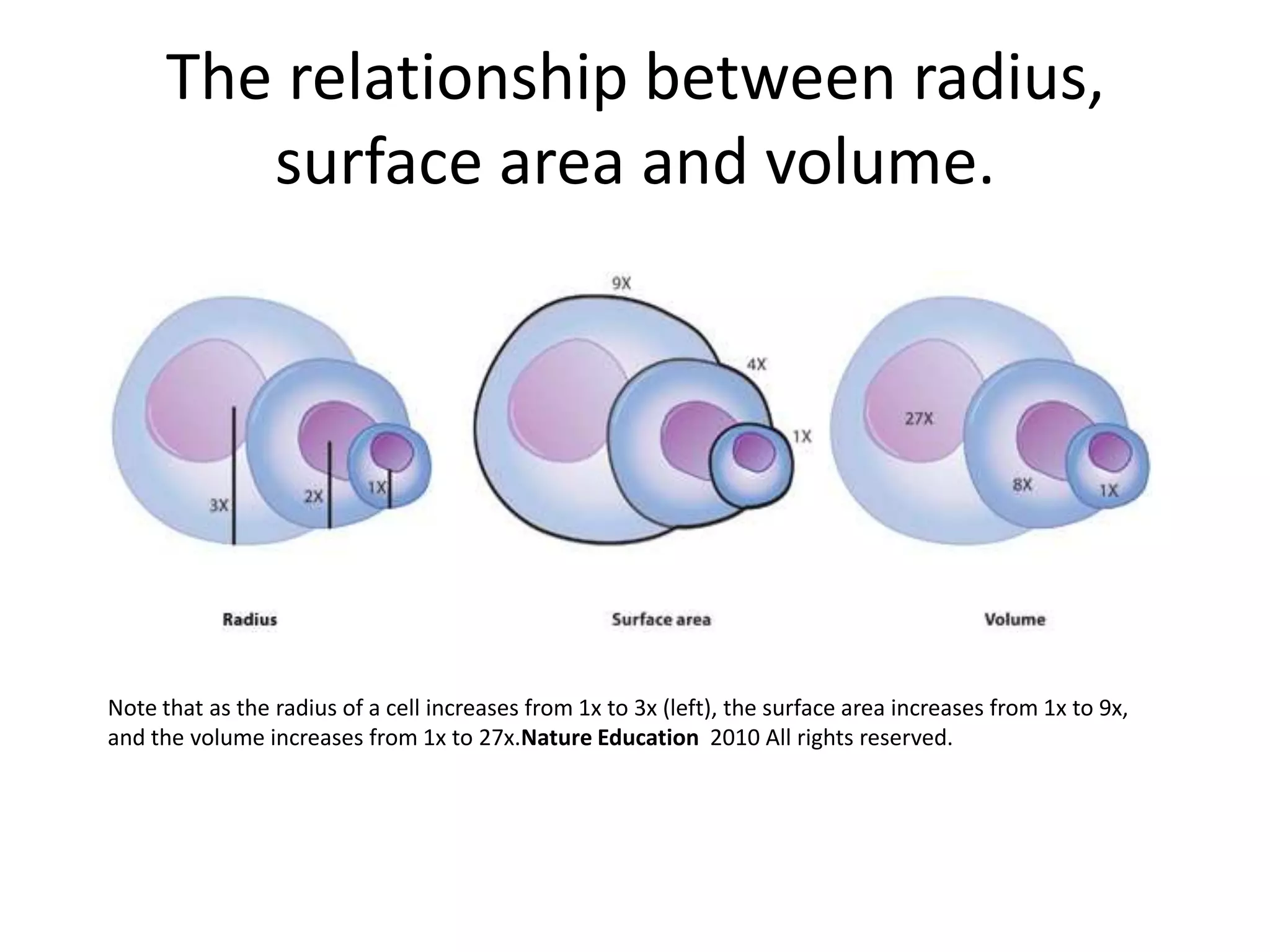
1) The document discusses how surface area to volume ratio limits cell size. As cells increase in size, their volume increases much faster than their surface area.
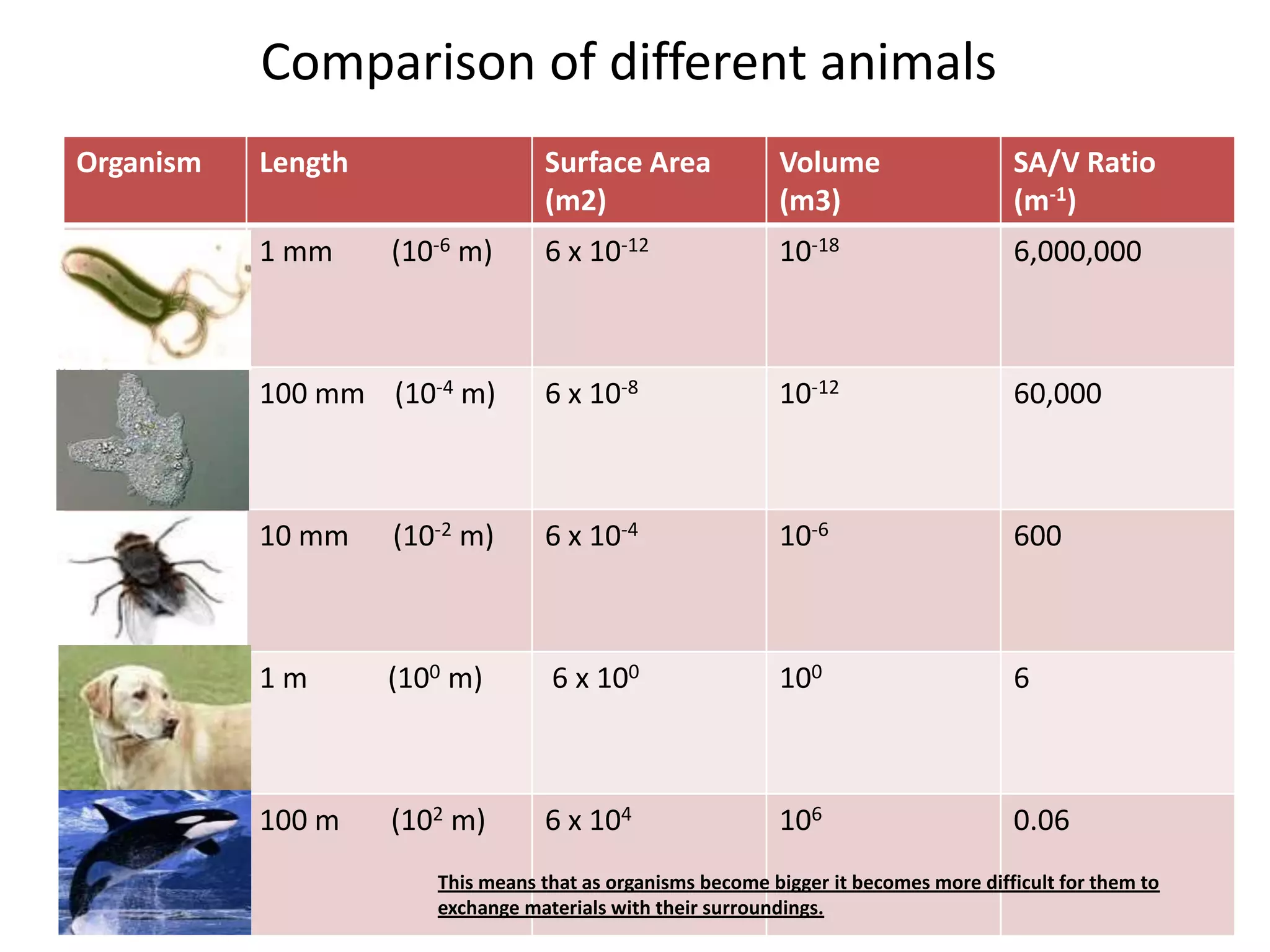
2) A smaller surface area to volume ratio makes it more difficult for cells to exchange materials by diffusion with their surroundings.
3) Organisms with smaller sizes, such as microbes, have much higher surface area to volume ratios that allow for more efficient exchange of materials compared to larger organisms.