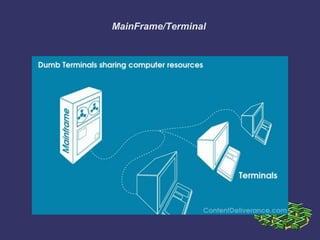
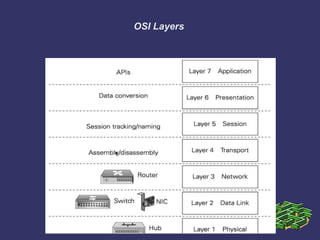
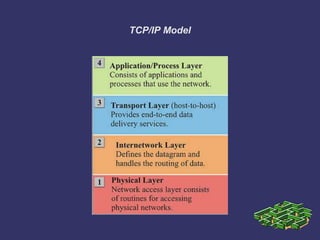
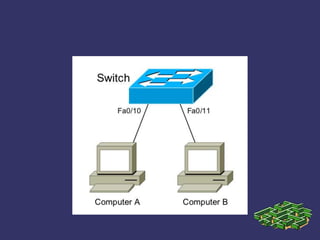
This document provides an overview of computer networking fundamentals. It covers topics such as network types (LANs and WANs), common network architectures (client-server, peer-to-peer, mainframe), OSI and TCP/IP models, Ethernet technologies, and common network devices (hubs, switches, routers). Each layer of the OSI model is described along with its purpose and functions. Ethernet cabling types and speeds are also outlined. The document serves as an introductory guide to basic internetworking concepts.