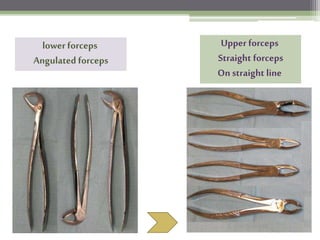
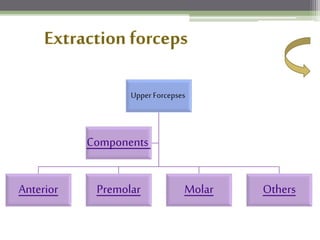
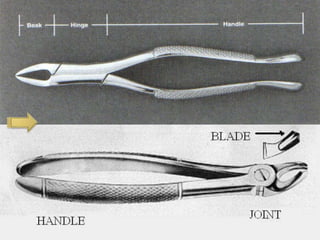
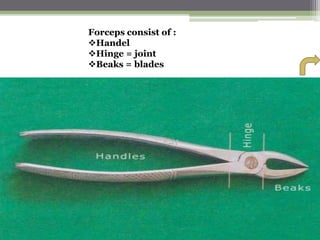
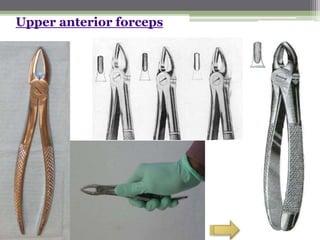
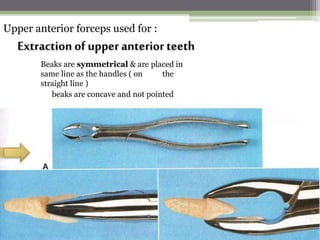
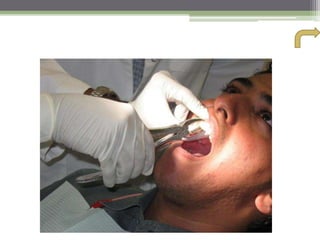
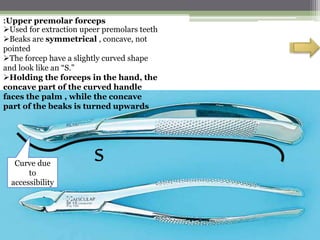
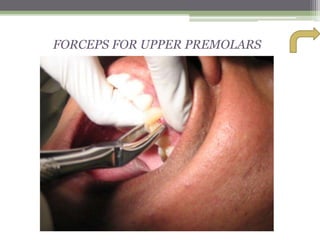
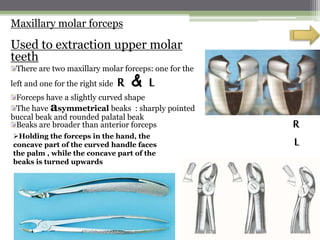
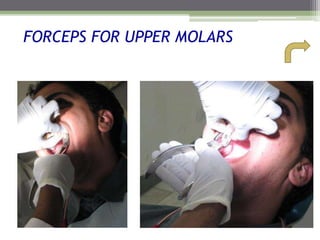
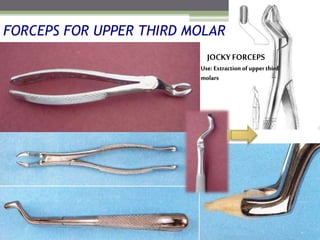
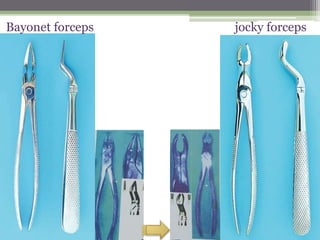
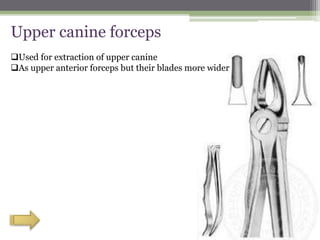
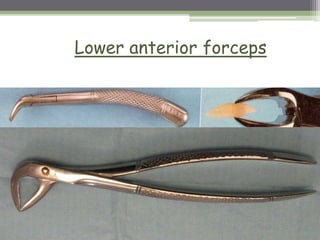
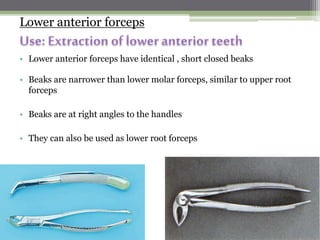
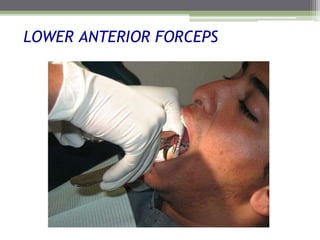
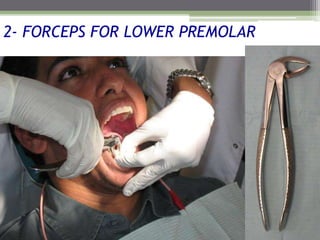
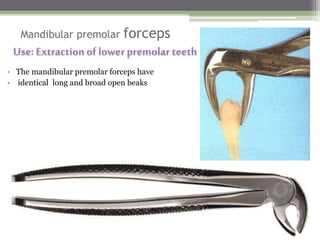
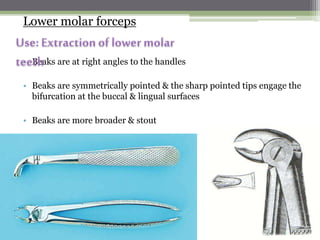
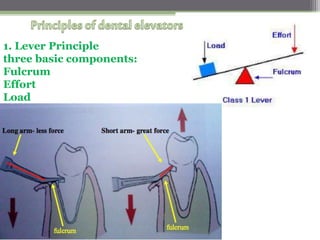
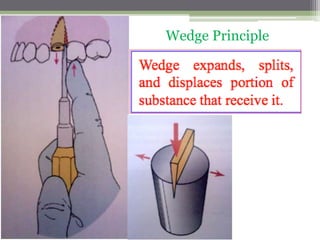
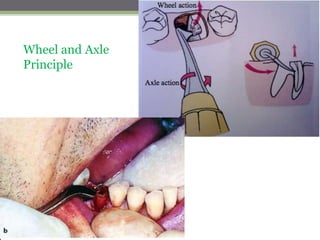
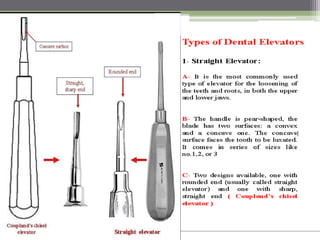
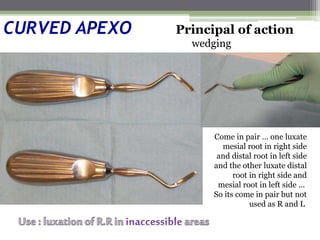
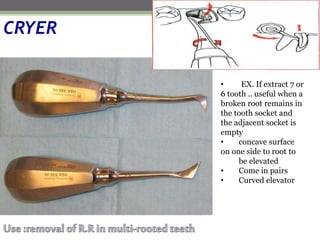
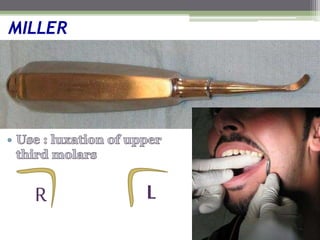
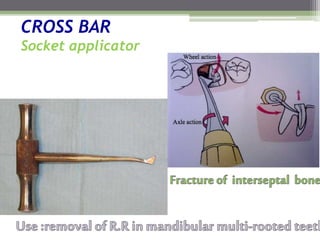
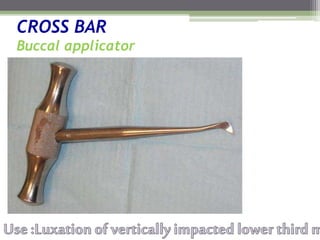
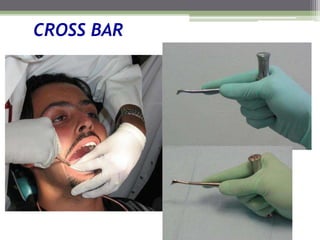
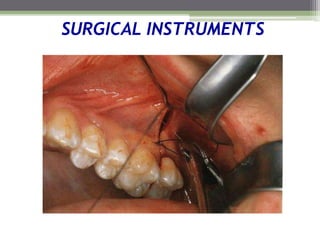
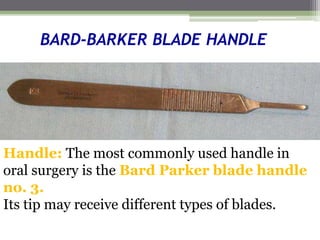
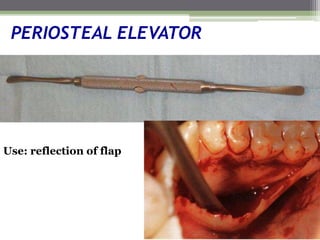
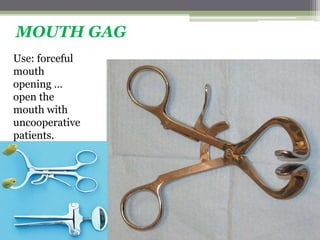
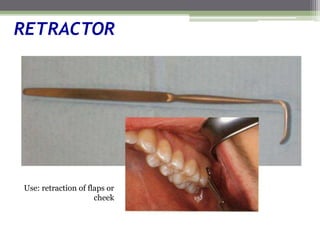
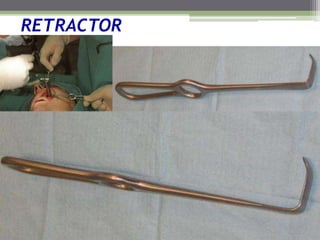
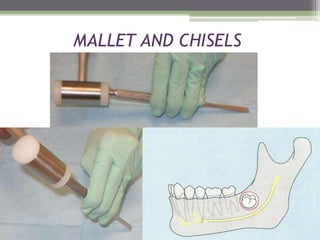
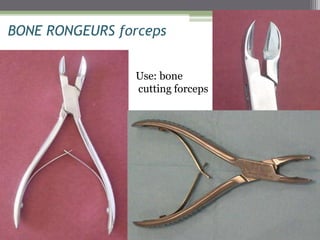
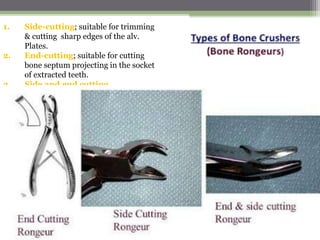
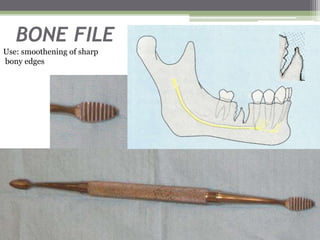
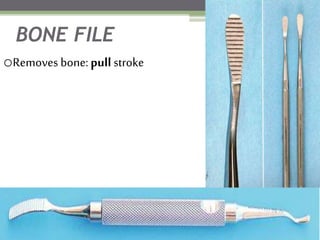
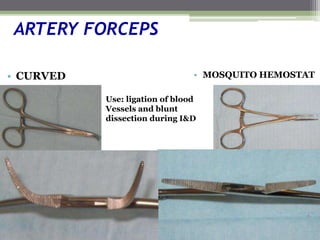
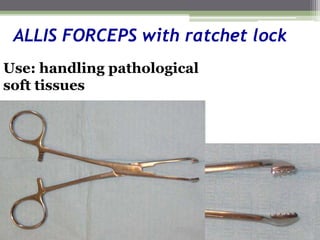
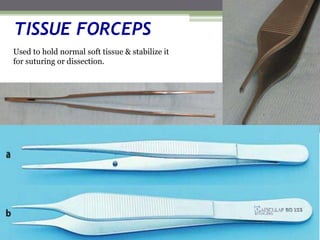
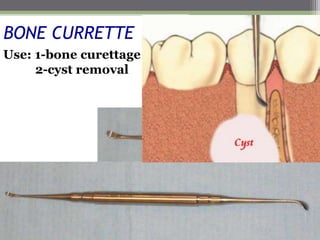
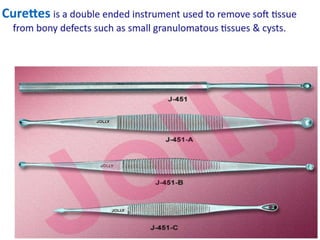
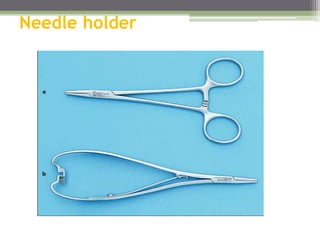
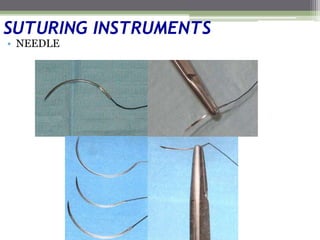
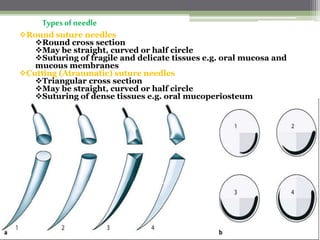
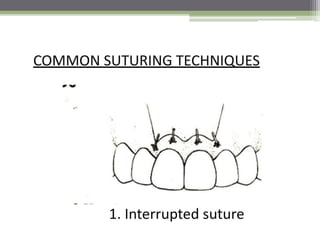
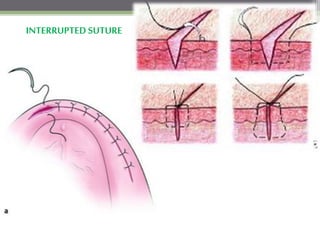
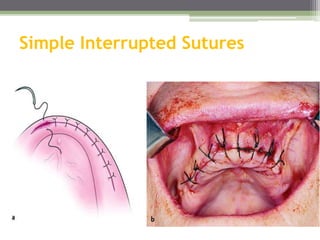
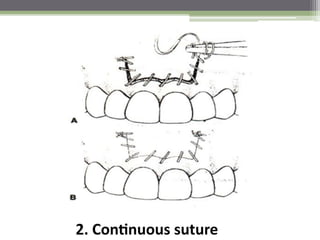
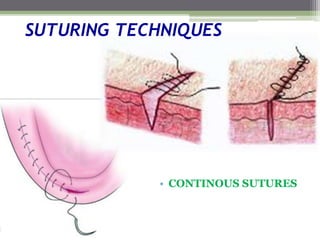
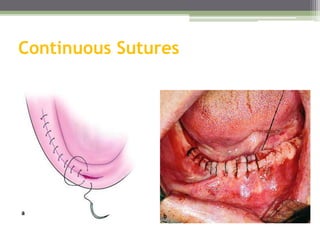
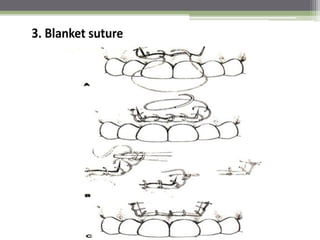
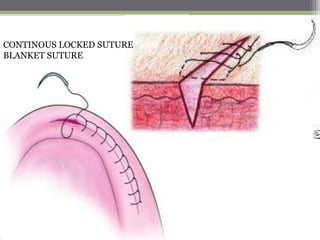
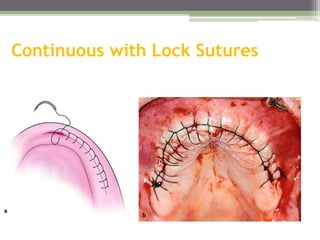
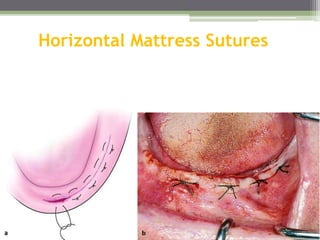
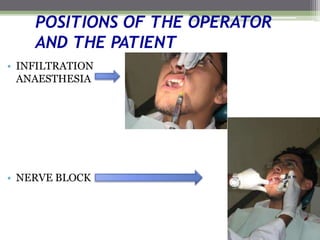
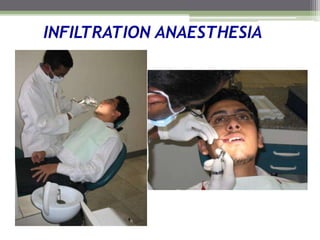
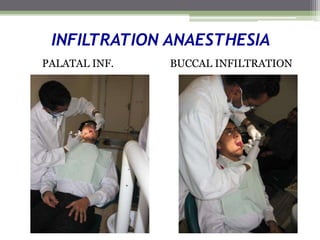
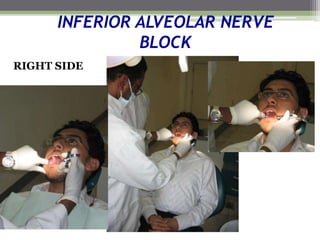
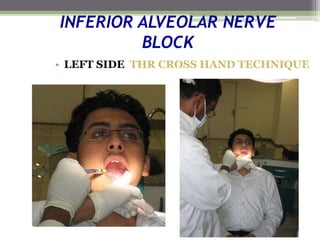
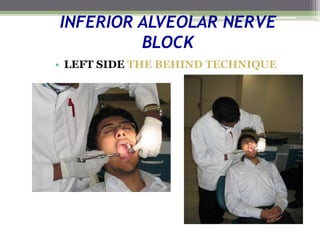
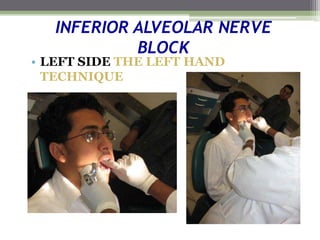
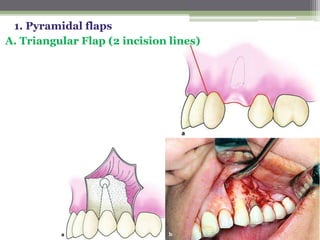
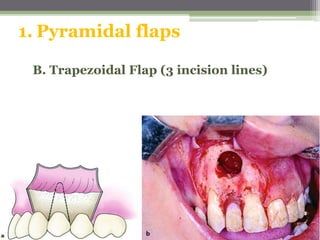
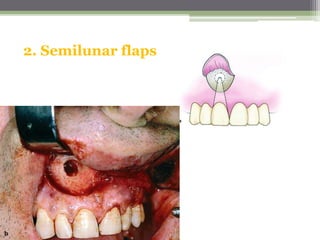
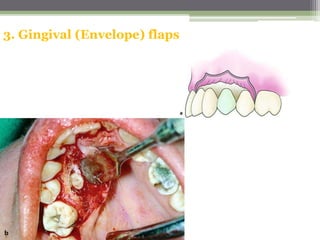
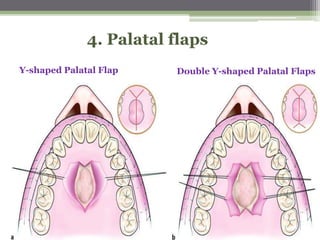
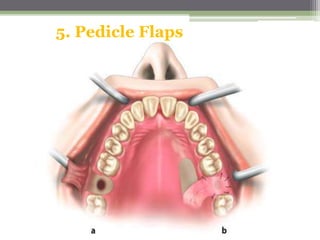
This document describes various surgical instruments used in dentistry. It discusses forceps for extracting different types of teeth, elevators for removing teeth and roots, surgical burs and chisels for bone removal, suturing needles and materials, and instruments for local anesthesia administration like needle holders. It also outlines incision designs for raising mucosal flaps and techniques for inferior alveolar nerve blocks. In summary, the document provides an overview of common dental extraction instruments and equipment as well as local anesthesia and surgical flap procedures.