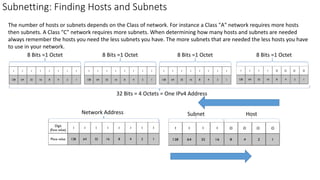
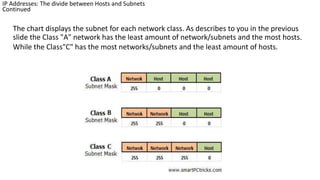
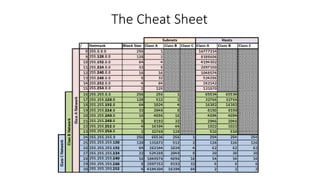
Subnetting is used to divide IP addresses among routers, switches and workstations to efficiently use addresses and ensure network operability. When creating a network, the number of hosts and subnets must be determined. A host is a device connected to the network, and a subnet divides a network into logical subnetworks. Subnetting allows using multiple networks from a single Class A, B or C network. The number of hosts and subnets depends on network class. Class A networks require more hosts, Class C more subnets. Finding subnets uses the formula 2^n where n is borrowed host bits. Finding hosts per subnet uses 2^n - 2, where n is host bits. You can determine the subnet mask if you know the IP address