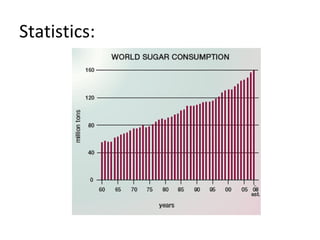
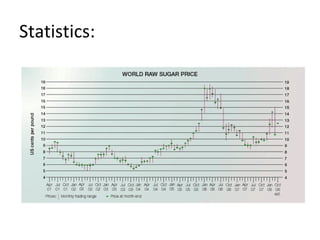
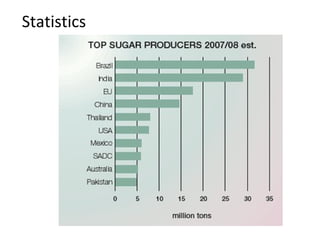
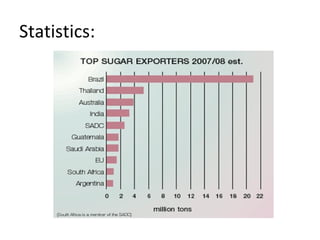
Sugar is produced from sugar cane and sugar beets. The sugar manufacturing process involves growing and harvesting the plants, preparing them for milling, milling to extract the juice, clarifying and evaporating the juice to form crystals, centrifuging to separate the crystals from the liquid, drying the crystals, and refining the sugar. Globally over 120 million tons of sugar are produced annually with approximately 70% coming from sugar cane.

![What is Sugar? What we call sugar, the chemist knows as 'sucrose', in the grouping called carbohydrates. The simplest of the sugars is glucose, C 6 H 12 O 6 Sucrose, C 12 H 22 O 11 , is a condensation molecule made up of two glucose molecules [less a water molecule to make the chemistry work].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sugarindustry-090323001847-phpapp01/85/Sugar-Industry-2-320.jpg)