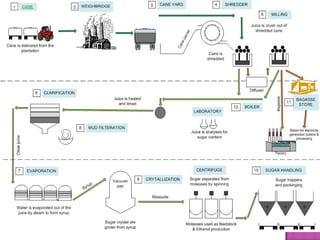
Pakistan has grown from having only two sugar mills in 1947 producing 7,932 tons of sugar to now having 82 functional sugar mills. Sugarcane is grown on over 1 million hectares and provides raw materials for the country's sugar mills. The sugar production process involves cleaning and slicing sugarcane, extracting juice, purifying and clarifying the juice, concentrating it through evaporation, crystallizing it, and then refining and packaging the raw sugar. Khoski sugar mill was established in 1965 and has a crushing capacity of 4,500 tons per day.