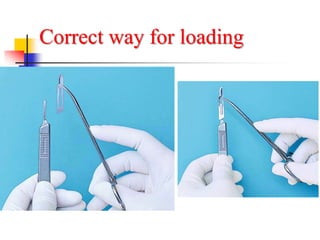
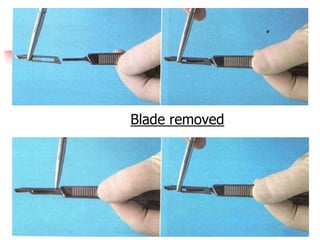
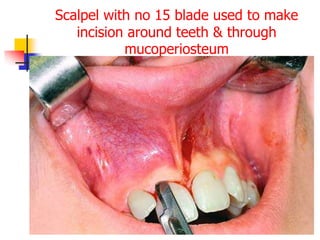
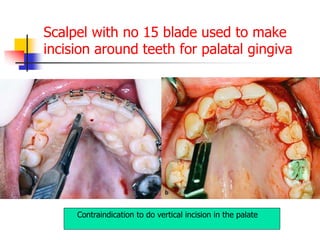
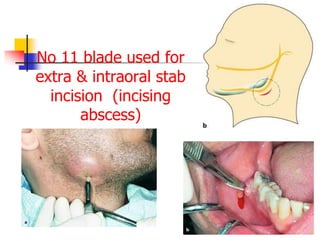
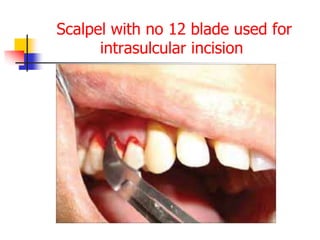
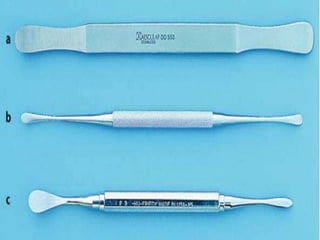
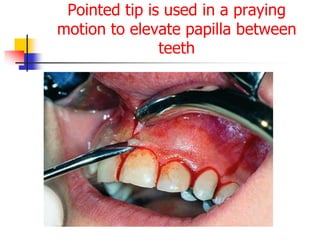
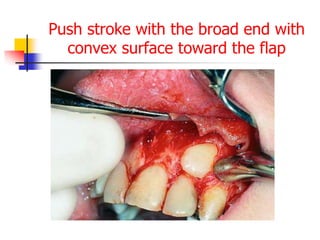
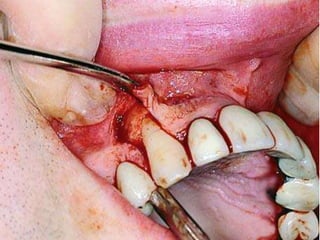
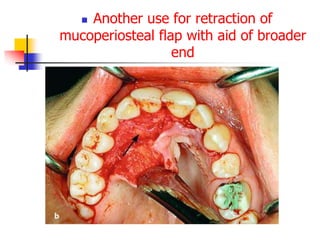
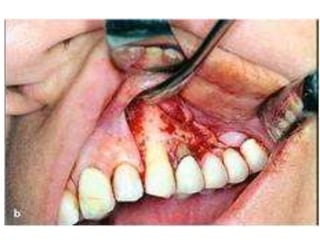
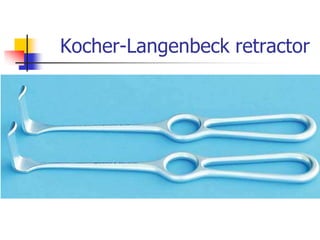
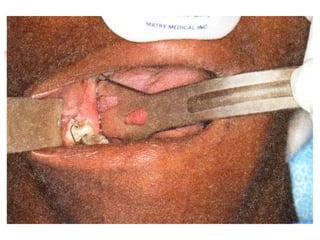
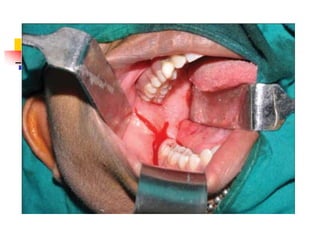
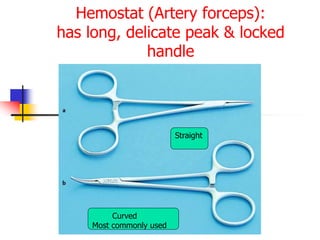
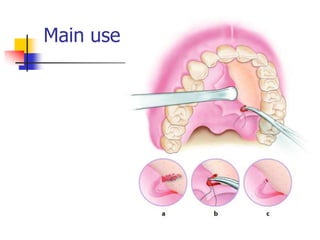
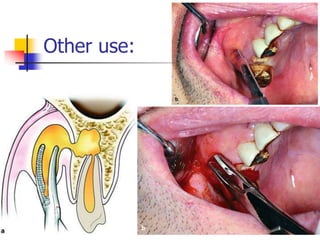
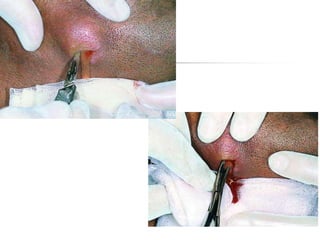
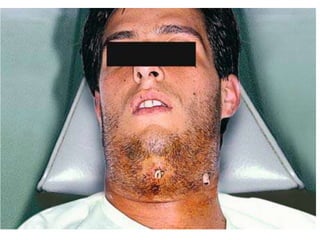
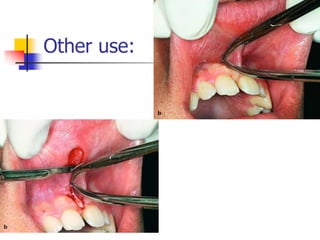
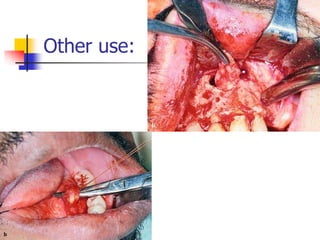
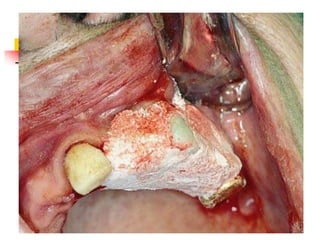
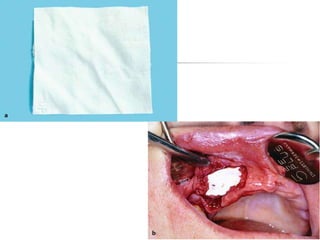
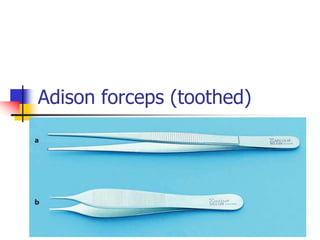
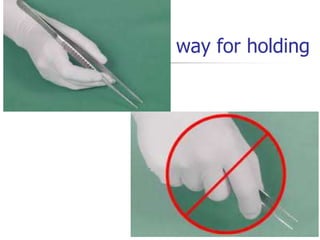
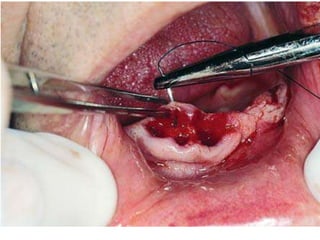
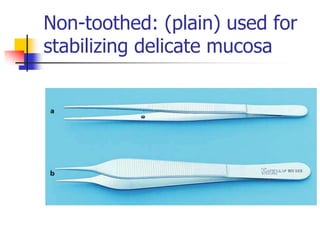
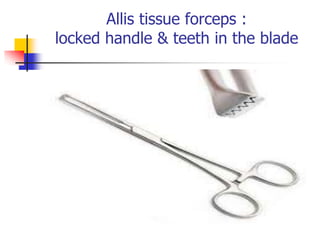
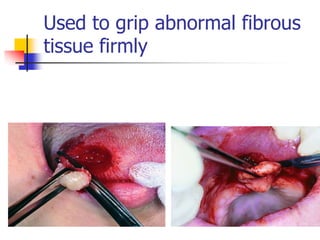
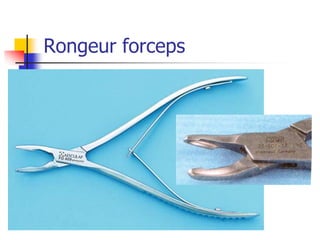
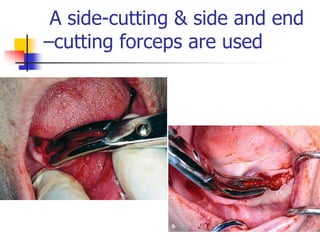
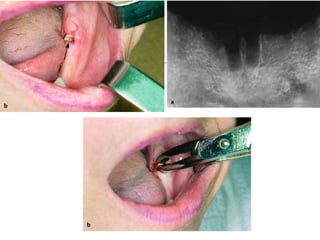
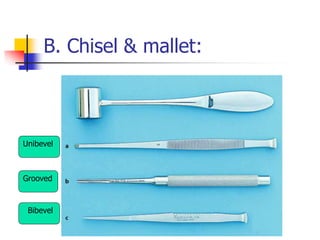
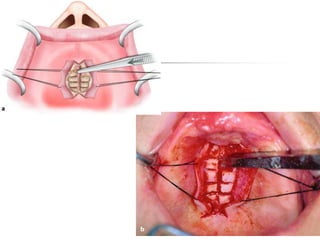
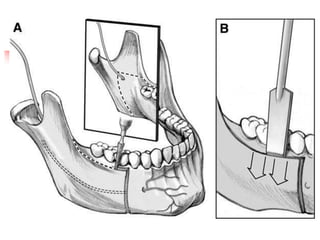
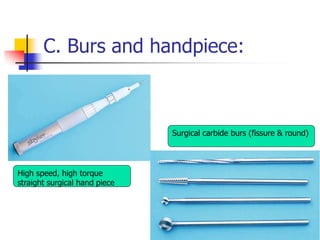
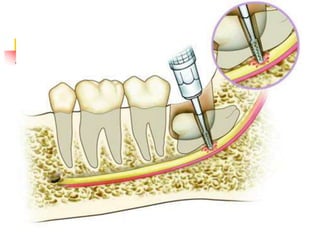
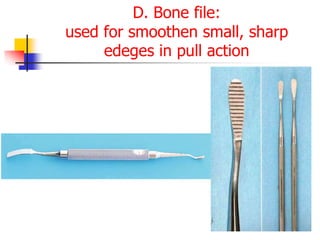
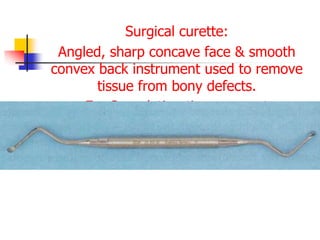
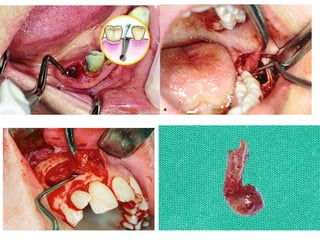
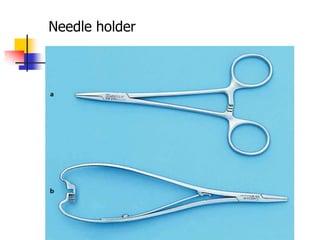
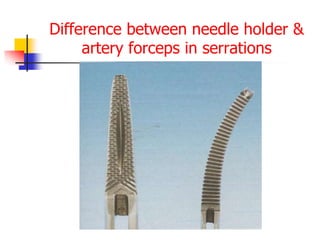
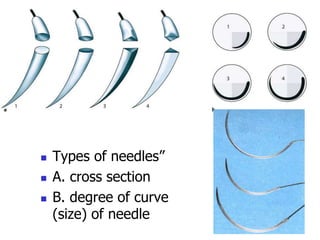
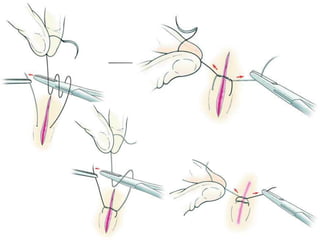
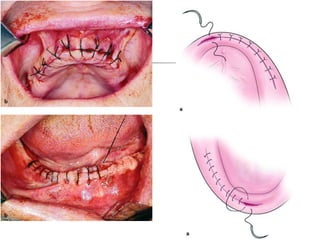
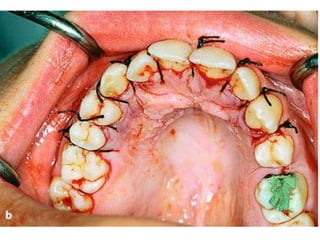
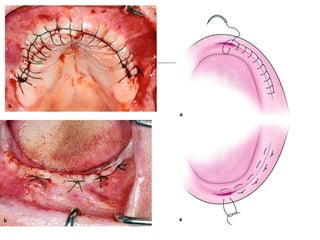
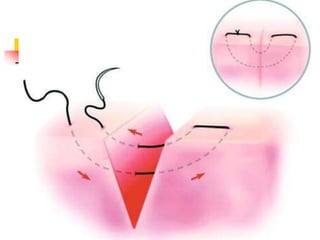
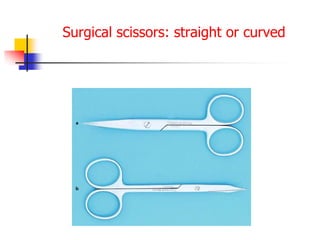
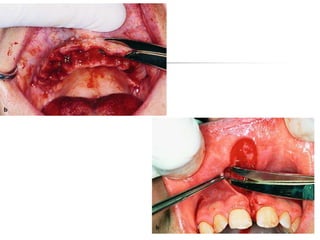
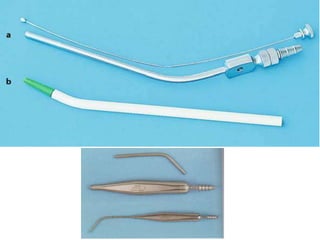
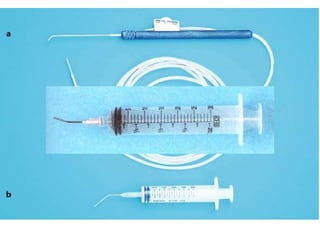
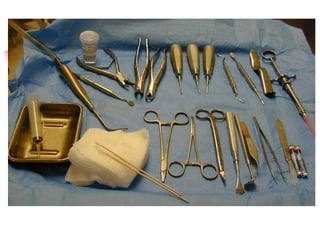
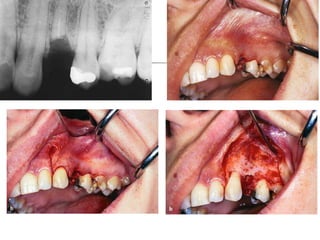
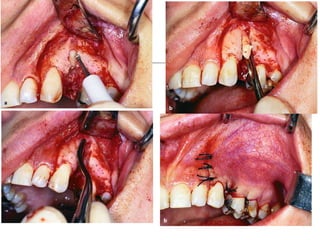
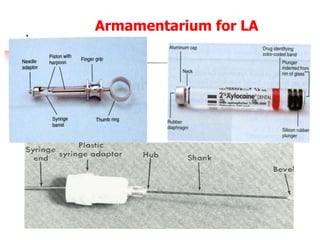
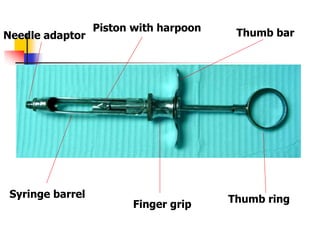
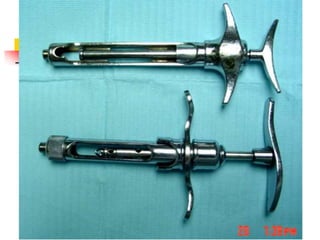
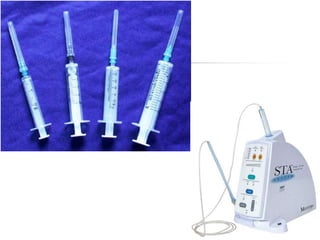
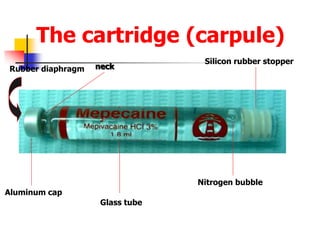
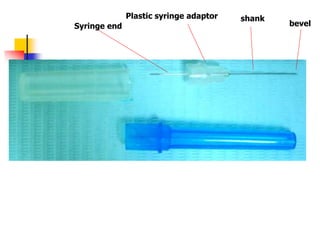
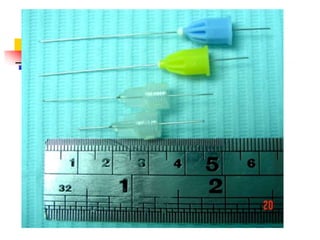
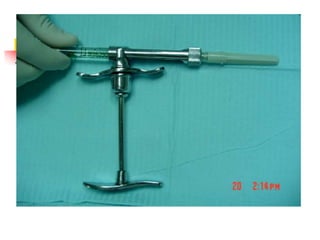
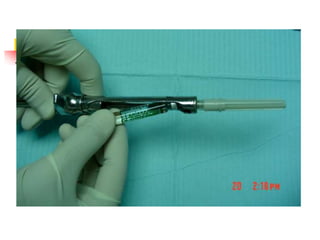
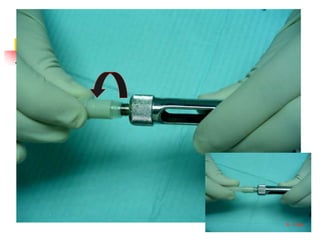
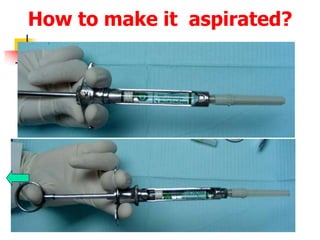
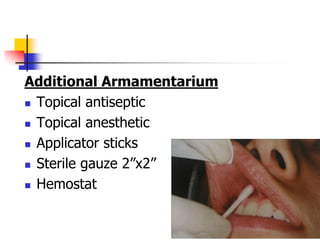
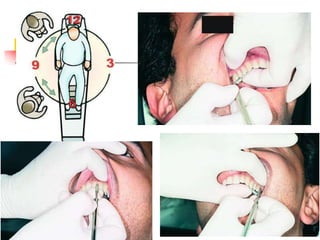
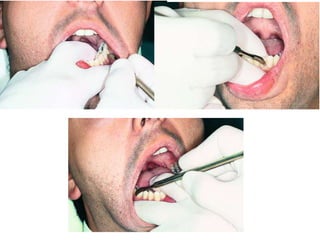
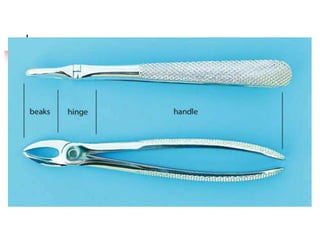
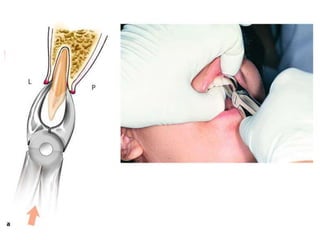
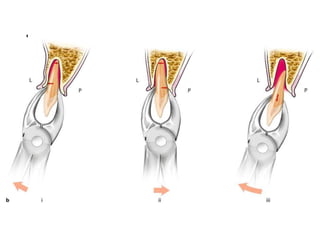
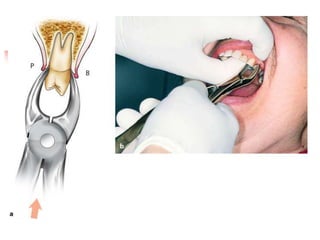
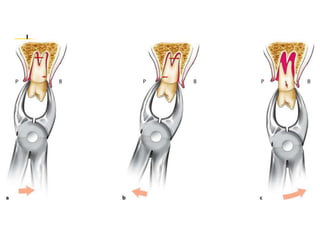
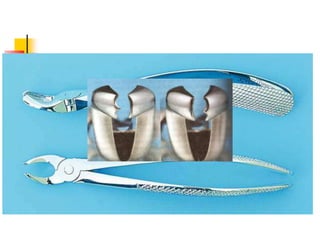
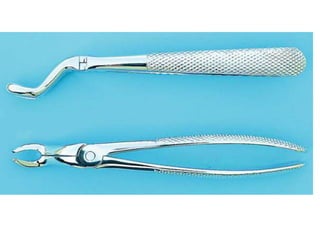
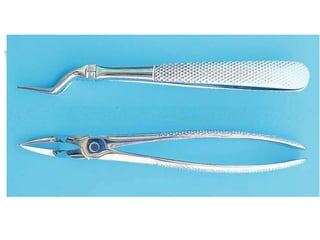
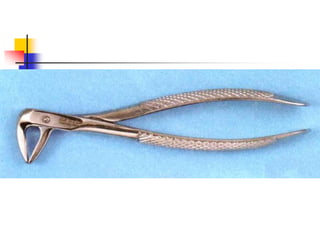
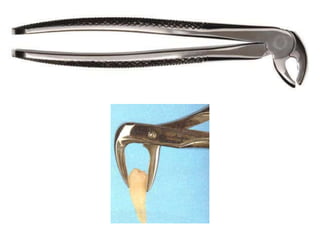
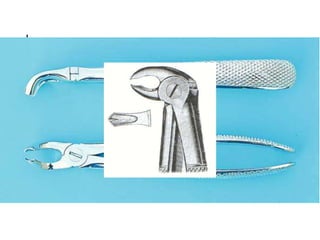
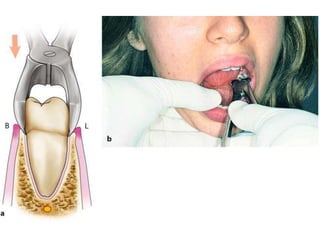
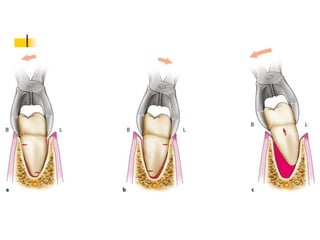
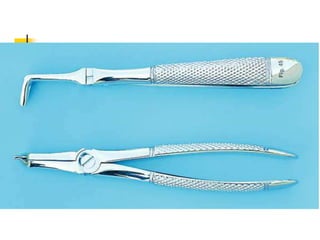
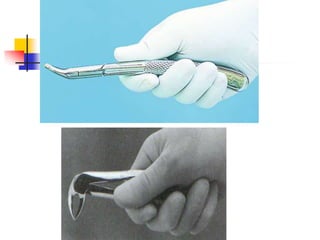
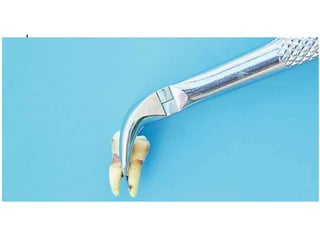
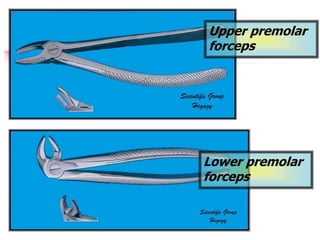
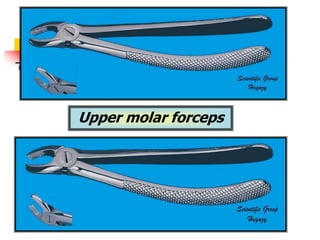
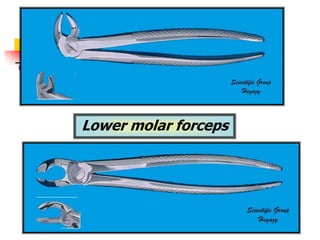
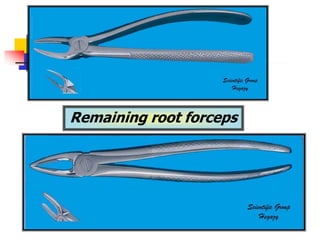
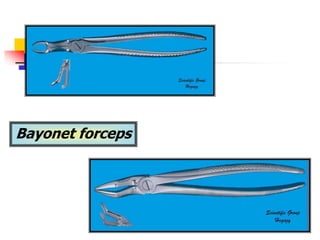
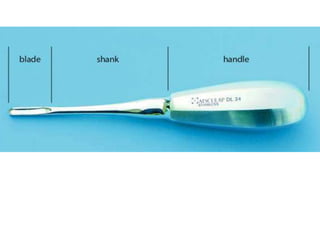
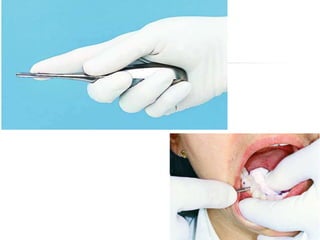
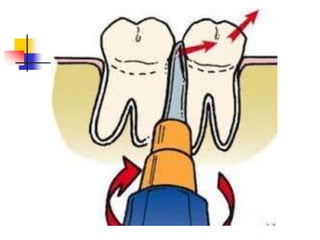
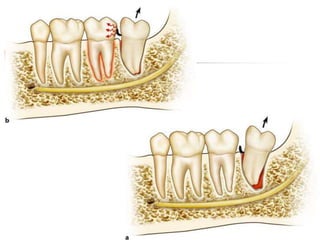
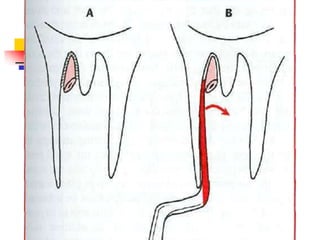
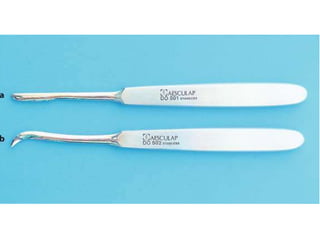
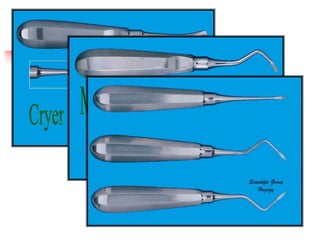
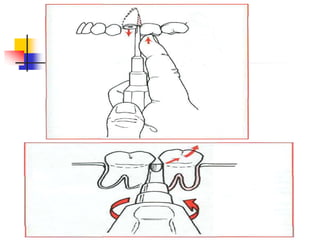
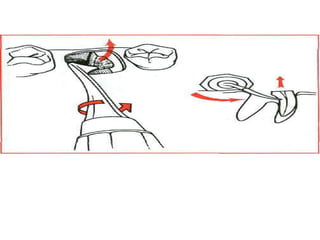
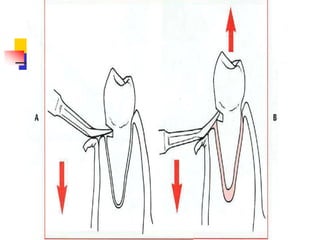
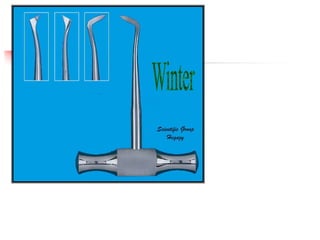
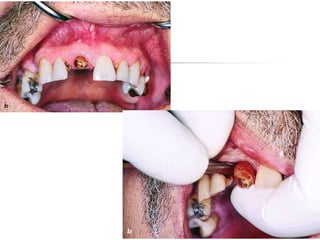
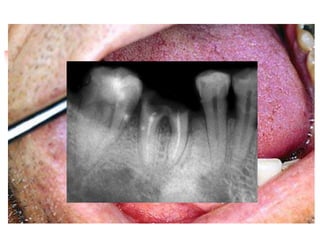
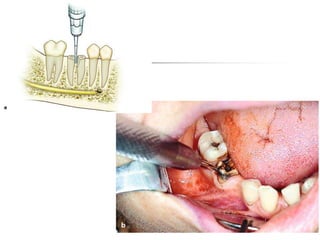
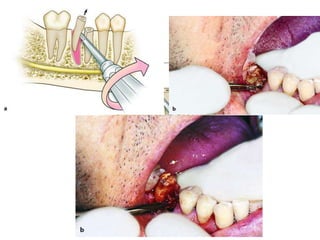
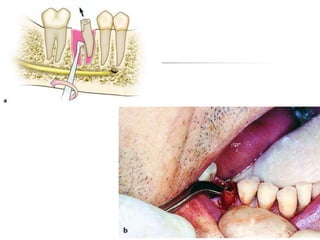
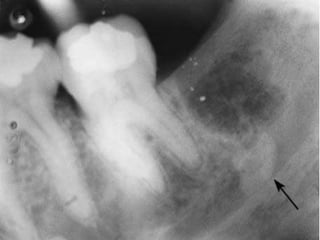
This document provides an overview of the basic armamentarium used in oral surgery. It describes various instruments used for tasks like transferring sterile instruments, incising tissue, elevating mucoperiosteum, retracting soft tissue, controlling hemorrhage, grasping tissue, removing bone and pathological tissue, suturing mucosa, holding the mouth open, suctioning, irrigating, extracting teeth, and administering local anesthesia. Diagrams and descriptions are provided for each type of instrument. The document emphasizes the importance of surgeons having knowledge of the appropriate use of high quality instruments.