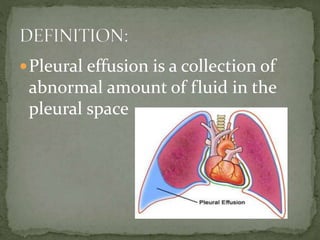
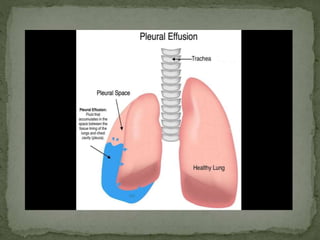
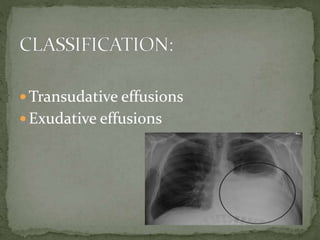
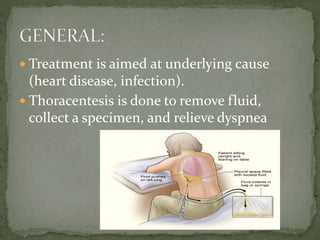
Pleural effusion is an abnormal collection of fluid in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. It is usually caused by underlying conditions that interfere with fluid drainage from the pleural space. There are two main types of pleural effusions - transudative effusions which contain low-protein fluid seen in conditions like heart failure, and exudative effusions which are high-protein fluids associated with inflammation from sources such as infection or cancer. Diagnosis involves imaging tests and thoracentesis to analyze the fluid. Treatment focuses on resolving the underlying cause, relieving symptoms, and preventing reaccumulation of fluid through procedures like chest tube drainage or pleurodesis.