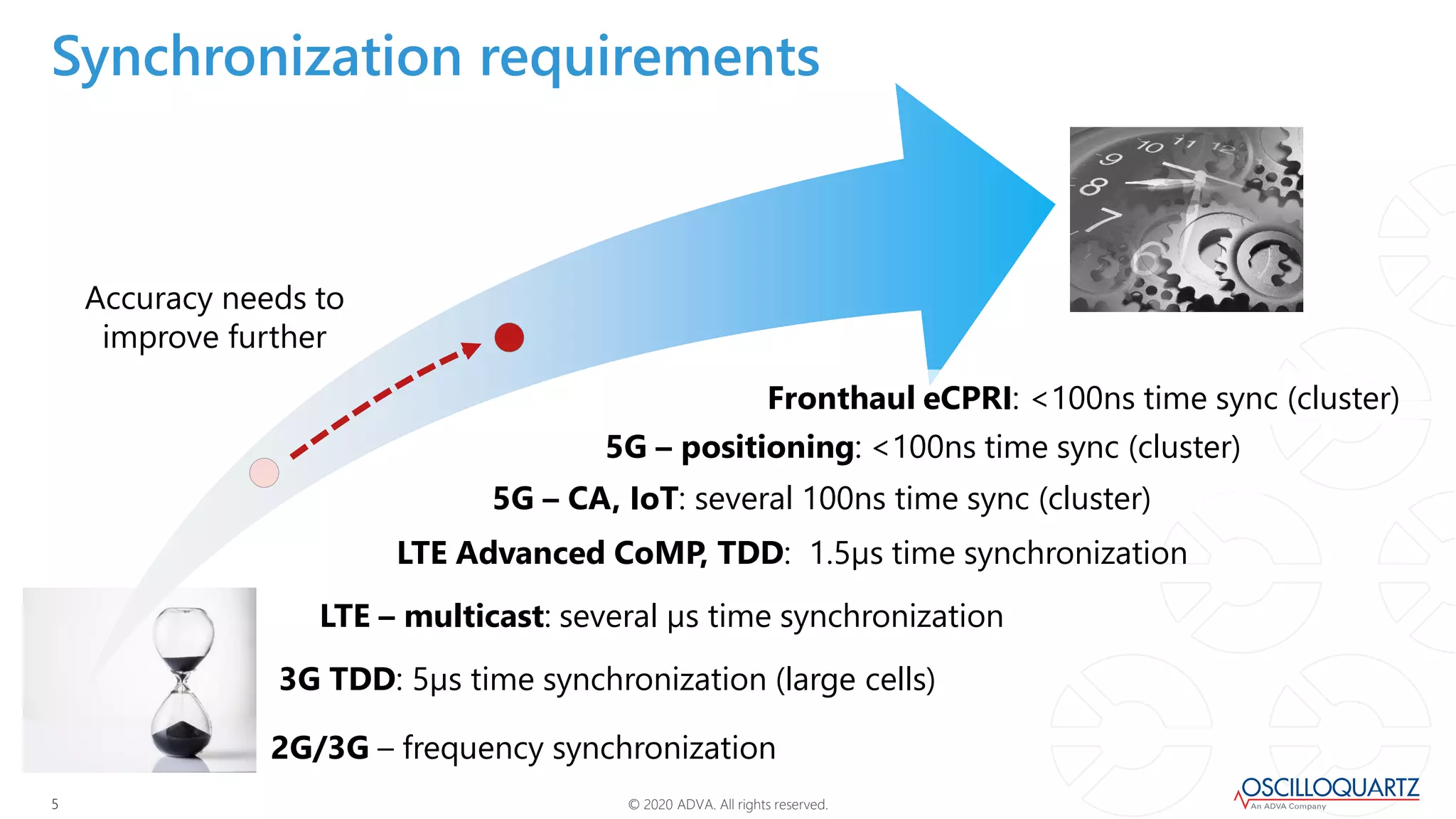
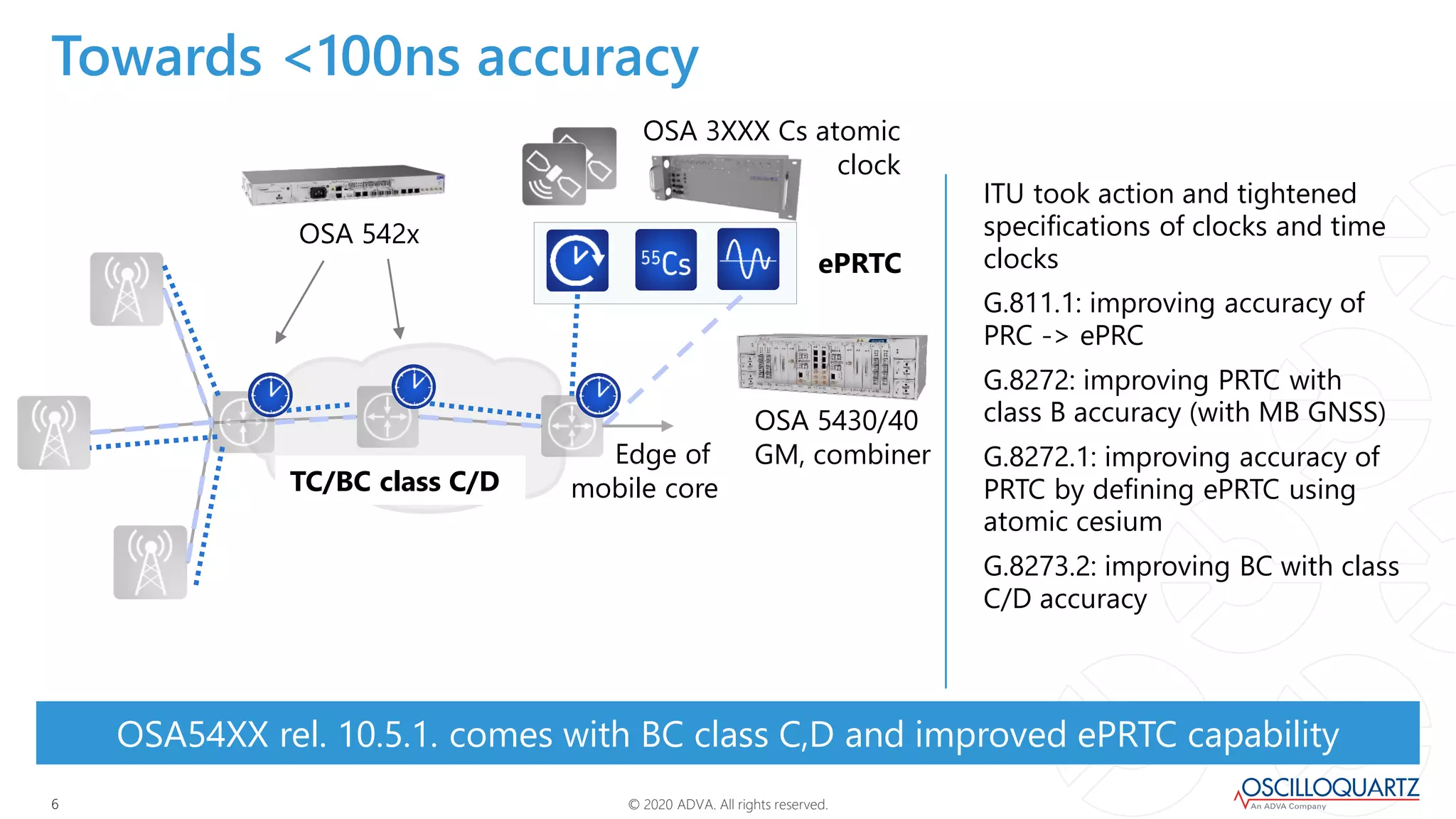
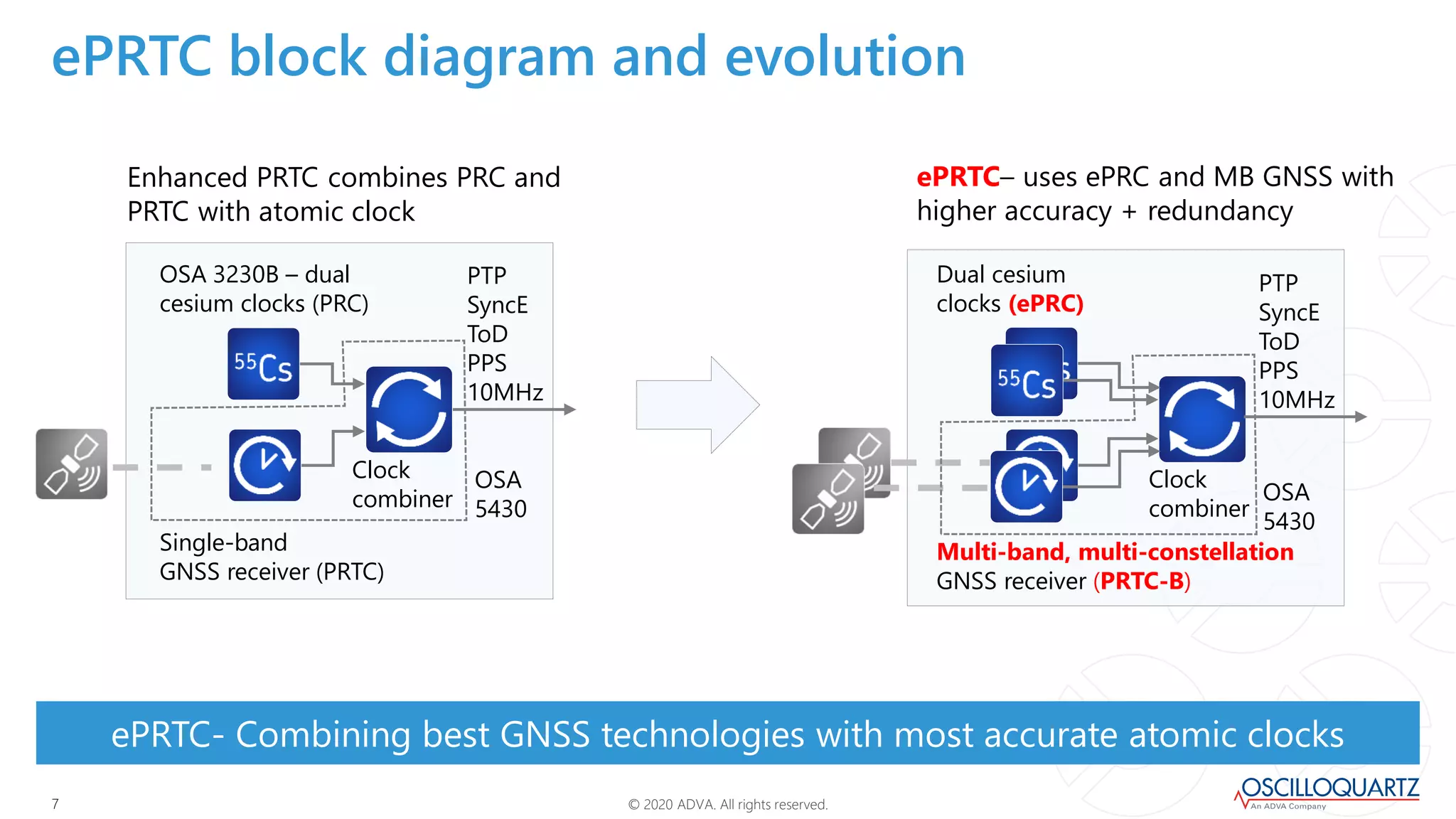
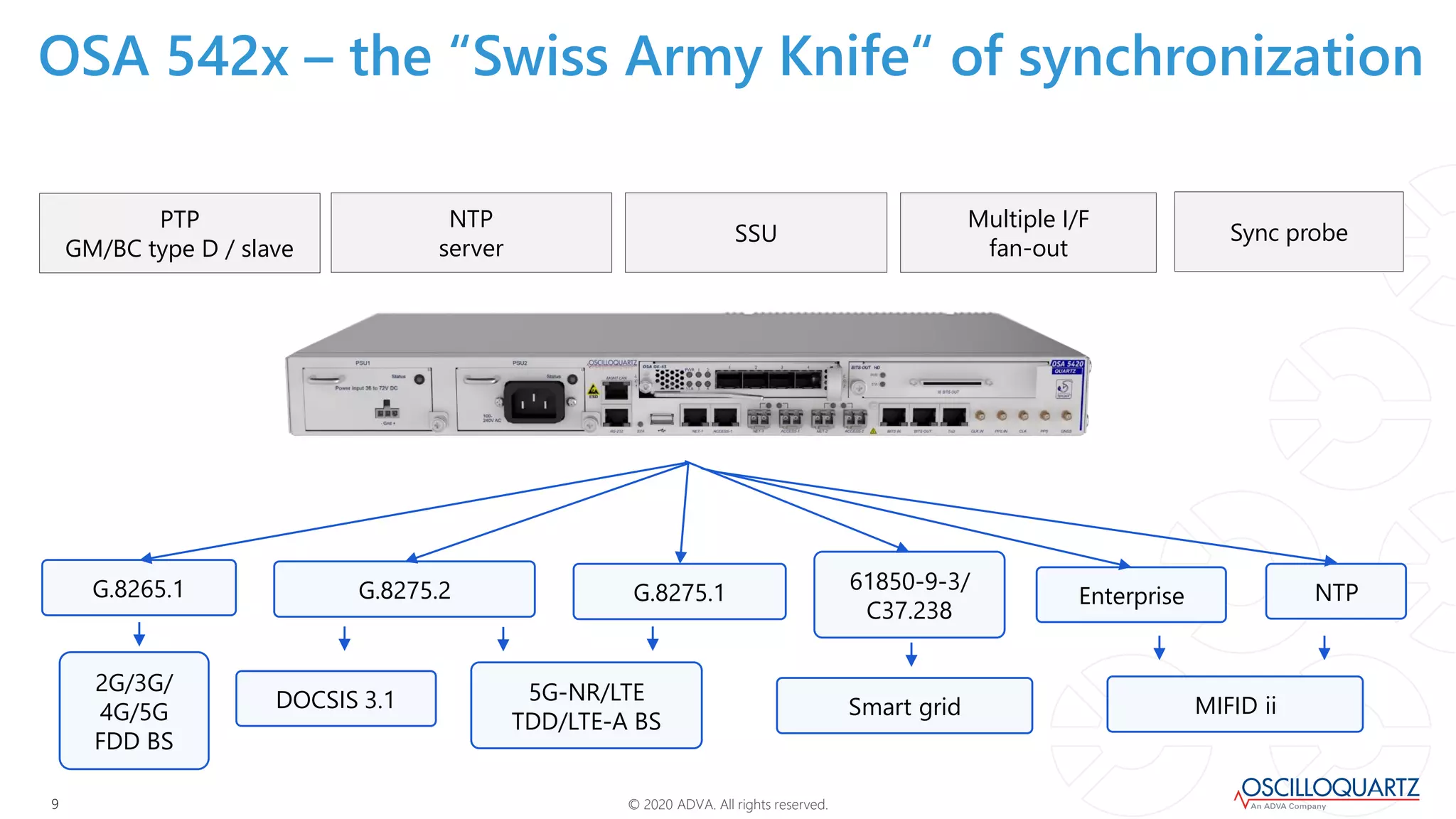
This document discusses synchronization techniques for 5G networks. It explains that frequency synchronization is established over mobile networks using SyncE and PRCs. Time synchronization is introduced using PTP and PRTCs sourced from satellite clocks, achieving moderate accuracy. Boundary and transparent clocks can improve PTP delivery accuracy when used in the packet network. The document outlines increasing synchronization accuracy requirements for newer technologies. It proposes using enhanced PRTCs combining GNSS and atomic clocks to achieve sub-100ns accuracy required for applications like 5G and fronthaul.