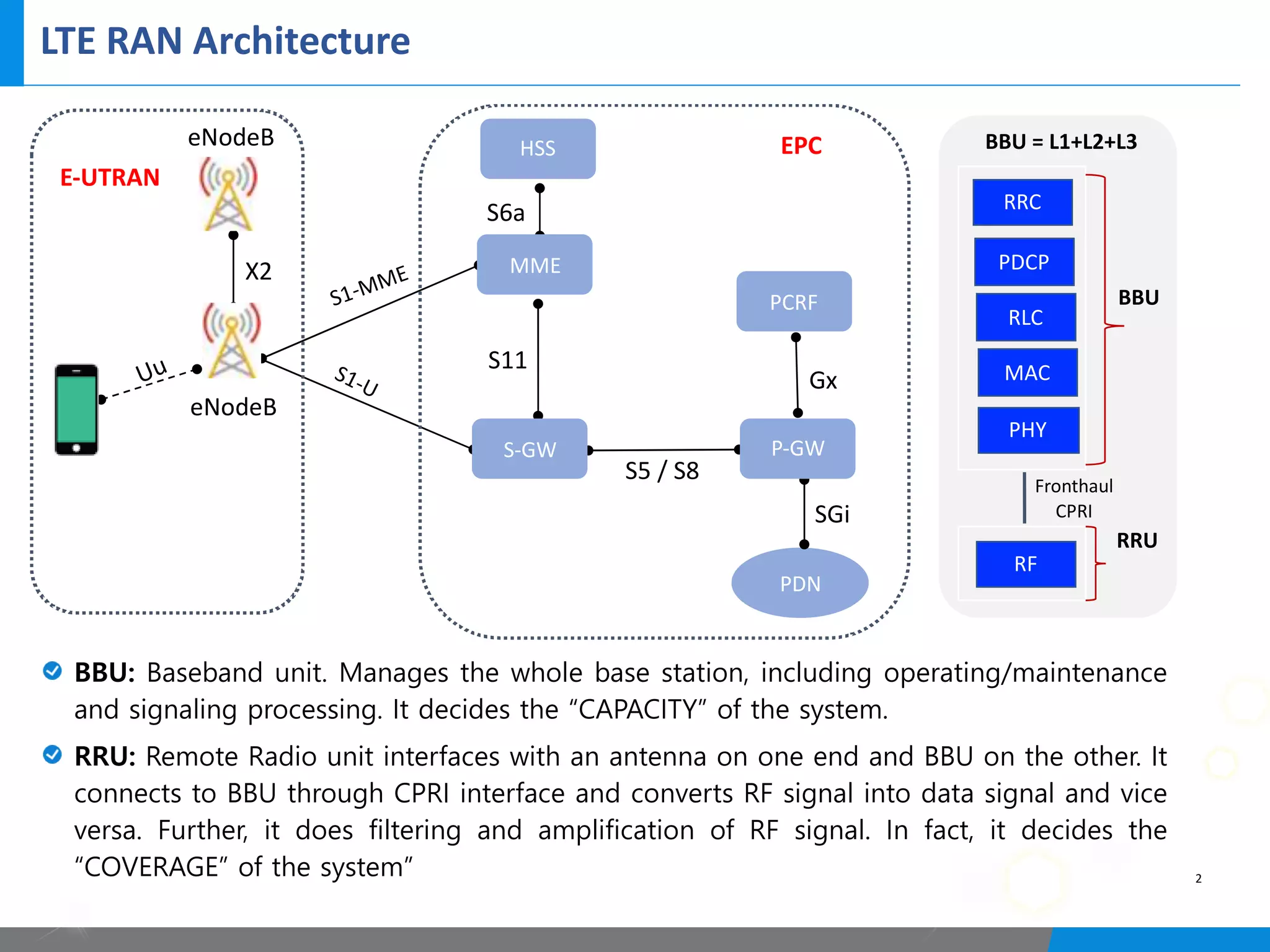
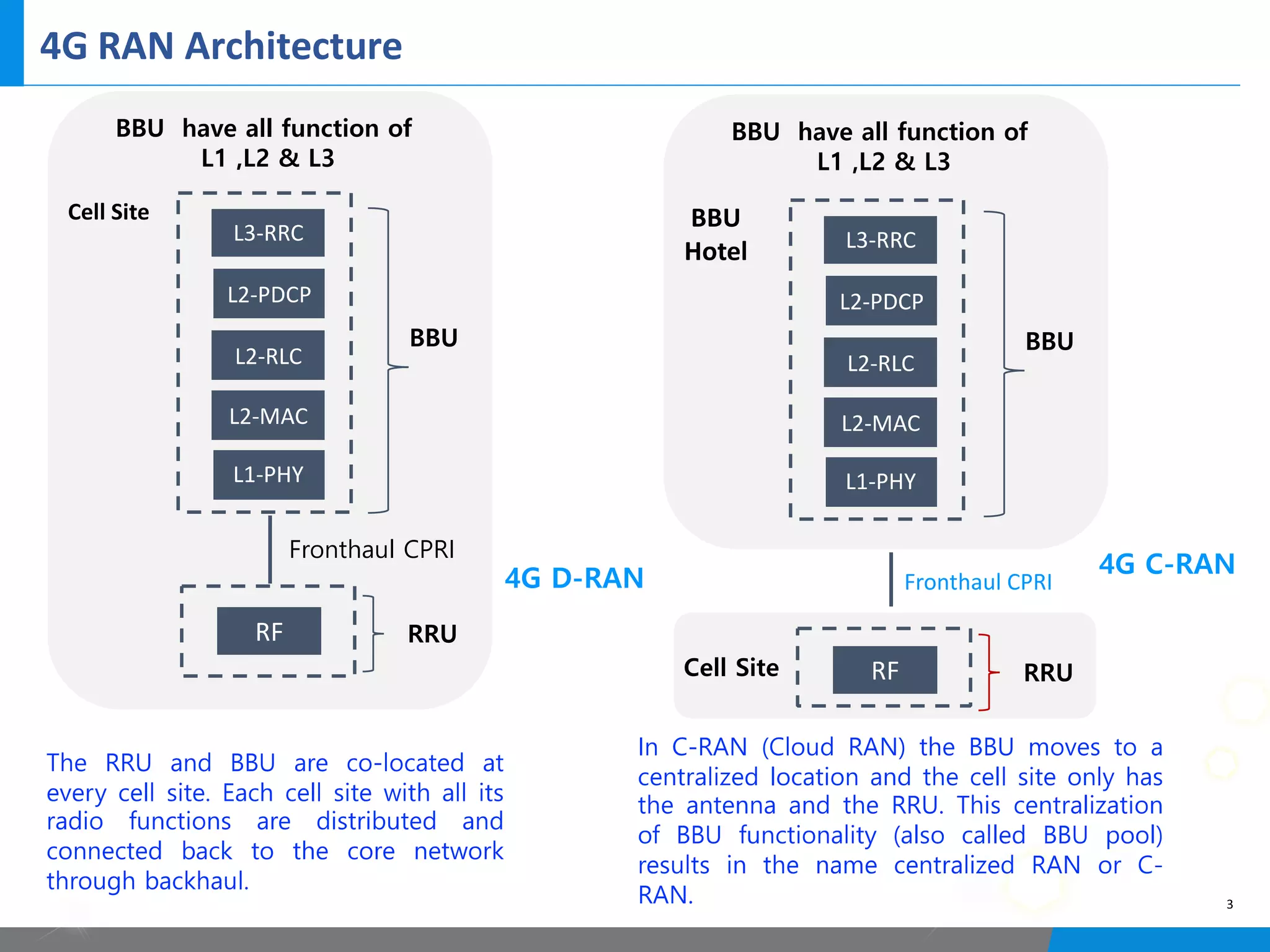
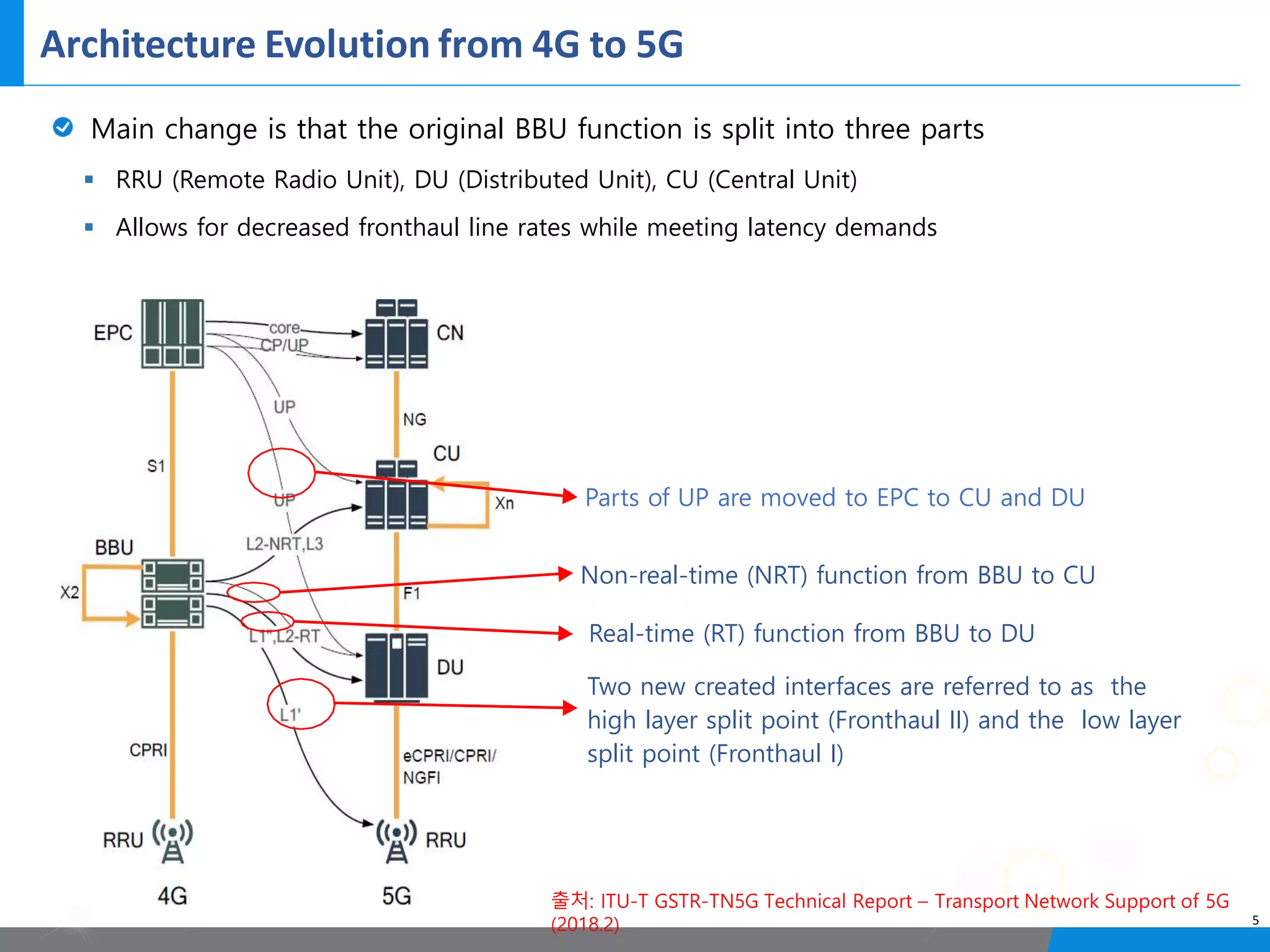
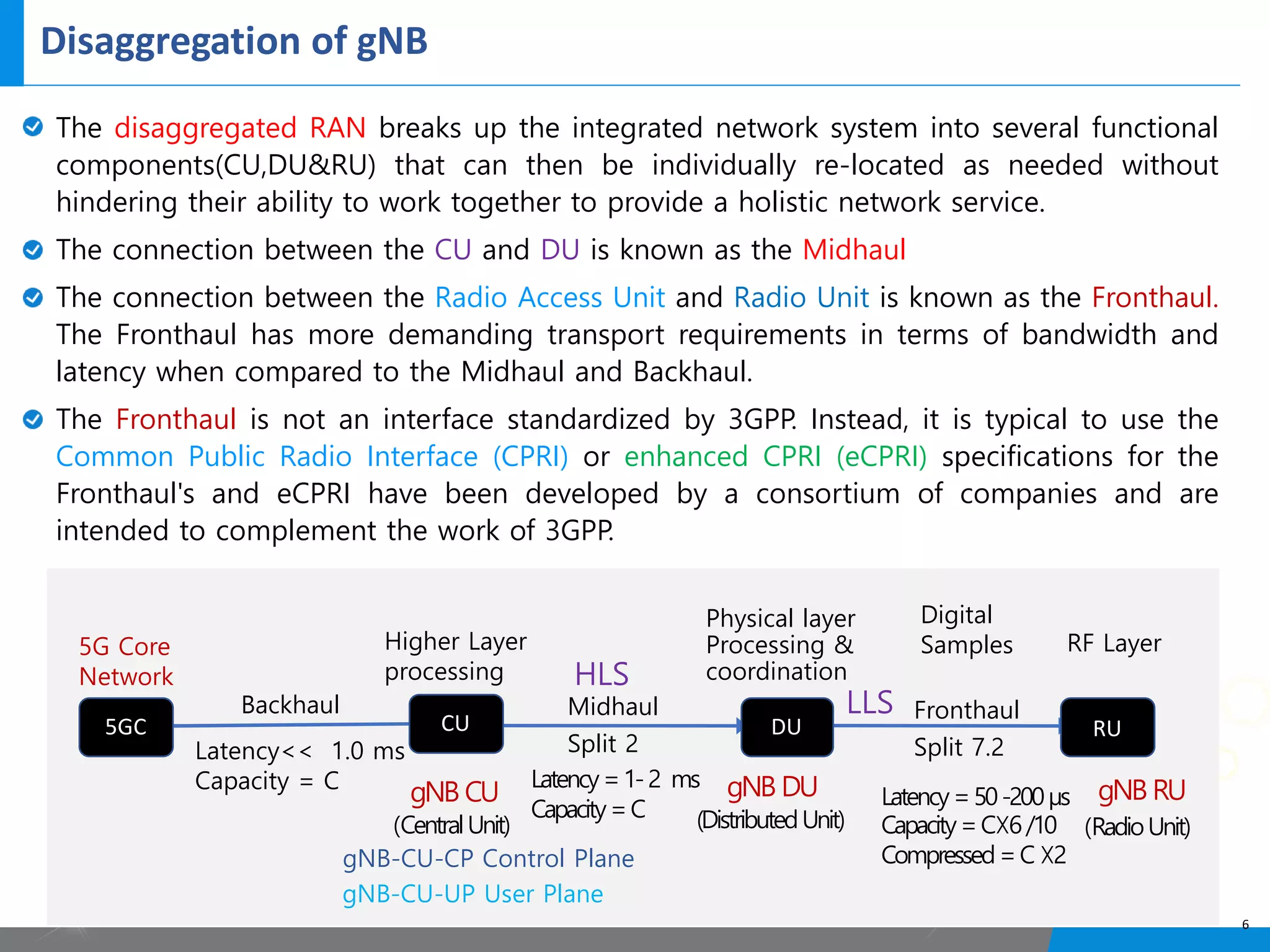
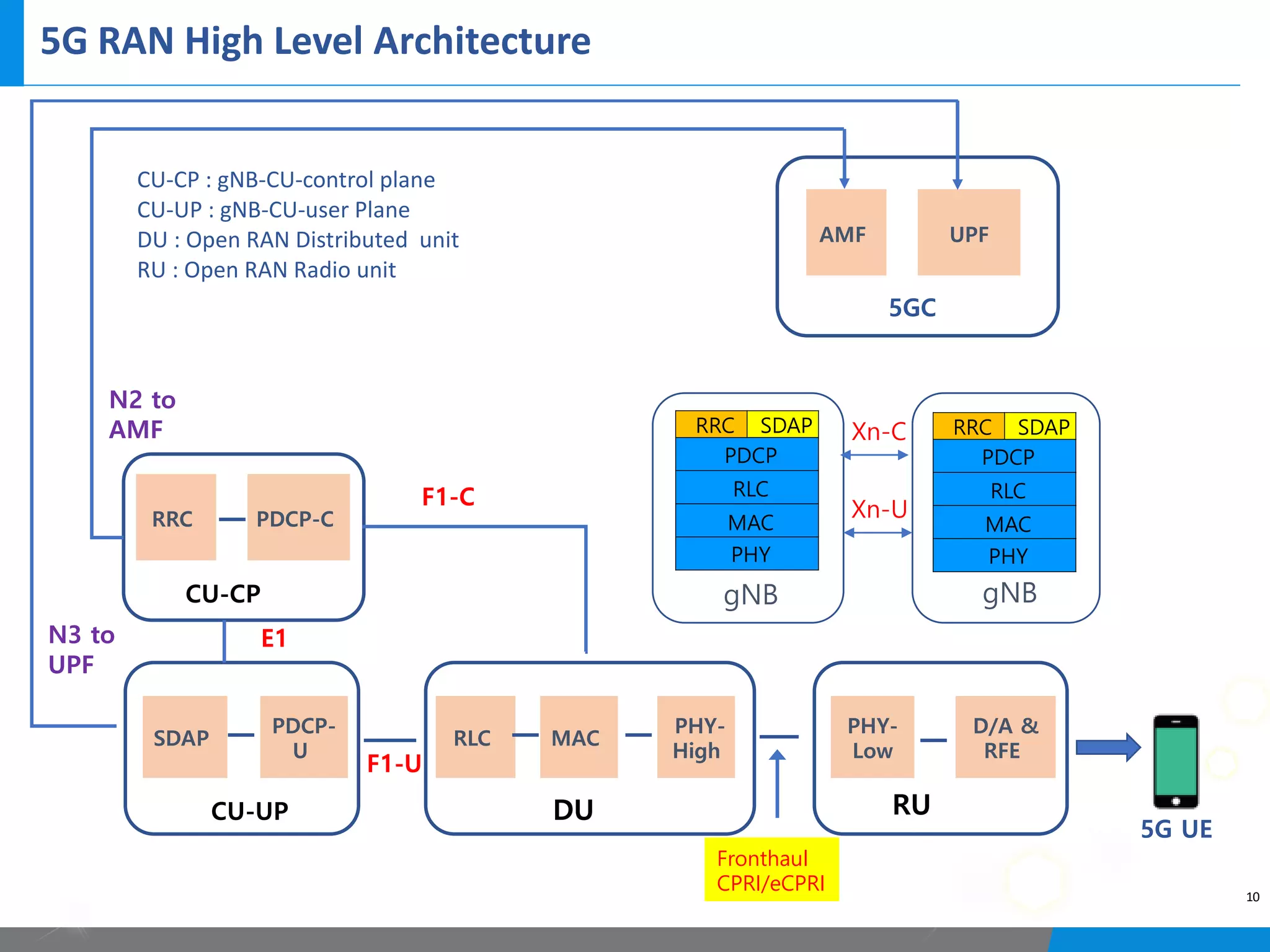
5G networks use a split architecture where the base station functions are split into centralized and distributed units. The central unit controls the radio resources and handles signaling, while distributed units perform scheduling and handle lower layer protocols. This allows flexible deployment and reduced latency. Control and user plane functions can also be separated into different central units for further optimization. The split architecture evolves from 4G to allow decreased fronthaul needs while meeting latency demands.