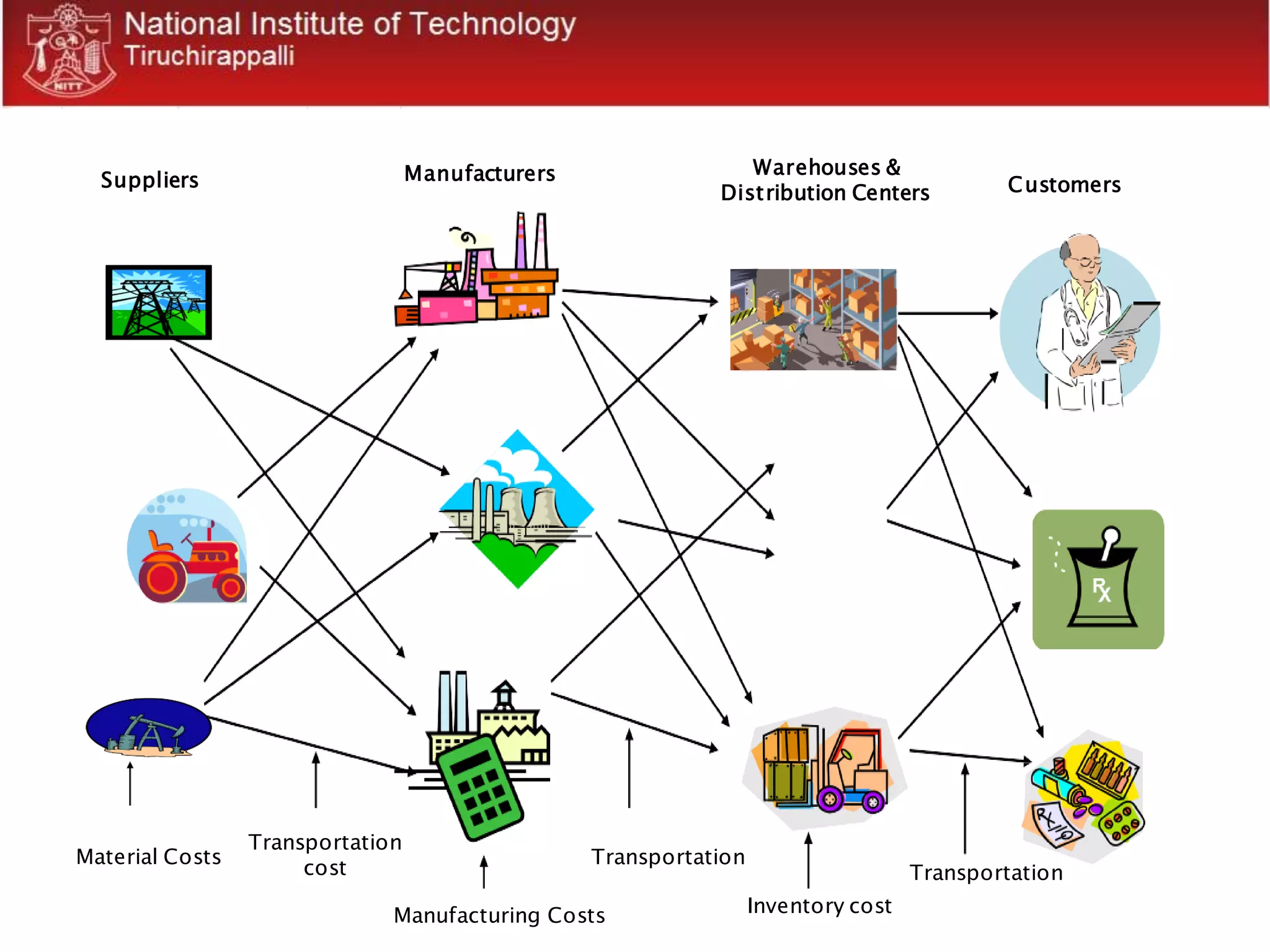
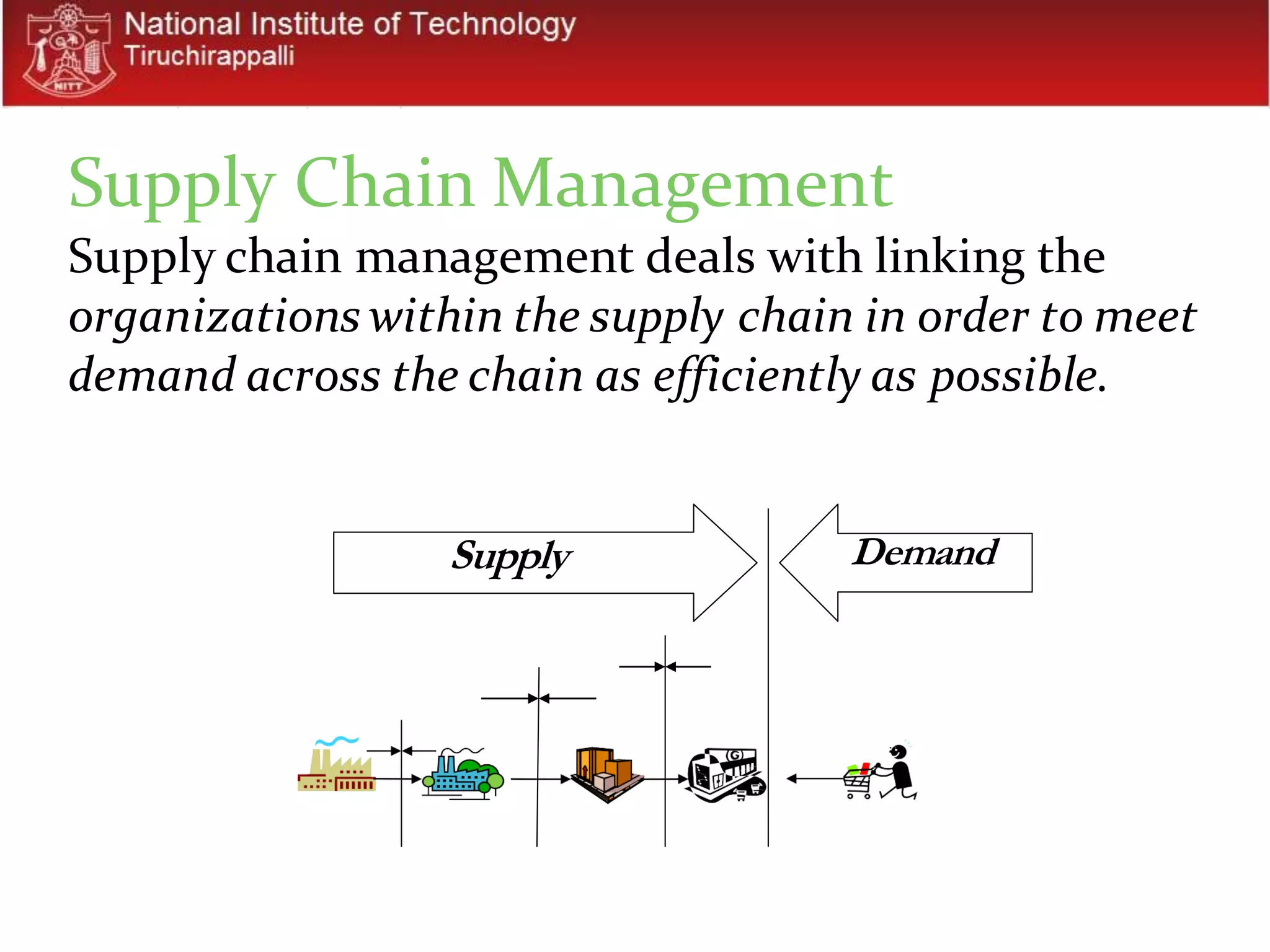
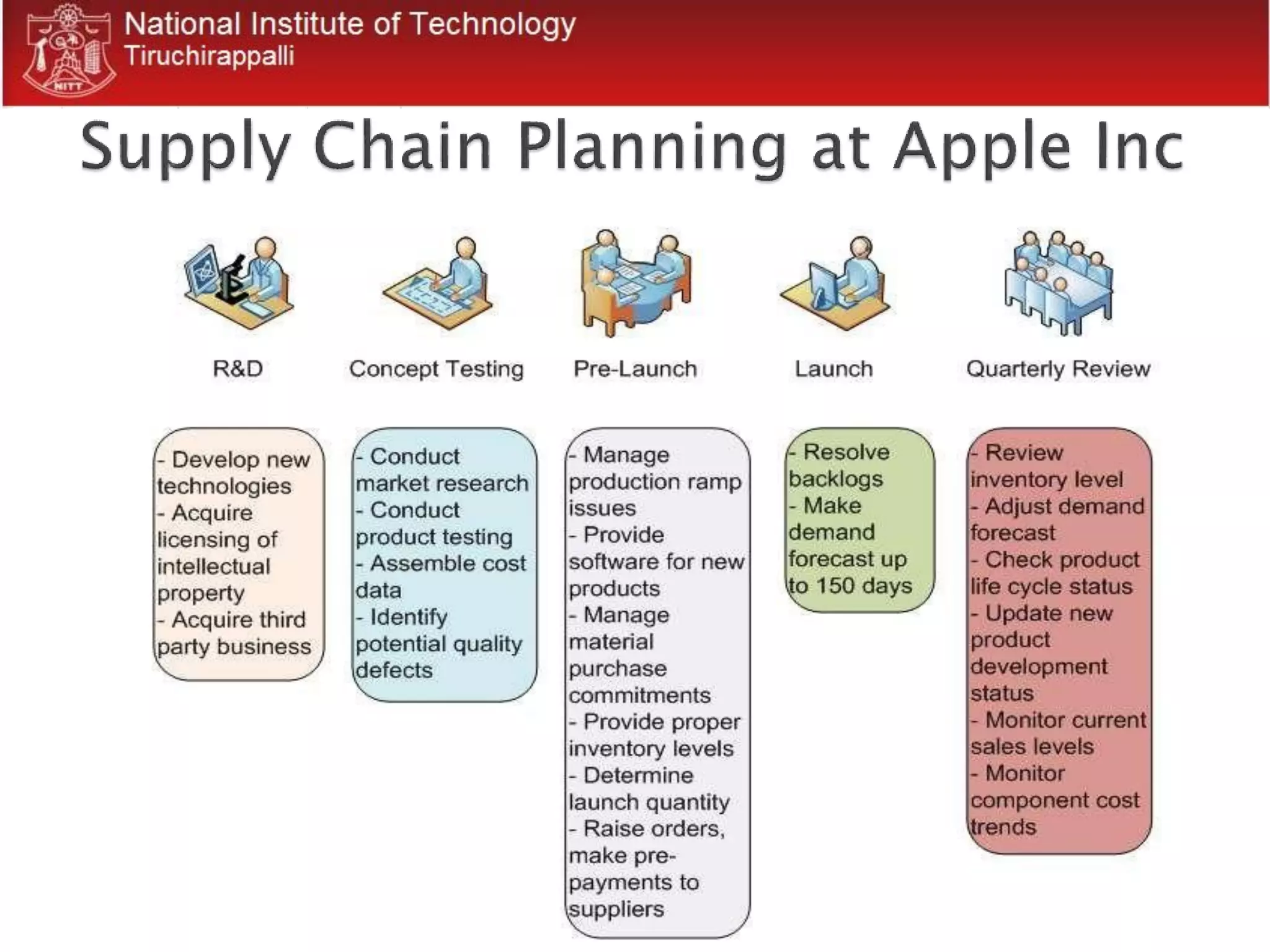
1. The document discusses supply chain management concepts including what a supply chain is, challenges in matching supply and demand, and strategies for managing inventory and coping with the bullwhip effect.
2. It provides examples of successful supply chain management by companies like Walmart, Dell, and L&T Construction including how they reduced costs and improved customer satisfaction through collaboration with suppliers and use of information technology.
3. Managing complex global supply chains, variability in demand and supplier performance, and conflicting objectives between members are some of the difficulties in supply chain management.