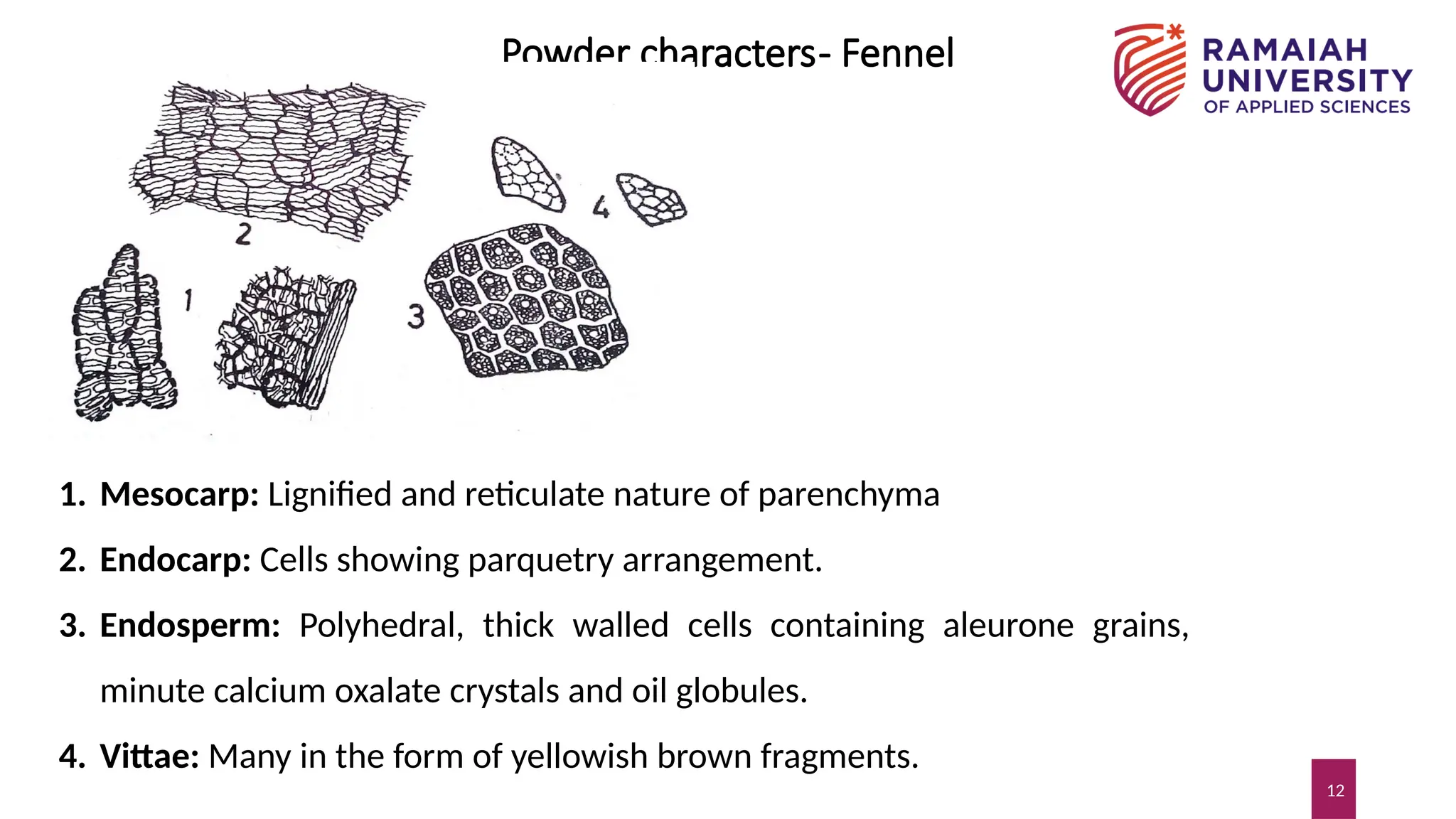
The document outlines the morphology, microscopy, and chemical constituents of fennel (Foeniculum vulgare), including its biological sources and geographical origins. It details the physical characteristics of fennel's fruits, such as shape, color, and aromatic properties, along with microscopic structures like the pericarp and vascular bundles. Additionally, the presentation discusses the uses of fennel, describing it as a carminative, appetizer, and galactagogue.