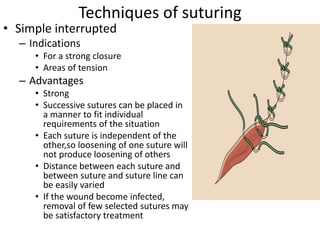
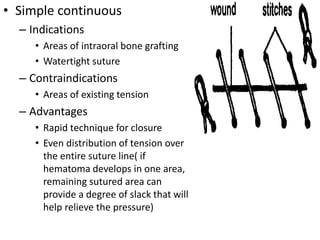
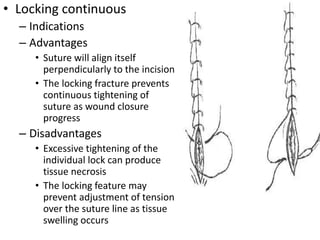
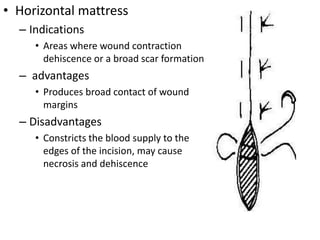
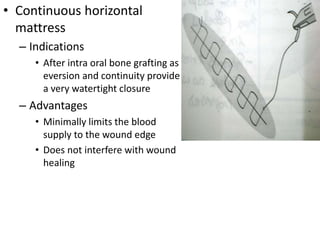
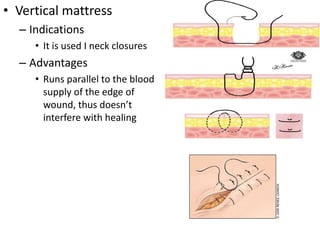
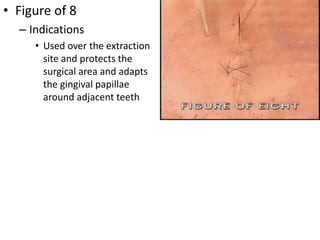
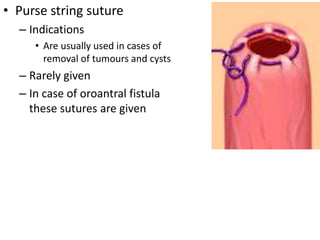
Suturing involves using threads or strands to approximate tissue surfaces and wound edges to assist in healing. There are absorbable and non-absorbable suture materials, including catgut, polyglycolic acid, polypropylene, and nylon. Absorbable sutures like polyglycolic acid degrade within 4-6 months by hydrolysis, while non-absorbable sutures like polypropylene must be removed after wound healing. Proper suturing technique includes perpendicular needle entry, equal depth and distance of placement, and avoidance of tension on tissues.