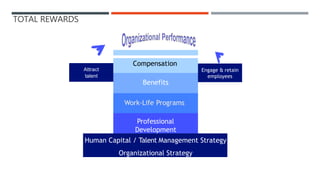
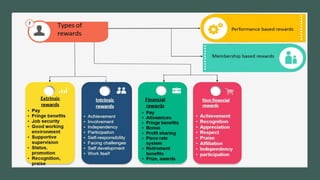
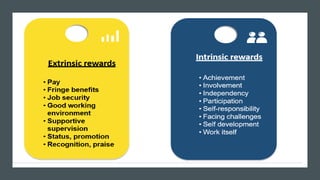
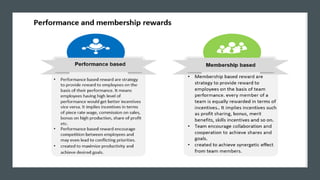
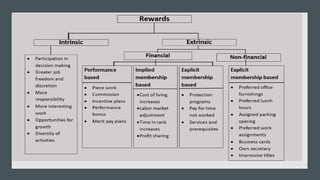
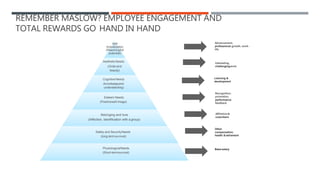
Reward management aims to reward employees fairly and consistently according to their value. Total rewards include all compensation and benefits that employees value in the employment relationship. Key elements of total rewards include fixed and variable compensation, employee benefits like health insurance and retirement plans, work-life programs, and professional development opportunities. An effective reward system is performance-based, transparent, cost-effective, need-based, unbiased, and competitive to attract, engage, and retain talent.