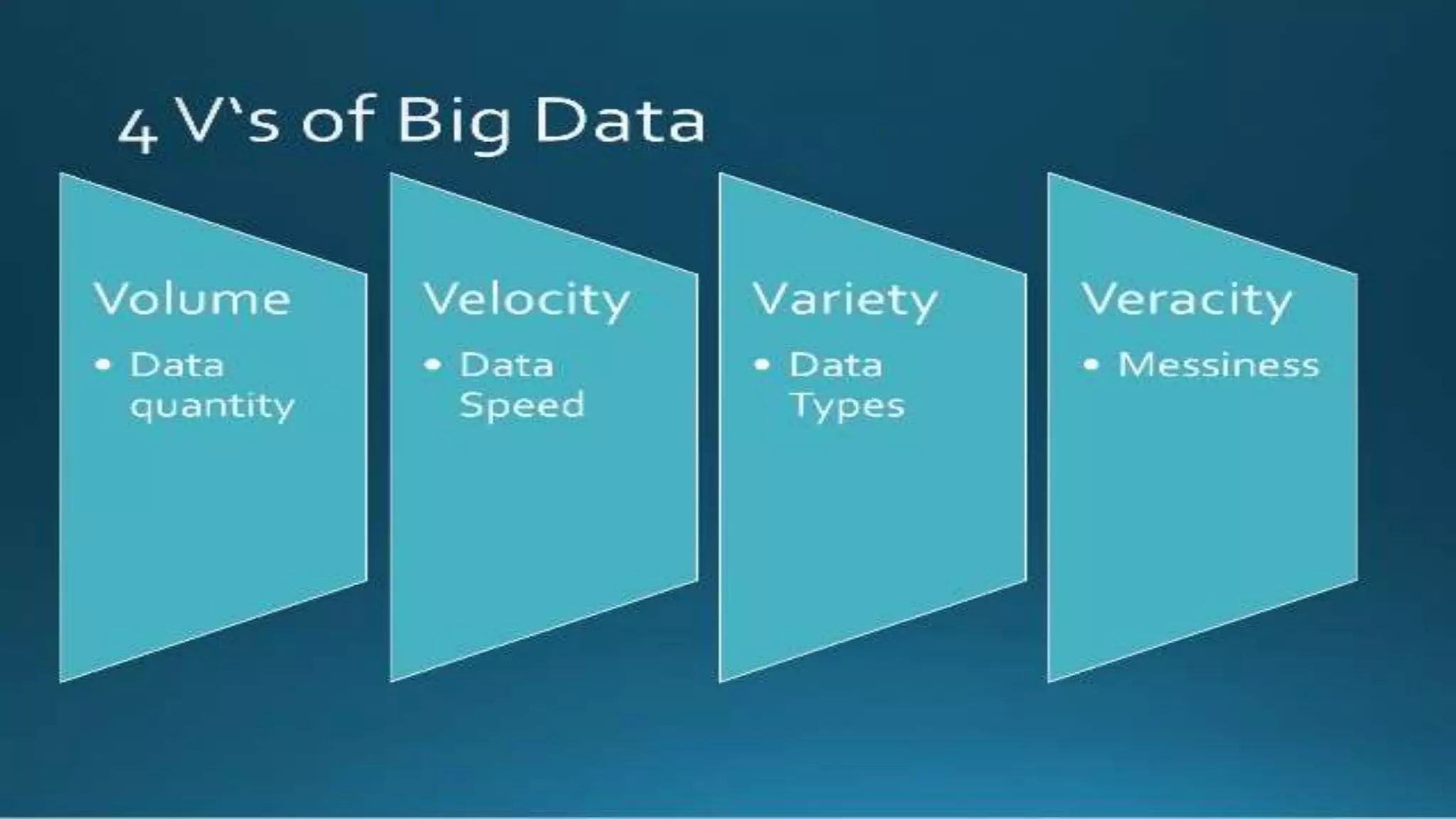
The document discusses big data, highlighting its importance as large volumes of structured and unstructured data that businesses encounter daily. It outlines who utilizes big data, its implications for supply chain management, and the opportunities it presents for enhancing efficiency and decision-making. Key benefits include improved customer service, optimized vendor management, and innovation in product design.