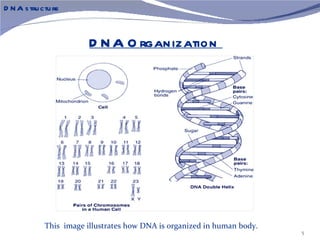
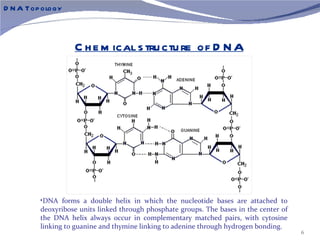
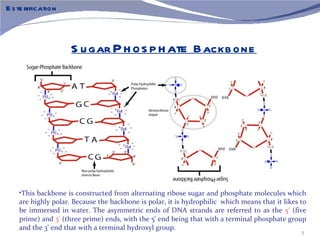
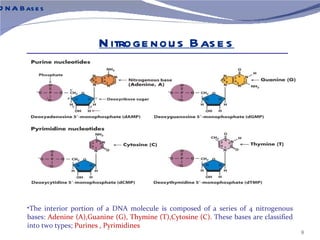
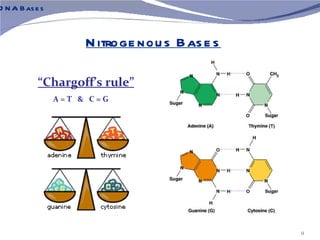
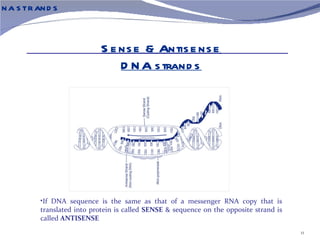
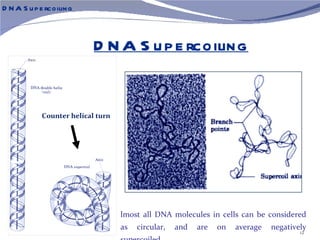
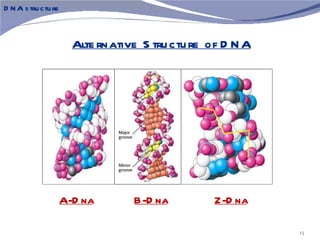
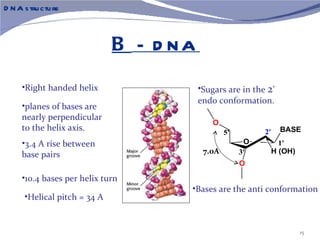
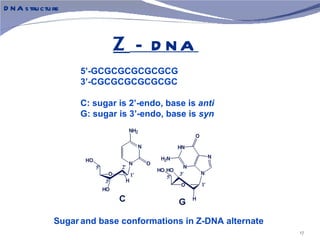
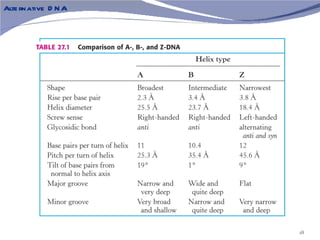
The document discusses the structure of DNA. It describes DNA as a double-stranded polymer made of deoxyribonucleotides. The structure takes a double helix shape with the strands running in opposite directions. Each strand is composed of a backbone of alternating sugar and phosphate groups joined by ester bonds. The strands are held together by bonds between complementary nitrogenous bases - adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine. DNA exists in different conformations including A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA which differ in their helical structures and base orientations.