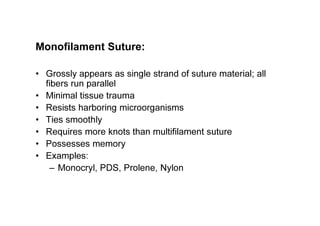
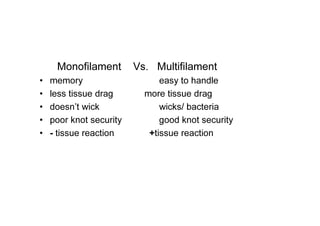
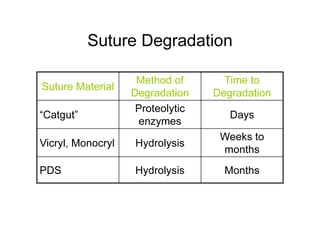
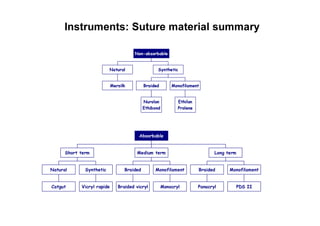
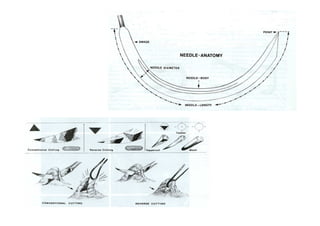
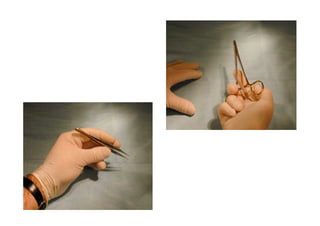
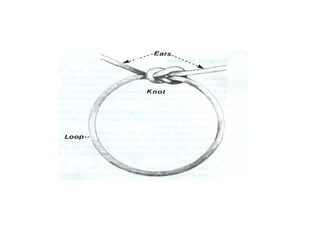
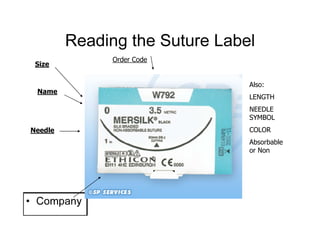
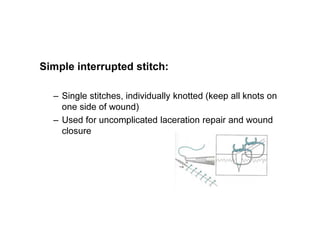
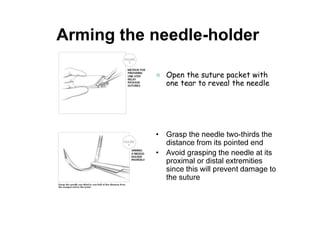
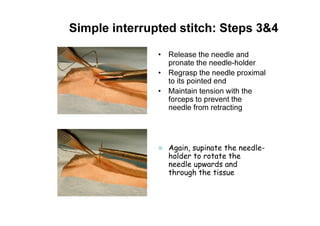
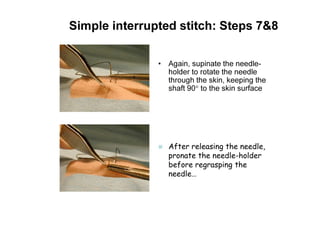
Sutures and suturing are used to approximate wound edges and promote healing. The goals of suturing include wound closure with adequate tension to prevent dead space but not cause ischemia, maintain hemostasis, permit primary intention healing, reduce pain, and provide support until tissue has healed. An ideal suture material is easy to use, has good knot security, causes minimal tissue reaction, resists bacteria, is strong but small, and affordable. Suture materials are categorized as absorbable or non-absorbable, natural or synthetic, and monofilament or multifilament. Common suture techniques include simple interrupted stitches, mattress stitches, and subcuticular stitches.