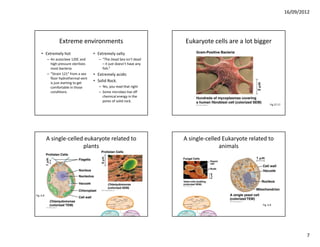
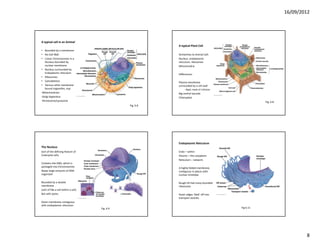
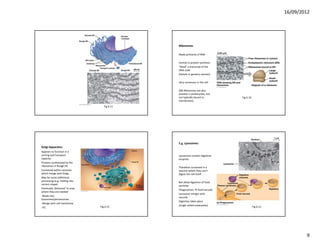
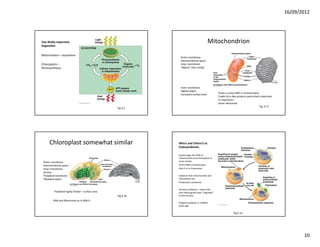
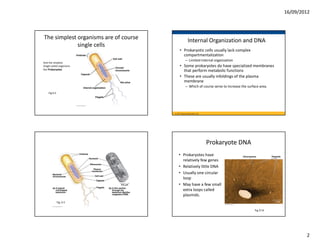
This document discusses cells and their role in living organisms. It begins by explaining that organisms need to exchange nutrients through their surface area, and keeping cells small helps maintain a high surface area to volume ratio to allow for efficient nutrient exchange. It then discusses the key characteristics of prokaryotic cells, the simplest type of cell, including their lack of internal compartmentalization, circular DNA structure, rapid reproduction through binary fission, and ability to transfer genes through plasmids. The document concludes by contrasting prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, noting key differences like prokaryotes lacking nuclei and organelles while eukaryotes have internal membrane-bound structures.


![16/09/2012
There are prokaryotes that...
• Get their energy from • Aerobic (use Oxygen)
inorganic chemicals • Anaerobic (cannot use
• “Breath” iron oxygen)
– Use iron as a final electron • E.g., Methanogens
acceptor in respiration “exhale” methane
– What we do with oxygen – What we do with CO2
• “Burn” iron
– Use iron as an original
electron donor in
respiration
– What we do with food.
Prokaryotes in the living world Exploring diversity of prokaryotes
• “The major biogeochemical • “Our view of the natural world [is
cycles on which we depend were changing] as radically as did our
in place three billion years ago, view of the cosmos when we
long before the appearance of began looking at it with
visible life, and are today technologies that allowed us to
maintained by the ‘invisibles’ and see more than can be seen with
their vast range of metabolisms.” the naked eye.”
• “Neglect of the invisible world is
• “The contribution of visible life to no longer any more acceptable
biodiversity is very small indeed.” than, say, teaching astronomy but
ignoring the existence of galaxies
beyond the Milky Way, or
teaching physics while refusing to
discuss anything smaller than a
Nee, 2004
pin head.”
Fig 27.15
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellsprokaryotesandeukaryotes-130108200428-phpapp02/85/Cells-prokaryotes-and-eukaryotes-5-320.jpg)