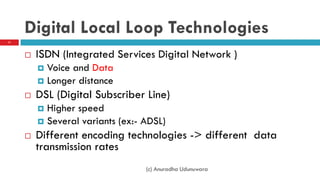
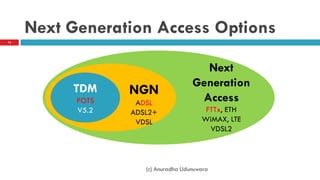
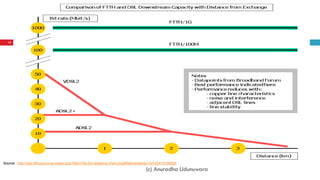
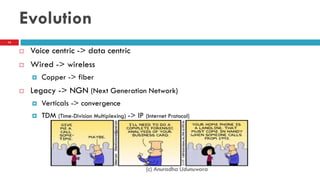
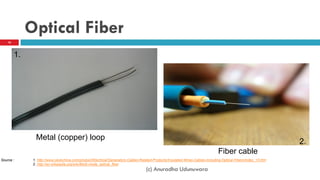
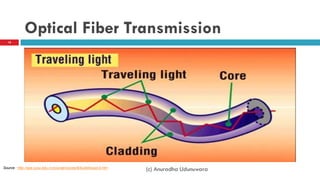
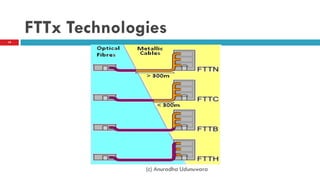
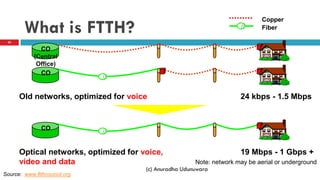
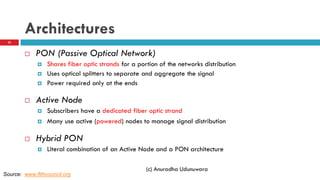
This document discusses fiber to the home (FTTH) networks. It begins by providing background on communications service providers and the evolution of access networks from copper wire to newer fiber optic technologies. Fiber access networks like passive optical networks (PON) are described as offering higher speeds and bandwidth. FTTH networks provide an ultimate network capacity and allow for new experiences like high definition TV, 3D content, and high-speed internet. The conclusion is that FTTH using optical fiber is a future-proof solution. The document is authored by Eng. Anuradha Udunuwara, an engineer with experience in telecommunications network strategy, architecture, and design.