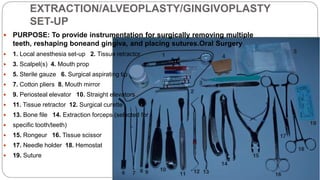
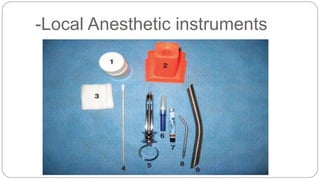
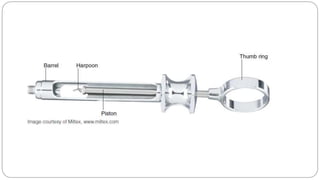
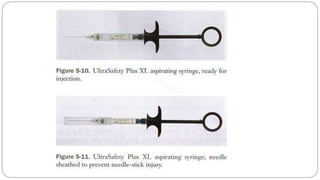
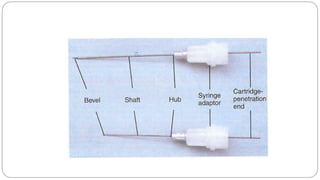
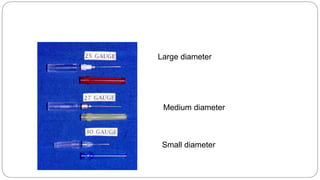
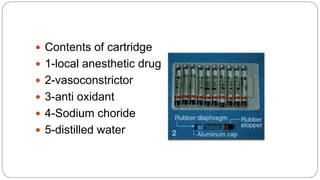
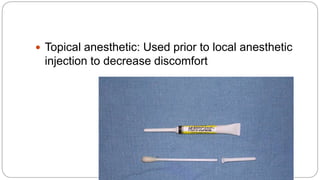
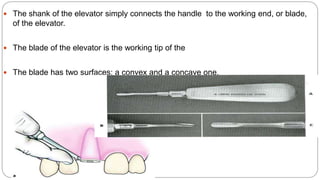
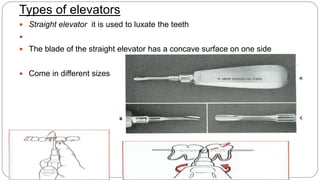
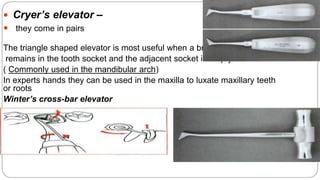
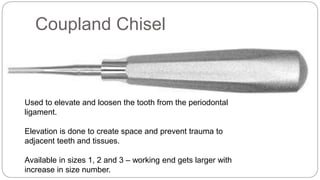
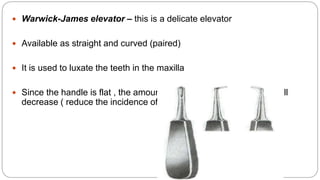
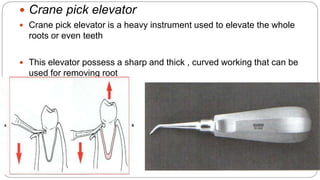
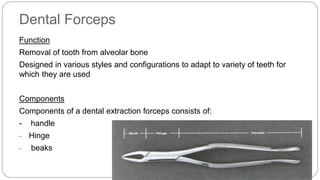
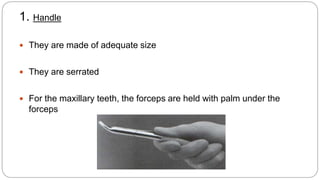
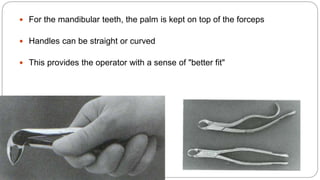
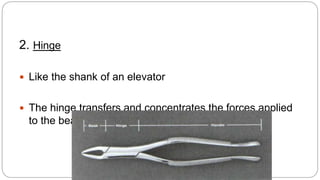
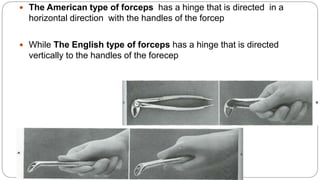
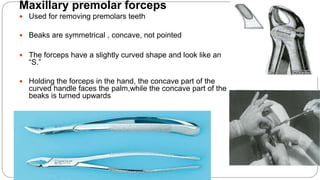
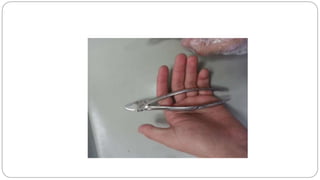
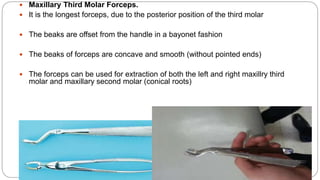
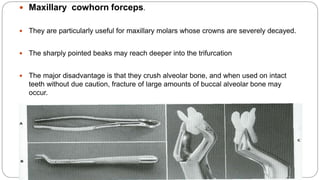
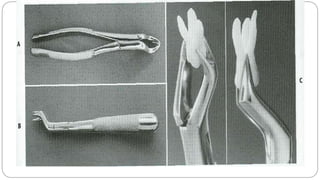
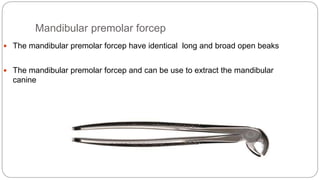
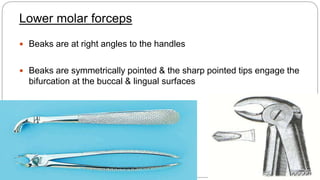
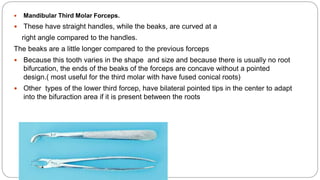
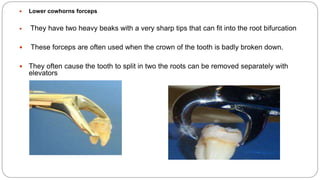
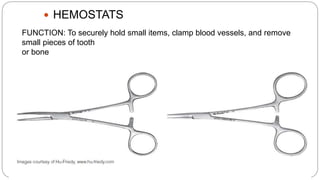
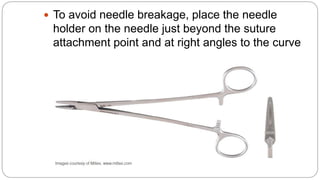
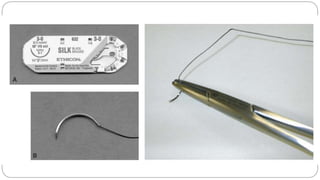
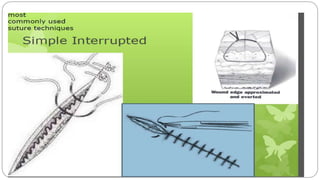
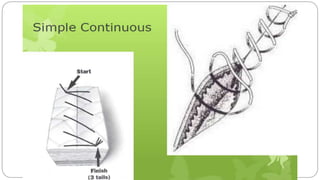
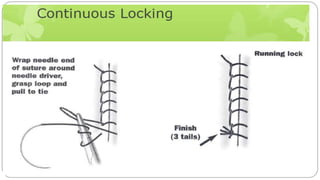
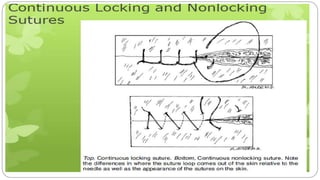
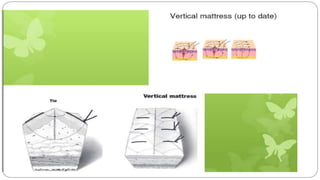
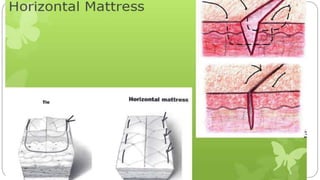
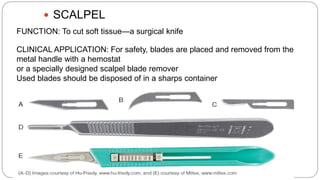
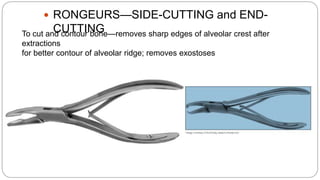
This document provides an overview of common instruments used in oral surgery procedures. It describes the purpose, features and clinical applications of basic extraction sets, local anesthesia equipment, elevators, forceps, hemostats, suture needles and various other instruments. Extraction forceps are discussed in detail, outlining the components and designs of different forceps used for extracting teeth in the upper and lower jaws. The document aims to inform readers about the armamentarium and equipment used for basic oral surgical procedures.