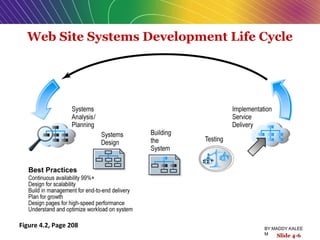
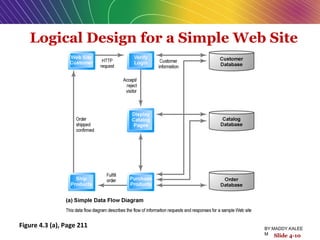
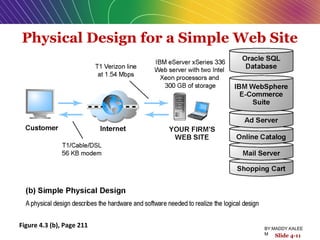
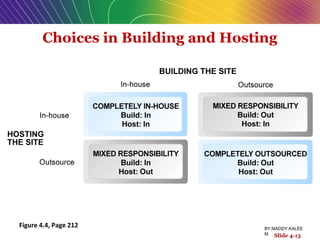
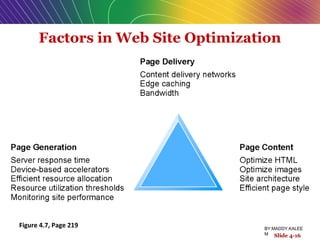
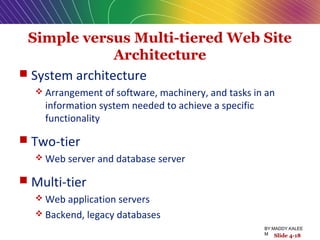
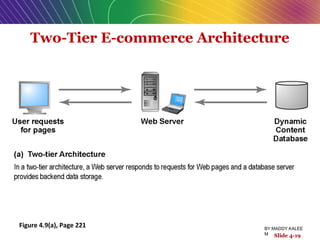
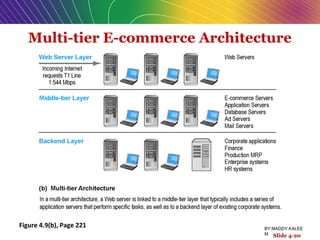
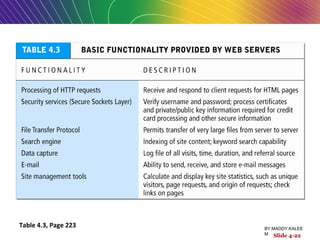
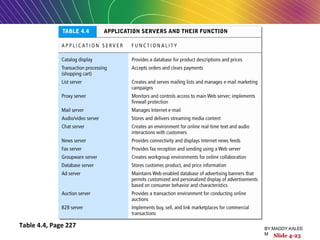
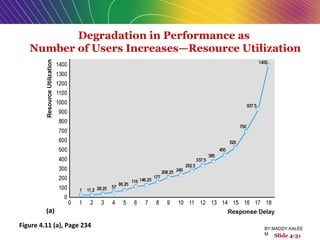
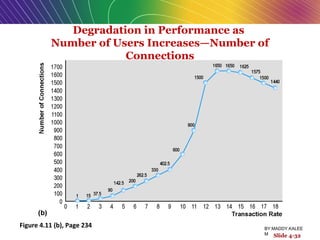
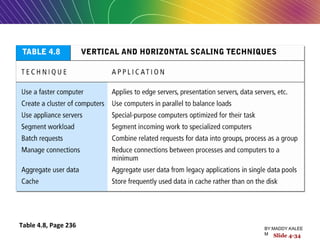
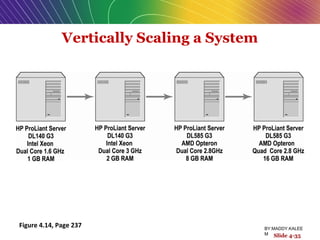
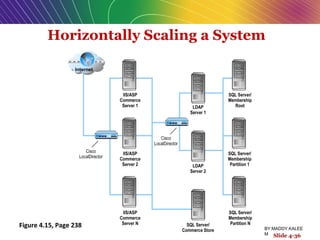
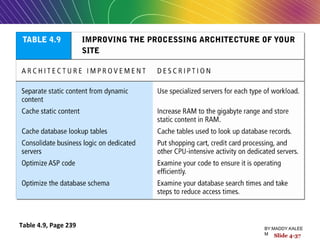
This document discusses the process of building an e-commerce website, including analyzing business objectives, designing the site architecture, selecting hardware and software, testing, and implementation. The key steps in building a site are analyzing business goals, designing the site structure and features, choosing appropriate technology and vendors, testing functionality, and maintaining the site over time. Considerations include whether to outsource development, budget requirements, and ensuring accessibility for all users.