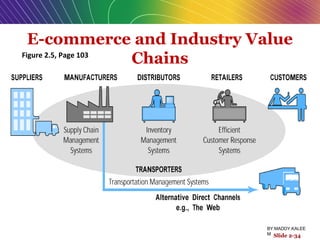
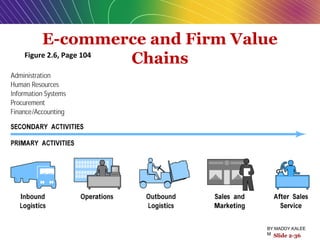
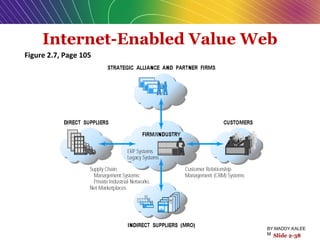
The document discusses e-commerce business models, detailing key characteristics and elements essential for successful online businesses, such as value propositions, revenue models, and competitive environment. It categorizes various business models including B2C, B2B, and emerging markets like C2C and m-commerce, while emphasizing the importance of marketing strategies and organizational structures. Additionally, it highlights how internet technologies can alter traditional business processes and enhance operational efficiencies.