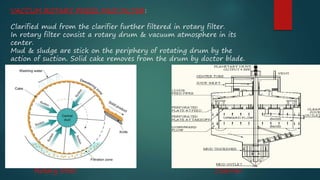
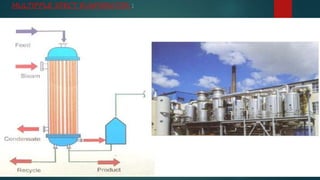
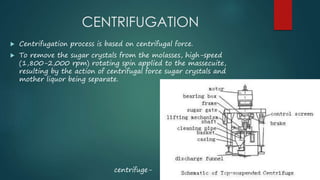
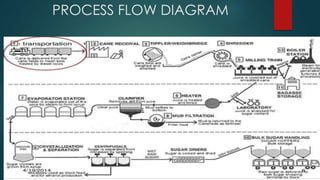
This document summarizes the production of sugar from sugar cane. It discusses the sources of sugar, the manufacturing process which includes harvesting, transportation, cutting, extraction of juice, filtration, evaporation, crystallization, centrifugation, drying and packing. It also discusses the byproducts of sugar production including bagasse, blackstrap molasses and filter cake. Finally, it provides information on major sugar producing areas in India and around the world.