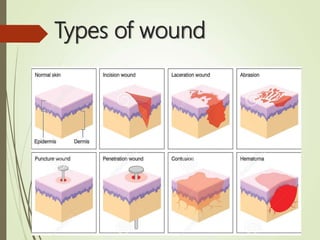
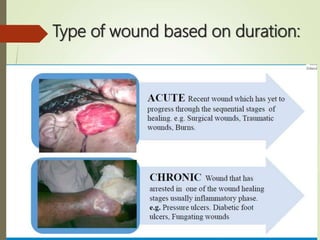
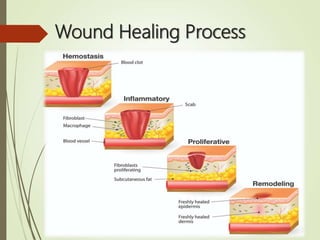
The document discusses wound care management, defining wounds as breakdowns in skin integrity due to various causes such as injury or disease. It highlights the importance of ongoing treatment in creating a conducive healing environment while preventing complications and loss of function. Various types of dressings and factors affecting wound healing are detailed, along with the steps essential for proper wound care management.