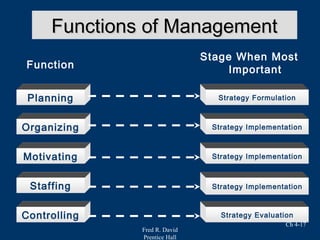
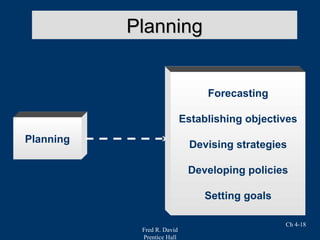
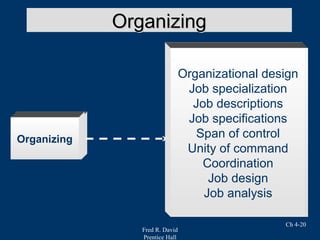
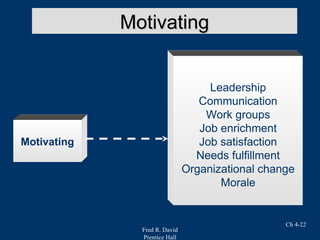
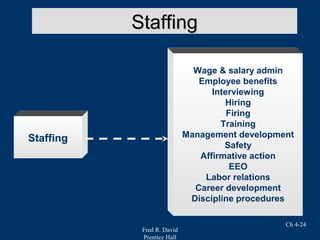
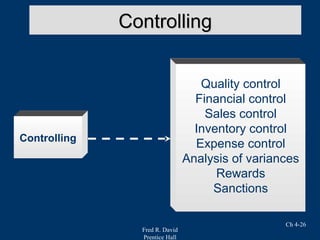
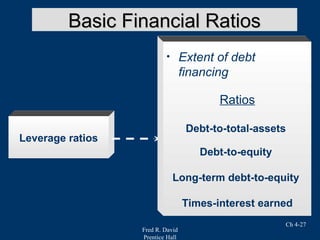
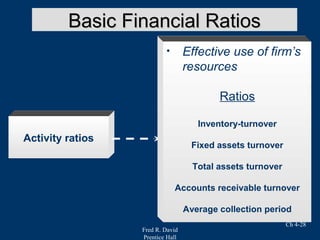
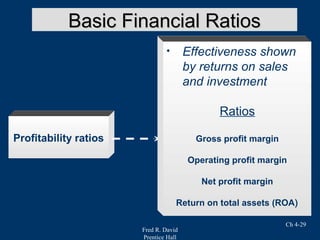
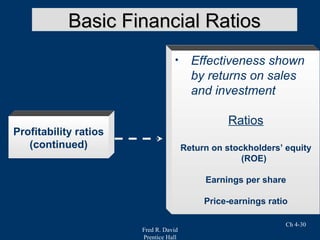
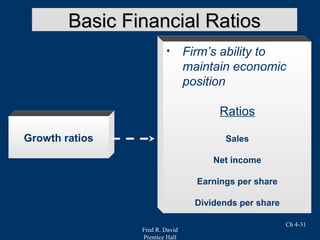
Chapter 4 of Fred R. David's strategic management text focuses on the internal assessment process, covering elements such as internal audits, the integration of strategy and culture, and the functions of management including planning, organizing, motivating, staffing, and controlling. It outlines the significance of understanding organizational strengths and weaknesses and the role of distinctive competencies in building a competitive advantage. Additionally, the chapter discusses financial ratio analysis as a means to evaluate internal business performance across different functional areas.