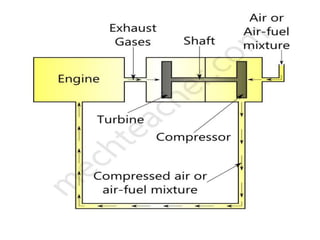
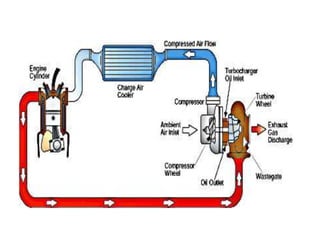
Forced induction engines use a compressor to increase the pressure and temperature of air entering the engine. A supercharger is a compressor driven directly by the engine's crankshaft, while a turbocharger uses a turbine powered by exhaust gases. Both methods compress more air into the engine, allowing for more fuel and greater power output compared to naturally aspirated engines. However, superchargers are less efficient since they draw power from the engine, while turbochargers recycle otherwise wasted exhaust energy.