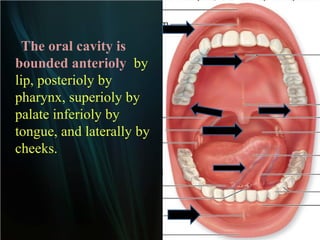
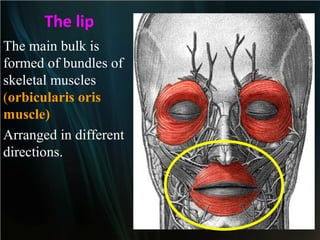
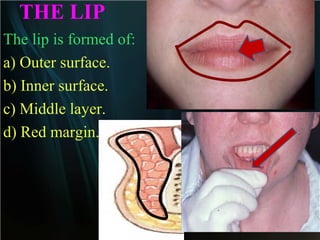
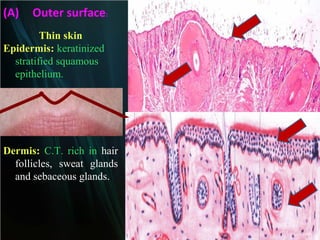
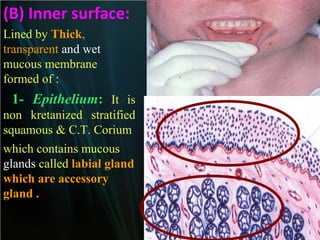
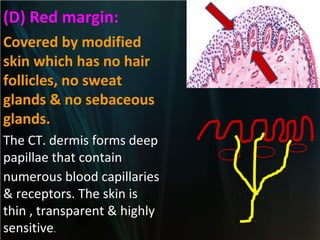
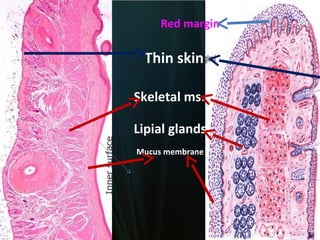
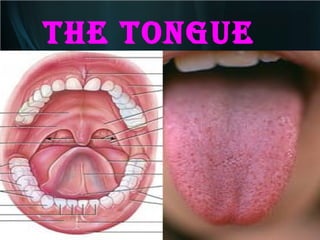
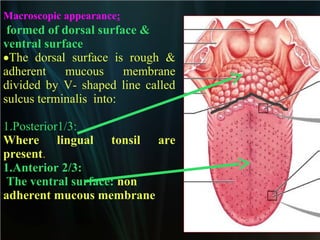
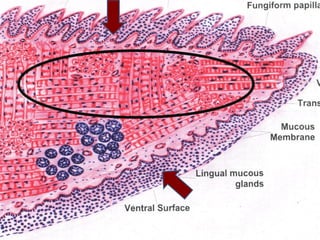
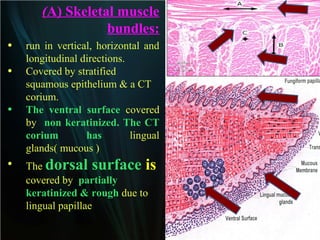
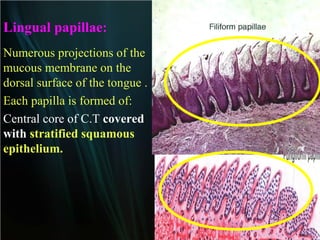
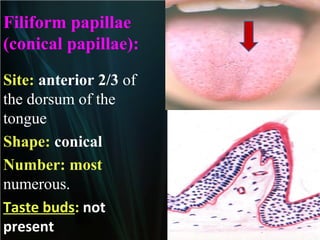
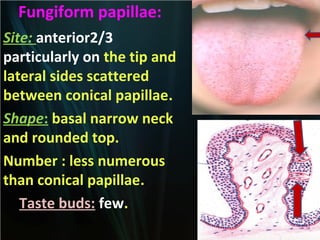
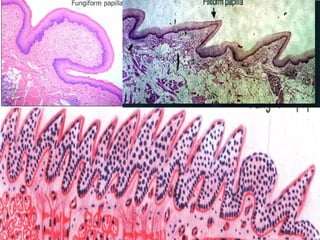
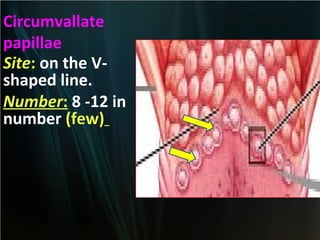
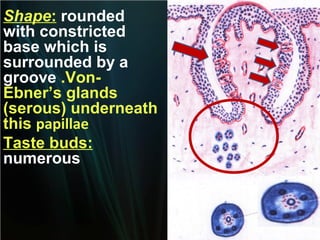
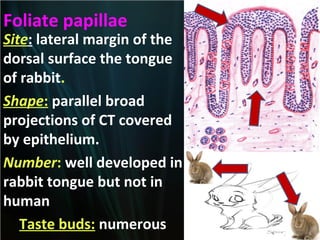
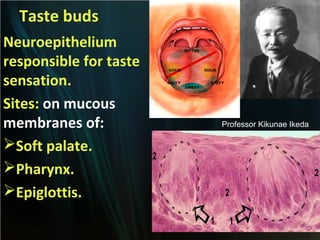
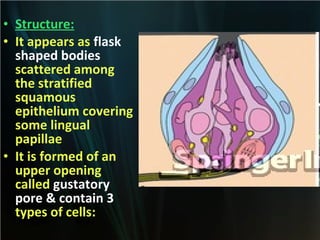
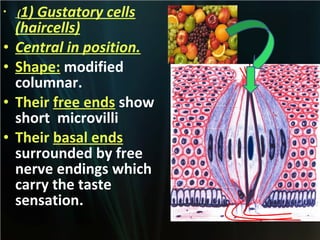
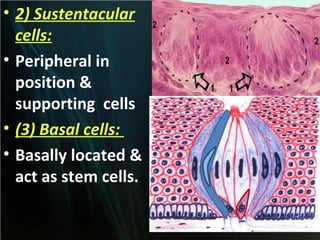
The document summarizes key aspects of the digestive system, including the lip and tongue. The lip has an outer skin surface and inner mucous membrane. It contains smooth muscles and labial glands. The tongue is covered by mucous membrane with four types of papillae (filiform, fungiform, circumvallate, foliate). Each papilla contains taste buds formed of gustatory and sustentacular cells. Taste buds are also present on other areas and detect the five basic tastes via nerve endings.