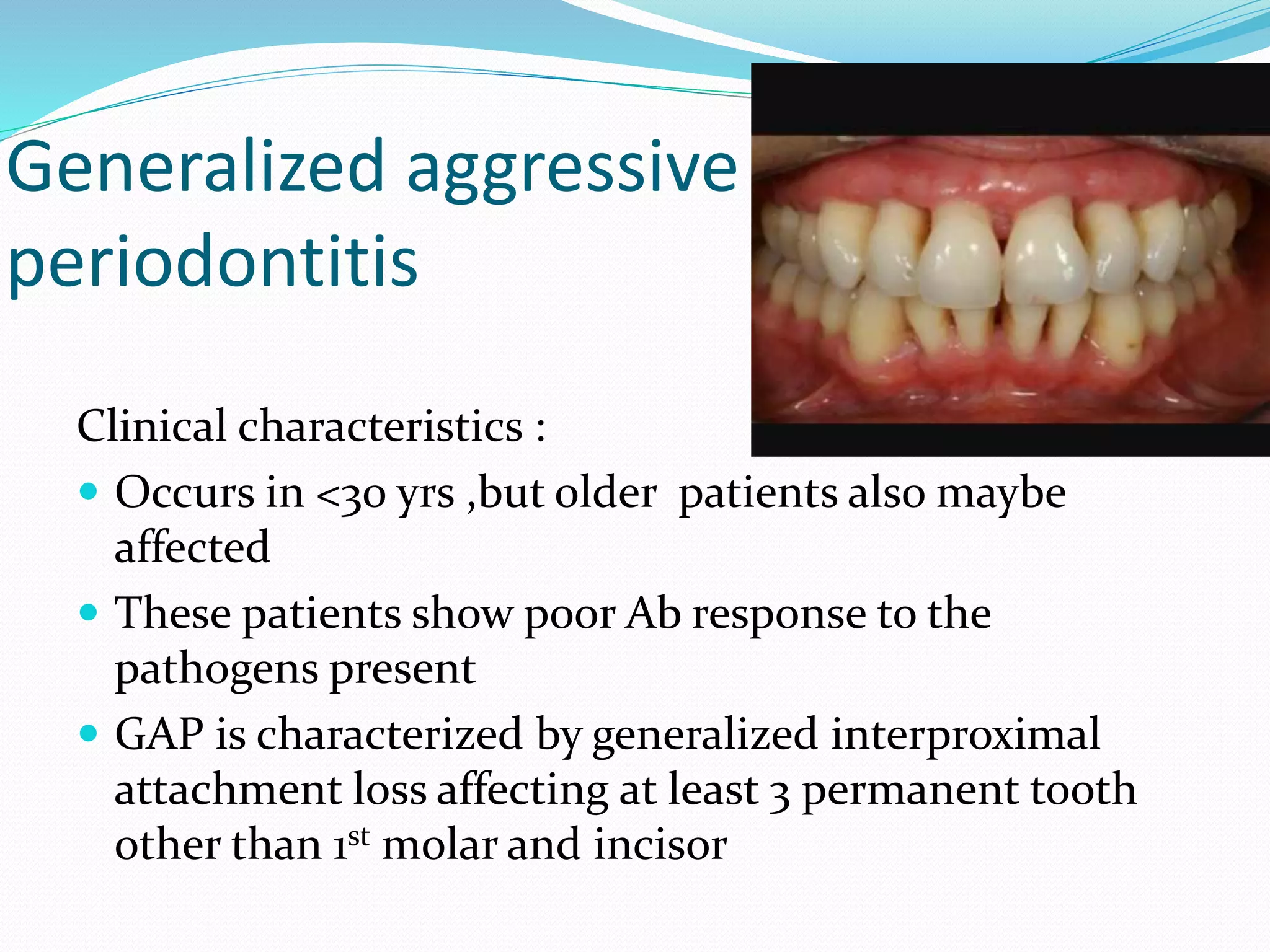
The document discusses aggressive periodontitis, classifying it into localized aggressive periodontitis (LAP) and generalized aggressive periodontitis (GAP), with descriptions of their clinical features, radiographic findings, risk factors, and treatment options. LAP typically affects adolescents with minimal inflammation and rapid bone loss, while GAP occurs in younger patients with systemic manifestations and more extensive periodontal destruction. Treatment varies from non-surgical therapies like antimicrobial use and patient education to surgical approaches when necessary.













![ LAP ,progress rapidly ,Rate of bone loss is about three
to four times faster than in chronic periodontitis
LAP, may include
Distolabial migration of the maxillary incisors with
concomitant diastema formation increasing mobility
of 1st molar
[also known as pathological migration]
Sensitivity of denuded root surfaces of thermal and
tactile stimuli](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aggressiveperiodontitissuraksha-180810135933/75/Aggressive-periodontitis-14-2048.jpg)