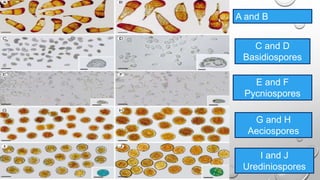
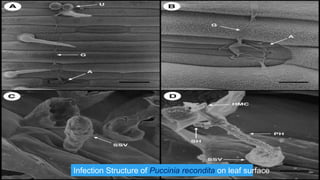
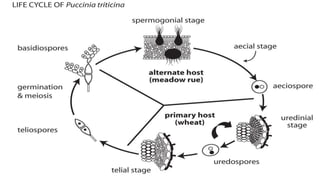
Brown rust of wheat, primarily caused by the fungus Puccinia recondita, is prevalent in northern and eastern India, leading to up to 90% yield loss. Symptoms include orange-brown pustules on leaves, which can result in reduced photosynthesis and impaired plant growth. Management practices involve early sowing, mixed cropping, and the application of specific fungicides and resistant wheat varieties.