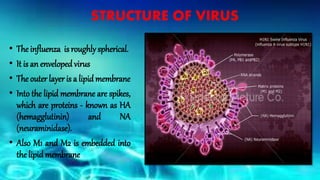
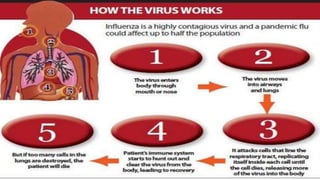
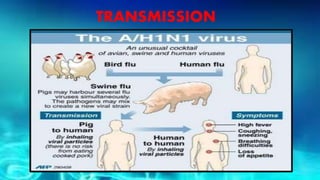
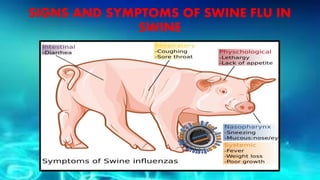
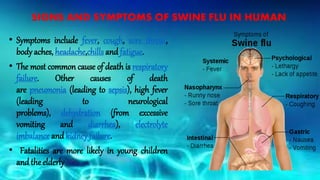
- Swine influenza, or swine flu, is a highly contagious respiratory disease in pigs caused by the H1N1 virus that can spread from pigs to humans.
- Outbreaks of swine flu were reported in India in late 2014 and early 2015, primarily in the western states.
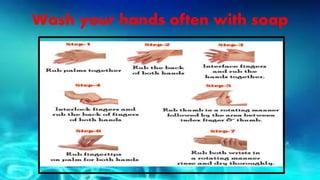
- Swine flu spreads from person to person through respiratory droplets from coughs or sneezes. Wearing masks can reduce transmission.
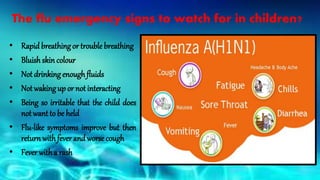
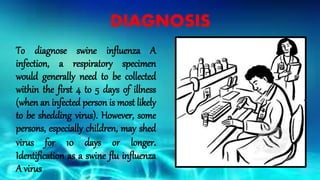
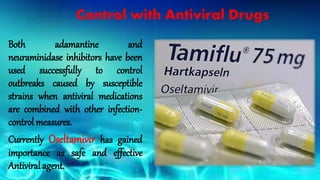
- Symptoms are similar to seasonal flu but can be severe and lead to respiratory failure, especially in young children, the elderly, and those with preexisting conditions. Diagnosis is through respiratory samples tested via RT-PCR within 5 days of symptoms. Vaccination and