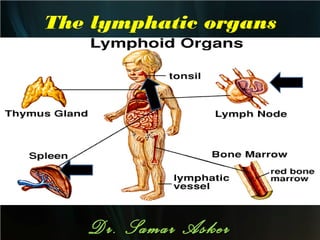
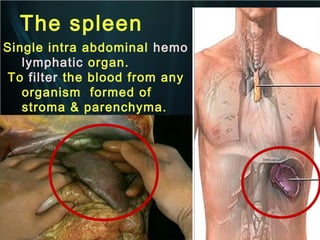
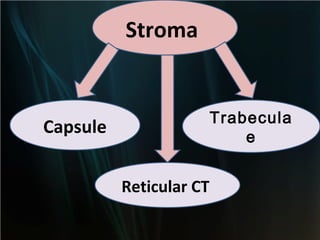
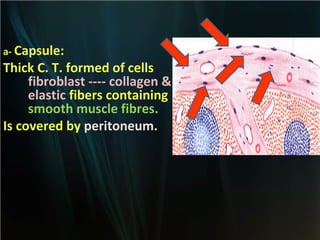
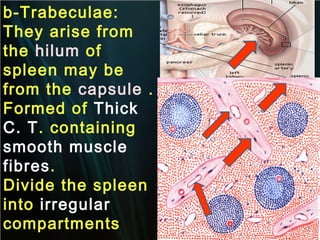
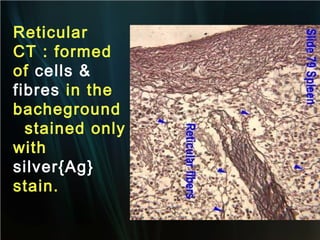
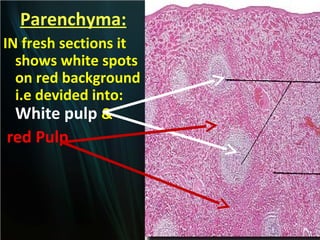
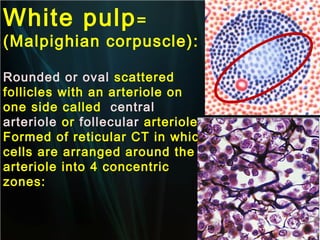
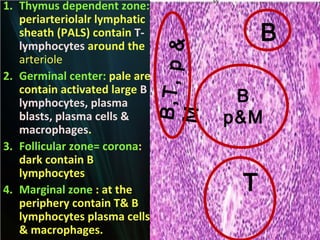
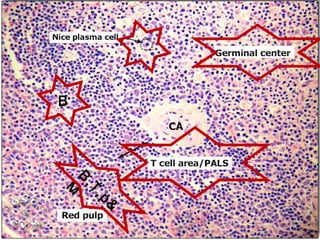
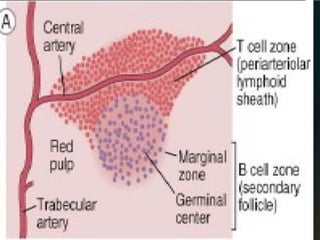
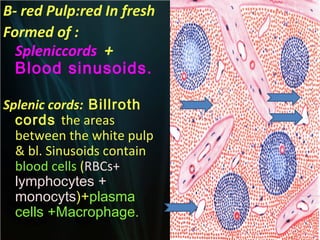
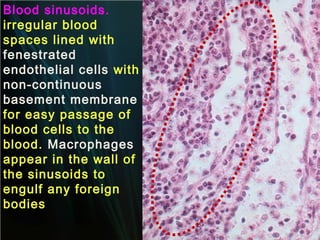
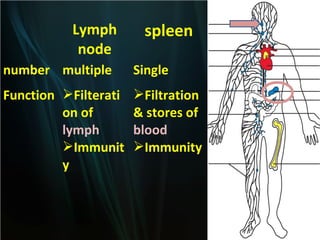
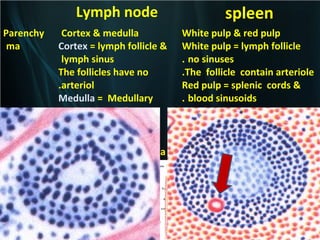
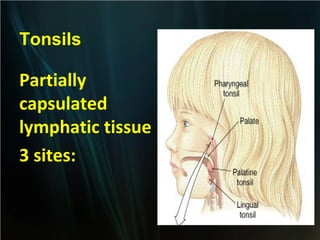
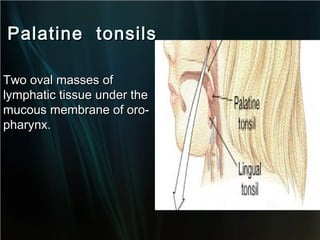
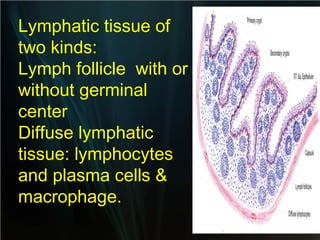
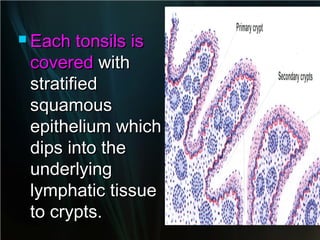
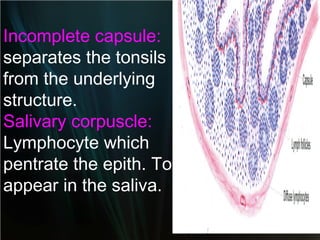
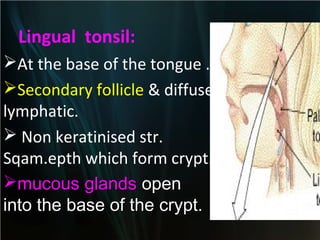
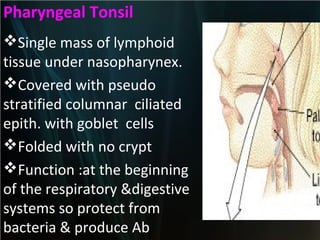
The spleen is a single intra-abdominal lymphatic organ that filters blood. It is composed of stroma including a capsule, trabeculae, and reticular connective tissue, as well as parenchyma consisting of white pulp and red pulp. The white pulp contains lymphocytes arranged in Malpighian corpuscles around arterioles. The red pulp is made up of splenic cords and blood sinusoids containing blood cells, macrophages, and platelets. The spleen functions to filter blood, form and store blood cells, and play an immunological role in trapping antigens.