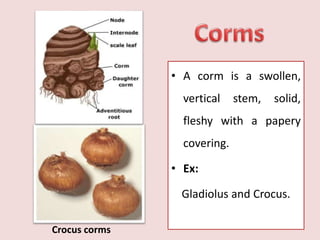
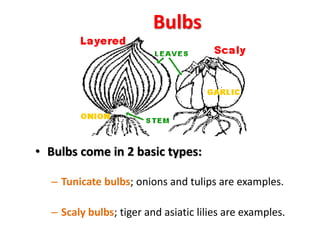
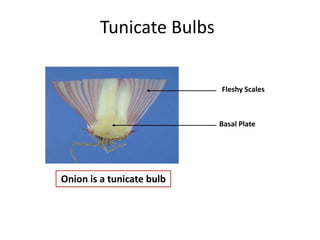
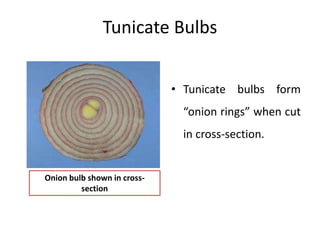
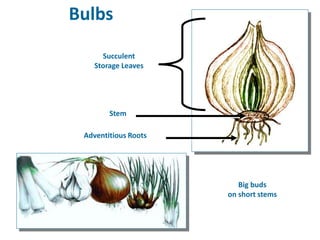
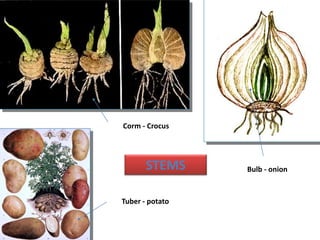
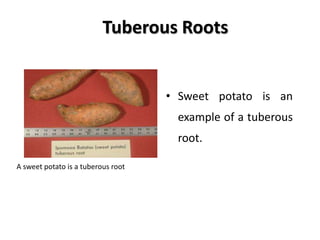
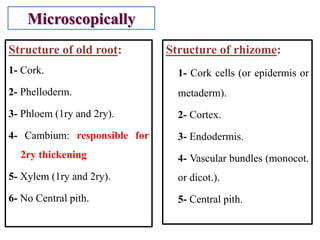
1. The document discusses several subterranean plant organs including rhizomes, roots, tubers, corms, bulbs, and their distinguishing characteristics.
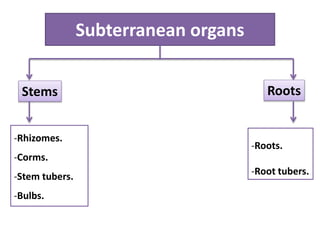
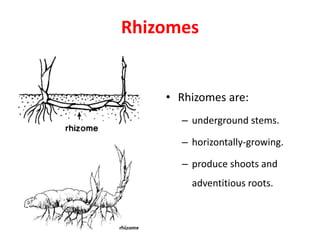
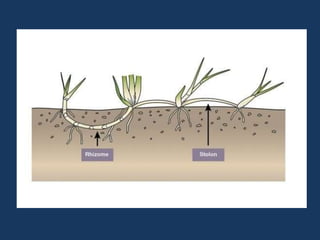
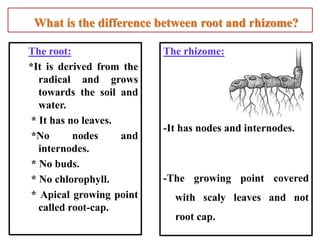
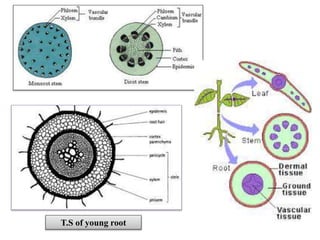
2. Rhizomes are described as horizontally-growing underground stems that produce shoots and adventitious roots, while roots derive from the radical and grow vertically towards soil and water.
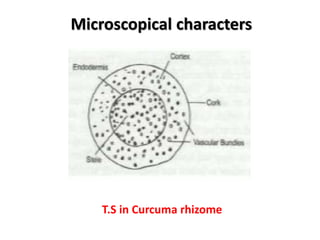
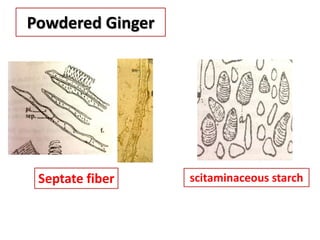
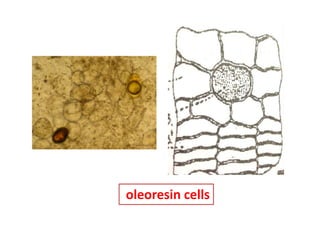
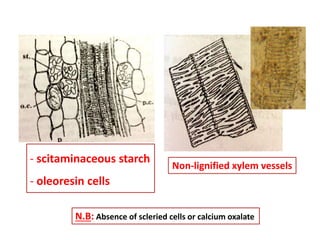
3. Ginger and turmeric are provided as examples of medicinal plants whose rhizomes are used as drugs, with details on active constituents and traditional medical uses.



















![• Gingerol (Gingerols):
- responsible for the pungency of ginger.
- An oily liquid consisting of homologous phenols.
- Its pungency is destroyed by boiling with 2%
potassium hydroxide.
- pharmacological activities such as antipyretic,
antitussive, hypotensive [5], cardiotonic, antiplatelet,
antiangiogenic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic,
cytotoxic, antitumor, anticancer, antioxidant,
antihepatotoxic, antifungal, cholagogic, and
antiemetic activities (Sujay Rai et al.2006).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subterraneanelsadat2018-180310211539/85/Subterranean-el-sadat-2018-38-320.jpg)