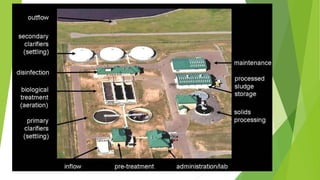
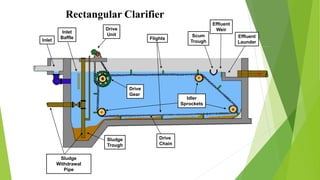
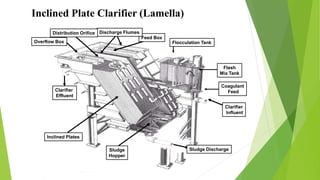
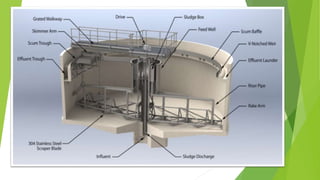
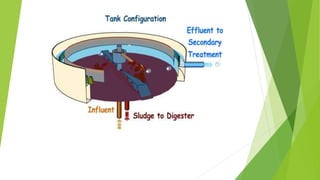
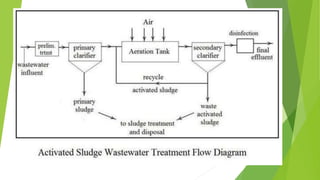
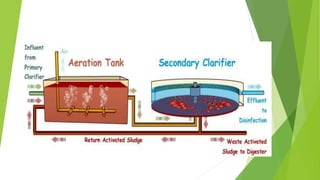
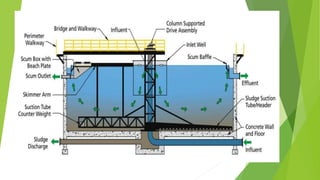
The document discusses clarifiers, which are settling tanks used to remove solids from liquid through sedimentation. There are two main types of clarifiers: rectangular and circular. Clarifiers work by allowing heavier solids to settle to the bottom while lighter materials such as scum float to the surface. Primary clarifiers are used to remove solids before biological wastewater treatment, typically removing 90-95% of settleable solids. Secondary clarifiers separate treated wastewater from activated sludge after biological processes. Design considerations for clarifiers include hydraulic loading, solid loading, detention time, and surface overflow rate.